Metaphorically, a snowball effect is a process that starts from an initial state of small significance and builds upon itself, becoming larger, and also perhaps potentially dangerous or disastrous, though it might be beneficial instead. This is a cliché in cartoons and modern theatrics and it is also used in psychology.

Positive feedback is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics.

Foreclosure is a legal process in which a lender attempts to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has stopped making payments to the lender by forcing the sale of the asset used as the collateral for the loan.

Nouriel Roubini is an Iranian-American economist. He teaches at New York University's Stern School of Business and is chairman of Roubini Macro Associates LLC, an economic consultancy firm.
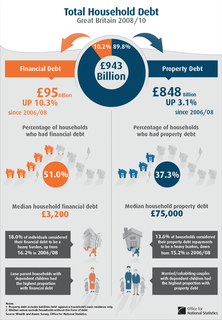
Household debt is defined as the combined debt of all people in a household. It includes consumer debt and mortgage loans. A significant rise in the level of this debt coincides historically with many severe economic crises and was a cause of the U.S. and subsequent European economic crises of 2007–2012. Several economists have argued that lowering this debt is essential to economic recovery in the U.S. and selected Eurozone countries.

The United States housing bubble was a real estate bubble affecting over half of the U.S. states. It was the impetus for the subprime mortgage crisis. Housing prices peaked in early 2006, started to decline in 2006 and 2007, and reached new lows in 2011. On December 30, 2008, the Case–Shiller home price index reported its largest price drop in its history. The credit crisis resulting from the bursting of the housing bubble is an important cause of the Great Recession in the United States.

A causal loop diagram (CLD) is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. The diagram consists of a set of words and arrows. Causal loop diagrams are accompanied by a narrative which describes the causally closed situation the CLD describes. Closed loops, or causal feedback loops, in the diagram are very important features of CLDs.
Leverage-point modeling (LPM) is a demonstrated approach for improved planning and spending for operations and support (O&S) activities. LPM is a continuous-event simulation technique that uses the system dynamics approach of model building. Dr. Nathaniel Mass championed the potential of LPM, and adapted it for the Department of Defense (DoD) as a tool for jumping to a higher performance curve as a means of offsetting higher costs and declining budgets. The purpose of LPM is to test policies and investments that improve mission capability for a given level of investment or funding. It is particularly used to evaluate investments in component reliability and parts availability.

A mortgage loan or simply mortgage, in civil law jurisdicions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is "secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word mortgage is derived from a Law French term used in Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken through foreclosure. A mortgage can also be described as "a borrower giving consideration in the form of a collateral for a benefit (loan)".
The United States subprime mortgage crisis was a multinational financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2010 that contributed to the 2007–2008 global financial crisis. It was triggered by a large decline in US home prices after the collapse of a housing bubble, leading to mortgage delinquencies, foreclosures, and the devaluation of housing-related securities. Declines in residential investment preceded the Great Recession and were followed by reductions in household spending and then business investment. Spending reductions were more significant in areas with a combination of high household debt and larger housing price declines.
Vicious Cycle may refer to:

Housing prices peaked in early 2005, began declining in 2006.

Observers and analysts have attributed the reasons for the 2001–2006 housing bubble and its 2007–10 collapse in the United States to "everyone from home buyers to Wall Street, mortgage brokers to Alan Greenspan". Other factors that are named include "Mortgage underwriters, investment banks, rating agencies, and investors", "low mortgage interest rates, low short-term interest rates, relaxed standards for mortgage loans, and irrational exuberance" Politicians in both the Democratic and Republican political parties have been cited for "pushing to keep derivatives unregulated" and "with rare exceptions" giving Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac "unwavering support".
This article provides background information regarding the subprime mortgage crisis. It discusses subprime lending, foreclosures, risk types, and mechanisms through which various entities involved were affected by the crisis.
Regulatory responses to the subprime crisis addresses various actions taken by governments around the world to address the effects of the subprime mortgage crisis.
This article is a subordinate article to the subprime mortgage crisis. It covers some of the miscellaneous effects of the crisis in more detail, to preserve the flow of the main page.
The Subprime mortgage crisis solutions debate discusses various actions and proposals by economists, government officials, journalists, and business leaders to address the subprime mortgage crisis and broader financial crisis of 2007–08.
A mortgage servicer is a company to which some borrowers pay their mortgage loan payments and which performs other services in connection with mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. The mortgage servicer may be the entity that originated the mortgage, or it may have purchased the mortgage servicing rights from the original mortgage lender. The duties of a mortgage servicer vary, but typically include the acceptance and recording of mortgage payments; calculating variable interest rates on adjustable rate loans; payment of taxes and insurance from borrower escrow accounts; negotiations of workouts and modifications of mortgage upon default; and conducting or supervising the foreclosure process when necessary.
Many factors directly and indirectly serve as the causes of the Great Recession that started in 2008 with the US subprime mortgage crisis. The major causes of the initial subprime mortgage crisis and the following recession include lax lending standards contributing to the real-estate bubbles that have since burst; U.S. government housing policies; and limited regulation of non-depository financial institutions. Once the recession began, various responses were attempted with different degrees of success. These included fiscal policies of governments; monetary policies of central banks; measures designed to help indebted consumers refinance their mortgage debt; and inconsistent approaches used by nations to bail out troubled banking industries and private bondholders, assuming private debt burdens or socializing losses.
The Making Home Affordable program of the United States Treasury was launched in 2009 as part of the Troubled Asset Relief Program. The main activity under MHA is the Home Affordable Modification Program.










