
The Kettle Valley Railway was a subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) that operated across southern British Columbia, west of Midway running to Rock Creek, then north to Myra Canyon, down to Penticton over to Princeton, Coalmont, Brookmere, Coquihalla and finally Hope where it connected to the main CPR line.

The Santa Cruz, Big Trees and Pacific Railway is operated as a seasonal tourist attraction in Northern California, also referred to as the "Beach Train". Its partner line, the Roaring Camp & Big Trees Narrow Gauge Railroad, is a heritage railroad.

The San Joaquin Valley Railroad is one of several short line railroad companies and is part of the Western Region Division of Genesee & Wyoming Inc. It operates over about 371 miles (597 km) of owned or leased track primarily on several lines in California's Central Valley/San Joaquin Valley around Fresno and Bakersfield. The SJVR has trackage rights over Union Pacific between Fresno, Goshen, Famoso, Bakersfield and Algoso. The SJVR also operated for the Tulare Valley Railroad (TVRR) from Calwa to Corcoran and Famoso.

The Fillmore and Western Railway was a heritage railway which operated on track owned by the Ventura County Transportation Commission. Visitors to Fillmore would see filming activity as well as sets and support equipment at the company's rail yard and along the tracks between Santa Paula and Piru. They stopped operating on the line in 2021.

The establishment of America's transcontinental rail lines securely linked California to the rest of the country, and the far-reaching transportation systems that grew out of them during the century that followed contributed to the state's social, political, and economic development. When California was admitted as a state to the United States in 1850, and for nearly two decades thereafter, it was in many ways isolated, an outpost on the Pacific, until the first transcontinental railroad was completed in 1869.

The Coast Line is a railroad line between Burbank, California and the San Francisco Bay Area, roughly along the Pacific Coast. It is the shortest rail route between Los Angeles and the Bay Area. Though not as busy as the Surf Line, the continuation of the Coast Line southbound to San Diego, it still sees freight movements and lots of passenger trains. The Pacific Surfliner, which runs from the San Diego Santa Fe Depot to San Luis Obispo via Union Station in Los Angeles, is the third busiest Amtrak route, and the busiest outside of the Northeast Corridor between Washington D.C. and Boston.

The Northwestern Pacific Railroad is a 271-mile (436 km) mainline railroad from the former ferry connections in Sausalito, California north to Eureka, with a connection to the national railroad system at Schellville. The railroad has gone through a complex history of different ownership and operators but has maintained a generic name of reference as the Northwestern Pacific Railroad, despite no longer being officially named that.

The McCloud Railway was a class III railroad operated around Mount Shasta, California. It began operations on July 1, 1992, when it took over operations from the McCloud River Railroad. The MCR was incorporated on April 21, 1992.

The Sacramento Northern Railway was a 183-mile (295 km) electric interurban railway that connected Chico in northern California with Oakland via the state capital, Sacramento. In its operation it ran directly on the streets of Oakland, Sacramento, Yuba City, Chico, and Woodland. This involved multiple car trains making sharp turns at street corners and obeying traffic signals. Once in open country, SN's passenger trains ran at fairly fast speeds. With its shorter route and lower fares, the SN provided strong competition to the Southern Pacific and Western Pacific Railroad for passenger business and freight business between those two cities. North of Sacramento, both passenger and freight business was less due to the small town agricultural nature of the region and due to competition from the paralleling Southern Pacific Railroad.

The Ventura River, in western Ventura County in southern California, United States, flows 16.2 miles (26.1 km) from its headwaters to the Pacific Ocean. The smallest of the three major rivers in Ventura County, it flows through the steeply sloped, narrow Ventura Valley, with its final 0.7 miles (1.1 km) through the broader Ventura River estuary, which extends from where it crosses under a 101 Freeway bridge through to the Pacific Ocean.

The North Pacific Coast Railroad (NPC) was a common carrier 3 ft (914 mm) narrow-gauge steam railroad begun in 1874 and sold in 1902 to new owners who renamed it the North Shore Railroad (California) (NSR) and rebuilt the southern section into a standard-gauge electric railway.
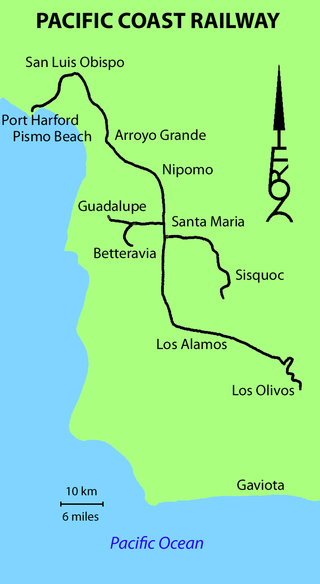
The Pacific Coast Railway was a 3 ft narrow gauge railway on the Central Coast of California. The original 10-mile (16 km) link from San Luis Obispo to Avila Beach and Port Harford was later built southward to Santa Maria and Los Olivos, with branches to Sisquoc and Guadalupe.

Ventura station is a passenger rail station in downtown Ventura, California. The station is served by Amtrak's Pacific Surfliner from San Luis Obispo to San Diego. Ten Pacific Surfliner trains serve the station daily. Of the 73 California stations served by Amtrak, Ventura was the 33rd-busiest in FY2010, boarding or detraining an average of approximately 125 passengers daily. The single platform is located on the south side of the tracks with a view of the Santa Barbara Channel and the Channel Islands. The Ventura Freeway is parallel with and on the north side of tracks.

The Nevada–California–Oregon Railway was a 3 ft narrow gauge railroad originally planned to connect Reno, Nevada, to the Columbia River. However, only 238 mi (383 km) of track were laid so service never extended beyond Lakeview, Oregon. Because of the company’s reputation for mismanagement, it was often called the "Narrow, Crooked & Ornery" railroad.

The Utah Division of the former Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad (D&RGW) is a rail line that connects Grand Junction, Colorado and Salt Lake City, Utah in the Western United States. It is now incorporated into the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) system as part of the Central Corridor. The modern Union Pacific has split the line into two subdivisions for operational purposes, the Green River Subdivision between Grand Junction and Helper, Utah and the Provo Subdivision from Helper to Salt Lake City. Daily passenger service is provided by Amtrak's California Zephyr; the BNSF Railway and Utah Railway have trackage rights over the line.
The Orange Belt Railway was a 3 ft narrow gauge railroad established in 1885 by Russian exile Peter Demens in Florida. It was one of the longest narrow gauge railroads in the United States at the time of its completion in 1888, with a mainline 152 miles (245 km) in length between Sanford and St. Petersburg. It carried citrus, vegetables, and passengers; and it interchanged with two standard gauge lines: the Jacksonville, Tampa and Key West Railway at Lake Monroe, and the Florida Central and Peninsular Railroad at Lacoochee.

The Los Angeles and San Gabriel Valley Railroad was a railroad founded on September 5, 1883, by James F. Crank with the goal of bringing a rail line to Pasadena, California from downtown Los Angeles, the line opened in 1886. Los Angeles and San Gabriel Valley Railroad was sold and consolidated on May 20, 1887 into the California Central Railway. In 1889 this was consolidated into Southern California Railway Company. On Jan. 17, 1906 Southern California Railway was sold to the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway and called the Pasadena Subdivision. The main line closed in 1994. The railroad later reopened as the MTA Gold Line Light Rail service in July 2003.

The Ventura River Parkway Trail is a southern California rail trail along the Ventura River in Ventura County. Roughly paralleling California State Route 33 for 16.5 mi (26.6 km) from Ventura to Ojai, it follows the route of the former Ventura and Ojai Valley Railroad that was abandoned between 1969 and 1995.

The Santa Paula Branch Line is a railway corridor in Ventura County, California. It connects Saugus and Santa Paula through the Santa Clara River Valley, though the route east of Piru is out of service. It opened for traffic by the Southern Pacific Railroad in 1887. Since 1995 the line has been owned by the Ventura County Transportation Commission.

The Visalia District was a railway line in California's San Joaquin Valley that ran from Corcoran, California to Calwa, California. The line was originally built by the San Francisco and San Joaquin Valley Railroad and later acquired by the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway.


















