
Velakkara revolt was a mutiny by the Velakkara division of the territorial army of the Sinhalese monarch Vijayabahu I of Polonnaruwa in the year 1084 CE.

Velakkara revolt was a mutiny by the Velakkara division of the territorial army of the Sinhalese monarch Vijayabahu I of Polonnaruwa in the year 1084 CE.
Around 1084 CE, another quarrel with the Chola kingdom erupted when some ambassadors of Vijayabahu sent to West Chalukya were harassed by them. Vijayabahu declared another war against the Chola Empire, and the Velakkaras were ordered by Vijayabahu to fight against them. The Velakkaras refused to fight against their Tamil kinsmen, and started a revolt against Vijayabahu. [1] [2]
They killed the royal guards and burnt down the palace. Vijayabahu fled to Wakirigala, but returned afterwards to recaptured back Polonnaruwa. The rebel leaders were captured and executed, and the Velakkaras set up a Tamil inscription in which they promised to protect the Relic of the tooth of the Buddha. [3]

Poḷonnaruwa, also referred as Pulathisipura and Vijayarajapura in ancient times, is the main town of Polonnaruwa District in North Central Province, Sri Lanka. The modern town of Polonnaruwa is also known as New Town, and the other part of Polonnaruwa remains as the royal ancient city of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa.

Kulottunga I also spelt Kulothunga, was a Chola Emperor who reigned from 1070 CE to 1122 CE succeeding his cousin Athirajendra Chola. He also served as the Eastern Chalukya king from 1061 CE to 1118 CE, succeeding his father Rajaraja Narendra. His birth name was Rajendra. He is related to the Chola dynasty through his mother's side and the Eastern Chalukyas through his father's side. His mother, Ammangaidevi, was a Chola princess and the daughter of emperor Rajendra I. His father was king Rajaraja Narendra of the Eastern Chalukya dynasty who was the nephew of Rajendra I and maternal grandson of Rajaraja I. According to historian Sailendra Nath Sen, his accession marked the beginning of a new era and ushered in a period of internal peace and benevolent administration.
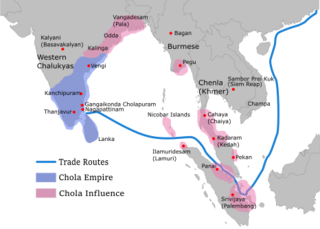
Rajendra Chola I , often referred to as Rajendra the Great, and also known as Gangaikonda Chola, and Kadaram Kondan was a Chola Emperor who reigned between 1014 and 1044 CE. He is considered the most significant ruler in early eleventh century South Asia for his role in patronising the arts, encouraging trade and expanding the Chola Empire to is greatest extent.

Rajadhiraja I was a Chola emperor, the most skilled military commander among the Chola rulers and the successor of his father, Rajendra I. He was the only Chola emperor who was killed while leading his army in war, and although he had a short reign, he helped his father conquer several territories as well as to maintain the Chola authority over most of Sri Lanka, Eastern Chalukya and Kalinga, among others. He also established imperial relations with overseas allies despite a series of revolts in the territory.

Ellalan was a member of the Tamil Chola dynasty, also known as "Manu Needhi Cholan", who upon capturing the throne became king of the Anuradhapura Kingdom, in present-day Sri Lanka, from 205 BCE to 161 BCE.

Queen Lilavati was the fourth woman in Sri Lankan history to rule as sovereign in her own right. Lilavati rose to prominence as the wife of Parakramabahu I, king of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa. Being of royal descent herself, she then ruled as sole monarch on three occasions in the near-anarchy following Parakramabahu's death, with the backing of various generals. The primary source for her life is the Culavamsa, specifically chapter LXXX.
Kalinga Magha or Gangaraja Kalinga Vijayabahu was an invader from the Kingdom of Kalinga who usurped the throne from Parakrama Pandyan II of Polonnaruwa in 1215. A massive migration followed of Sinhalese people to the south and west of Sri Lanka, and into the mountainous interior, as they.attempted to escape his power. Magha was the last ruler to have his seat in the traditional northern seat of native power on the island, known as Rajarata; so comprehensive was his destruction of Sinhalese power in the north that all of the successor kingdoms to Rajarata existed primarily in the south of the island.
Rajendra Chola II often referred to as Rajendradeva Chola was a Chola emperor who reigned from 1052 CE to 1064 CE. He was made Rajendra succeeded his brother Rajadhiraja I after his death at the Battle of Koppam. Rajendra had served as a Co-regent under his brother from 1044 CE to 1052 CE. When he acceded the throne, the Chola Empire was at its peak stretching from Southern India to Vengai(Bengal) to parts of Southeast Asia. Rajendra has maintained the territories of his predecessor. During his reign, the Chola Empire was prosperous and had a large influence in trade throughout the Indian Ocean.
Virarajendra Chola was a Chola emperor, who spent a major part of his life as a subordinate to two of his elder brothers Rajadhiraja I and Rajendra II, he is the son of Rajendra I. During his early reign he granted the maintenance of a school to study the Vedas, Sastras and grammar; a hostel was provided for the students. A hospital named Virasolan was also provided by him for the sick people. The famous grammatical work in Tamil, Virasoliyam was written by Buddhamitra during his reign.
The Chola military was the combined armed forces of the Chola Empire organized during two separate Tamil golden ages, the Sangam Period and the Medieval Era. The Chola military fought dozens of wars, it also underwent numerous changes in structure, organization, equipment and tactics, while conserving a core of lasting Tamil traditions.

Parākramabāhu I, or Parakramabahu the Great, was the king of Polonnaruwa from 1153 to 1186. He oversaw the expansion and beautification of his capital, constructed extensive irrigation systems, reorganised the country's army, reformed Buddhist practices, encouraged the arts and undertook military campaigns in South India and Burma. The adage "Not even a drop of water that comes from the rain must flow into the ocean without being made useful to man" is one of his most famous utterances.
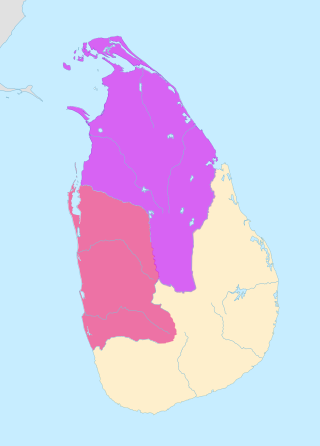
The Kingdom of Polonnaruwa was the Sinhalese kingdom that expanded across the island of Sri Lanka and several overseas territories, from 1070 until 1232. The kingdom started expanding its overseas authority during the reign of Parakramabahu the Great.
Vikramabahu was a medieval king of Sri Lanka. Following the death of his father in 1029, Vikramabahu led the resistance movement against the Chola invaders of the country, ruling from the southern principality of Ruhuna. He spent a number of years building up his forces to drive out the Chola, but died before he could launch his military campaign.
Kitti Sri Megha, also referred to as Kittisrimegha, was a medieval king of the principality of Dakkinadesa in Sri Lanka. The nephew of King Vijayabahu I, he attempted to seize the throne of Sri Lanka along with his two brothers in 1110 CE, but was defeated by Vickramabahu I. He then retreated to the south of the country, which he initially ruled with his younger brother Sri Vallabha. He later ascended to the throne of Dakkinadesa following the death of his older brother Manabharana.

Vijayabahu I, also known as Vijayabahu the Great, was a medieval king of Sri Lanka. Born to a royal bloodline, Vijayabahu grew up under Chola occupation. He assumed rulership of the Ruhuna principality in the southern parts of the country in 1055. Following a seventeen-year-long campaign, he successfully drove the Cholas out of the island in 1070, reuniting the country for the first time in over a century. During his reign, he re-established Buddhism in Sri Lanka and repaired much of the damage caused to infrastructure during the wars. He offered the Thihoshin Pagoda(Lord of Sri Lanka Buddha image) to Burma king Alaungsithu and it is now still in Pakokku.

The Chola conquest and occupation of Anuradhapura Kingdom was a military invasion of the Kingdom of Anuradhapura by the Chola Empire. It can be seen as an ensuing conflict between Chola and Sinhalese kings after the initial conflict between Chola and the Pandya-Sinhalese alliance during conquest of the Pandya Kingdom by Chola king Paranthka I. After the defeat, Pandya king Rajasimha took his crown and the other regalia and sought refuge in Anuradhapura. The Paranthka made several futile attempts to regain regalia, including invasion of Sri Lanka on a date between 947 and 949 CE during the reign of Sinhalese king Udaya IV. Therefore, one of the driving motives behind the invasions of Anuradhapura by the Cholas' was their desire to possess these royal treasures. The conquest started with the invasion of the Anuradhapura Kingdom in 993 CE by Rajaraja I when he sent a large Chola army to conquer the kingdom and absorb it into the Chola Empire. Most of the island was subsequently conquered by 1017 CE and incorporated as a province of the vast Chola empire during the reign of his son Rajendra Chola I. The Chola occupation would be overthrown in 1070 CE through a campaign of Sinhalese Resistance led by Prince Kitti, a Sinhalese royal. The Cholas fought many subsequent wars and attempted to reconquer the Sinhalese kingdom as the Sinhalese were allies of their arch-enemies, the Pandyas. The period of Chola entrenchment in northern Sri Lanka lasted in total about three-quarters of a century, from roughly 993 CE to 1070 CE, when Vijayabahu I recaptured the north and expelled the Chola forces restoring Sinhalese sovereignty.

The Polonnaruwa Agreement was part of the settlement of a dispute between Vijayabahu I and Velakkara mercenaries of Polonnaruwa Kingdom, made after a 1084 revolt had been defeated.

The Polonnaruwa period was a period in the history of Sri Lanka from 1017, after the Chola conquest of Anuradhapura and when the center of administration was moved to Polonnaruwa, to the end of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa in 1232.
Utthama Chola, was the son of Rajendra Chola II.

Panakaduwa copper plate is a Sri Lankan copper plate made at the request of King Vijayabahu I for a high-ranking general called Budalna. The main reason for this to be inscribed on the plate is the aid that was given by him to juvenile prince Kirthi and his family during his pre-regnal days from the Cholas. The king triumphed over the Chola ruler and victoriously led his army to mainland India. It was apparently completed around 1082-83 in the 27th year of his reign.