In philosophy, the brain in a vat is a scenario used in a variety of thought experiments intended to draw out certain features of human conceptions of knowledge, reality, truth, mind, consciousness, and meaning. It is an updated version of René Descartes's evil demon thought experiment originated by Gilbert Harman. Common to many science fiction stories, it outlines a scenario in which a mad scientist, machine, or other entity might remove a person's brain from the body, suspend it in a vat of life-sustaining liquid, and connect its neurons by wires to a supercomputer which would provide it with electrical impulses identical to those the brain normally receives. According to such stories, the computer would then be simulating reality and the "disembodied" brain would continue to have perfectly normal conscious experiences, such as those of a person with an embodied brain, without these being related to objects or events in the real world.

Softwood is wood from gymnosperm trees such as conifers. The term is opposed to hardwood, which is the wood from angiosperm trees.

Paperboard is a thick paper-based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker than paper and has certain superior attributes such as foldability and rigidity. According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a grammage above 250 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single- or multi-ply.
An invoice, bill or tab is a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer, relating to a sale transaction and indicating the products, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services the seller had provided the buyer.

Particle board – also known as particleboard, low-density fibreboard (LDF), and chipboard – is an engineered wood product manufactured from wood chips, sawmill shavings, or even sawdust, and a synthetic resin or other suitable binder, which is pressed and extruded. Oriented strand board, also known as flakeboard, waferboard, or chipboard is similar, but uses machined wood flakes offering more strength. All of these are composite materials that belong to the spectrum of fiberboard products.

The ampulla of Vater, also known as the hepatopancreatic ampulla or the hepatopancreatic duct, is formed by the union of the pancreatic duct and the common bile duct. The ampulla is specifically located at the major duodenal papilla.
Taxation in the Netherlands is defined by the income tax, the wage withholding tax, the value added tax and the corporate tax.
Coated paper is paper which has been coated by a mixture of materials or a polymer to impart certain qualities to the paper, including weight, surface gloss, smoothness or reduced ink absorbency. Various materials, including Kaolinite, calcium carbonate, Bentonite, and talc can be used to coat paper for high quality printing used in packaging industry and in magazines. The chalk or china clay is bound to the paper with synthetic viscosifiers, such as styrene-butadiene latexes and natural organic binders such as starch. The coating formulation may also contain chemical additives as dispersants, resins, or polyethylene to give water resistance and wet strength to the paper, or to protect against ultraviolet radiation.
Cardboard is a generic term for a heavy-duty paper.
The discography of CMX starts in 1985 and continues to this day. During this time, the band has released fifteen studio albums, two box set compilations, 20 top ten singles on the Finnish charts, four EPs, and a DVD.

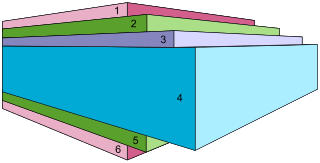
Folding boxboard, also referred to as FBB or by the DIN Standard 19303 codes of GC or UC, is a paperboard grade made up of multiple layers of chemical and mechanical pulp. This grade is made up of mechanical pulp in between two layers of chemical pulp.The top layer is of bleached chemical pulp with an optional pigment coating. This is a low-density material with high stiffness and has a slightly yellow colour, mainly on the inside. The major end uses of folding boxboard are health and beauty products, frozen, chilled and other foods, confectionaries, pharmaceuticals, graphical uses and cigarettes.

Solid bleached board (SBB) or solid bleached sulphate (SBS) is a virgin fibre grade of paperboard.
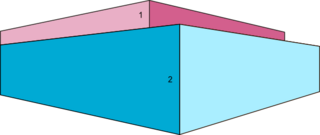
Solid unbleached board, also known as SUB, is a grade of paperboard typically made of unbleached chemical pulp. Most often it comes with two to three layers of mineral or synthetic pigment coating on the top and one layer on the reverse side. Recycled fibres are sometimes used to replace the unbleached chemical pulp.
This article refers to Taxation in Afghanistan.
Cardboard is a generic term for heavy-duty paper-based products having greater thickness and superior durability or other specific mechanical attributes to paper; such as foldability, rigidity and impact resistance. The construction can range from a thick sheet known as paperboard to corrugated fiberboard which is made of multiple corrugated and flat layers.

The Band Box Diner is the oldest operating diner in the Elliot Park neighborhood of Minneapolis, Minnesota. The restaurant, located at 729 South 10th Street, is modeled on the White Castle chain, but is entirely locally built. It was opened by Harry Wyman and his wife Bert in 1939. They eventually built 15 Band Boxes in the chain by 1950. All of the restaurants were in Minneapolis, with the exception of one in Columbia Heights. In 1953, the Wymans sold the chain, and by 1972, this location was the only one that remained. It was purchased in 1998. Its new owners hired architects Robert Roscoe and Karen Gjerstad to plan the restoration and expansion of the building.

Seh Vatal is a village in Baryaji Rural District, on the border of the Central District of Sardasht County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 179, in 42 families.
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally, based on the increase in value of a product or service at each stage of production or distribution. VAT essentially compensates for the shared services and infrastructure provided in a certain locality by a state and funded by its taxpayers that were used in the elaboration of that product or service. Not all localities require VAT to be charged and goods and services for export may be exempted. VAT is usually implemented as a destination-based tax, where the tax rate is based on the location of the consumer and applied to the sales price. Confusingly, the terms VAT, GST, consumption tax and sales tax are sometimes used interchangeably. VAT raises about a fifth of total tax revenues both worldwide and among the members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). As of 2018, 166 of the 193 countries with full UN membership employ a VAT, including all OECD members except the United States, which uses a sales tax system instead.