Related Research Articles
H.263 is a video compression standard originally designed as a low-bit-rate compressed format for videotelephony. It was standardized by the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) in a project ending in 1995/1996. It is a member of the H.26x family of video coding standards in the domain of the ITU-T.

The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by ISO and IEC that sets standards for media coding, including compression coding of audio, video, graphics, and genomic data; and transmission and file formats for various applications. Together with JPEG, MPEG is organized under ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 – Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information.

A video codec is software or hardware that compresses and decompresses digital video. In the context of video compression, codec is a portmanteau of encoder and decoder, while a device that only compresses is typically called an encoder, and one that only decompresses is a decoder.

JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi, with the intention of superseding their original JPEG standard, which is based on a discrete cosine transform (DCT), with a newly designed, wavelet-based method. The standardized filename extension is .jp2 for ISO/IEC 15444-1 conforming files and .jpx for the extended part-2 specifications, published as ISO/IEC 15444-2. The registered MIME types are defined in RFC 3745. For ISO/IEC 15444-1 it is image/jp2.

The Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) is the joint committee between ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 and ITU-T Study Group 16 that created and maintains the JPEG, JPEG 2000, JPEG XR, JPEG XT, JPEG XS, JPEG XL, and related digital image standards. It also has the responsibility for maintenance of the JBIG and JBIG2 standards that were developed by the former Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group.
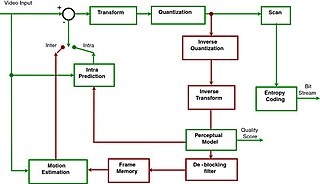
Advanced Video Coding (AVC), also referred to as H.264 or MPEG-4 Part 10, is a video compression standard based on block-oriented, motion-compensated coding. It is by far the most commonly used format for the recording, compression, and distribution of video content, used by 91% of video industry developers as of September 2019. It supports a maximum resolution of 8K UHD.
The Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group (JBIG) was a group of experts nominated by national standards bodies and major companies to work to produce standards for bi-level image coding. The "joint" refers to its status as a committee working on both ISO and ITU-T standards. It was one of two sub-groups of ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29, Working Group 1, whose official title is Coding of still pictures.
MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual is a video compression format developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC standards. It uses block-wise motion compensation and a discrete cosine transform (DCT), similar to previous standards such as MPEG-1 Part 2 and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2.
The macroblock is a processing unit in image and video compression formats based on linear block transforms, typically the discrete cosine transform (DCT). A macroblock typically consists of 16×16 samples, and is further subdivided into transform blocks, and may be further subdivided into prediction blocks. Formats which are based on macroblocks include JPEG, where they are called MCU blocks, H.261, MPEG-1 Part 2, H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2, H.263, MPEG-4 Part 2, and H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. In H.265/HEVC, the macroblock as a basic processing unit has been replaced by the coding tree unit.

Thomas Wiegand is a German electrical engineer who substantially contributed to the creation of the H.264/AVC, H.265/HEVC, and H.266/VVC video coding standards. For H.264/AVC, Wiegand was one of the chairmen of the Joint Video Team (JVT) standardization committee that created the standard and was the chief editor of the standard itself. He was also a very active technical contributor to the H.264/AVC, H.265/HEVC, and H.266/VVC video coding standards. Wiegand also holds a chairmanship position in the ITU-T VCEG of ITU-T Study Group 16 and previously in ISO/IEC MPEG standardization organizations. In July 2006, video coding work of the ITU-T was jointly led by Gary J. Sullivan and Wiegand for the preceding six years. It was voted as the most influential area of the standardization work of the CCITT and ITU-T in their 50-year history. Since 2018, Wiegand has served as chair of the ITU/WHO Focus Group on Artificial Intelligence for Health (FG-AI4H). Since 2014, Thomson Reuters named Wiegand in their list of “The World’s Most Influential Scientific Minds” as one of the most cited researchers in his field.
Gary Joseph Sullivan is an American electrical engineer who led the development of the AVC, HEVC, and VVC video coding standards and created the DirectX Video Acceleration (DXVA) API/DDI video decoding feature of the Microsoft Windows operating system. He is currently Director of Video Research and Standards at Dolby Laboratories and is the chair of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 and of the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG).
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding. In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware.
The ISO base media file format (ISOBMFF) is a container file format that defines a general structure for files that contain time-based multimedia data such as video and audio. It is standardized in ISO/IEC 14496-12, a.k.a. MPEG-4 Part 12, and was formerly also published as ISO/IEC 15444-12, a.k.a. JPEG 2000 Part 12.
A video coding format is a content representation format of digital video content, such as in a data file or bitstream. It typically uses a standardized video compression algorithm, most commonly based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) coding and motion compensation. A specific software, firmware, or hardware implementation capable of compression or decompression in a specific video coding format is called a video codec.
MPEG-H is a group of international standards under development by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). It has various "parts" – each of which can be considered a separate standard. These include a media transport protocol standard, a video compression standard, an audio compression standard, a digital file format container standard, three reference software packages, three conformance testing standards, and related technologies and technical reports. The group of standards is formally known as ISO/IEC 23008 – High efficiency coding and media delivery in heterogeneous environments. Development of the standards began around 2010, and the first fully approved standard in the group was published in 2013. Most of the standards in the group have been revised or amended several times to add additional extended features since their first edition.
Motion JPEG 2000 is a file format for motion sequences of JPEG 2000 images and associated audio, based on the MP4 and QuickTime format. Filename extensions for Motion JPEG 2000 video files are .mj2 and .mjp2, as defined in RFC 3745.
High Efficiency Image File Format (HEIF) is a digital container for storing individual digital images and image sequences. The standard covers multimedia files that can also include other media streams, such as timed text, audio and video.
Versatile Video Coding (VVC), also known as H.266, ISO/IEC 23090-3, and MPEG-I Part 3, is a video compression standard finalized on 6 July 2020, by the Joint Video Experts Team (JVET) of the VCEG working group of ITU-T Study Group 16 and the MPEG working group of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29. It is the successor to High Efficiency Video Coding. It was developed with two primary goals – improved compression performance and support for a very broad range of applications.

The ITU-T Study Group 16 (SG16) is a statutory group of the ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) concerned with multimedia coding, systems and applications, such as video coding standards. It is responsible for standardization of the "H.26x" line of video coding standards, the "T.8xx" line of image coding standards, and related technologies, as well as various collaborations with the World Health Organization, including on safe listening (H.870) accessibility of e-health (F.780.2), it is also the parent body of VCEG and various Focus Groups, such as the ITU-WHO Focus Group on Artificial Intelligence for Health and its AI for Health Framework.
References
- ↑ "Sakae Okubo". ITU . Retrieved 2017-01-27.
- 1 2 "The History of Video File Formats Infographic". RealNetworks . 22 April 2012. Retrieved 5 August 2019.
- ↑ Ghanbari, Mohammed (2003). Standard Codecs: Image Compression to Advanced Video Coding. Institution of Engineering and Technology. pp. 1–2. ISBN 9780852967102.
- ↑ Recommendation ITU-T H.271
- ↑ ITU (2006-10-02). "Video Coding Work Voted Most Influential". Archived from the original on 2007-09-30. Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ↑ ITU (2006-07-20). "Fifty Years of Excellence in Telecommunication/ICT Standards" . Retrieved 2015-06-18.
- ↑ ITU-T. "Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding - JCT-VC" . Retrieved 2010-03-07.
- ↑ ITU (2015-05-17). "17 May: ITU's 150th Anniversary Celebrations" . Retrieved 2015-03-07.
- ↑ Pfaff, Jonathan; Halford, Jonathan (20 October 2023). "Call for evidence on the coding of biomedical waveform data" (PDF). ITU . Retrieved 27 April 2024.
- ↑ "New video codec to ease pressure on global networks". ITU. 2013-01-25. Retrieved 2013-01-25.
- ↑ Todd Spangler (2013-01-25). "ITU OKs Next-Generation Video Codec Standard". Multichannel News. Archived from the original on 2013-12-12. Retrieved 2013-01-25.
- ↑ "ITU-T Work Programme". ITU. Retrieved 2013-01-27.