
Eritrea is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered on the northeast and east by the Red Sea, on the west and northwest by Sudan, on the south by Ethiopia, and on the southeast by Djibouti. The country has a high central plateau that varies from 1,800 to 3,000 meters (5,906–9,843 ft) above sea level. A coastal plain, western lowlands, and some 350 islands comprise the remainder of Eritrea's land mass.
Zula ግእዝ ዙላ saba ሰብኣ 𐩸𐩡 is a small town in central Eritrea. It is situated near the head of Annesley Bay, on the Red Sea coast. Four kilometers away is the archeological site of Adulis, which was an emporium and the port of Axum.

Ethiopia is located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Sudan and South Sudan to the west, and Kenya to the south. Ethiopia has a high central plateau, the Abyssinian Highlands that varies from 1,290 to 3,000 m above sea level, with some 25 mountains whose peaks rise over 4,000 meters (13,200ft), the highest being Ras Dashen at 4,543 meters (14,538ft).

The Tigray Region is the northernmost regional state in Ethiopia. The Tigray Region is the homeland of the Tigrayan, Irob and Kunama people. Its capital and largest city is Mekelle. Tigray is the fifth-largest by area, the fourth-most populous, and the fifth-most densely populated of the 11 regional states.

The J-series is Honda's fourth production V6 engine family introduced in 1996, after the C-series, which consisted of three dissimilar versions. The J-series engine was designed in the United States by Honda engineers. It is built at Honda's Anna, Ohio, and Lincoln, Alabama, engine plants.

The Mareb River, also known as the Gash River, is a river flowing out of central Eritrea. Its chief importance is defining part of the boundary between Eritrea and Ethiopia, between the point where the Mai Ambassa enters the river at 14°53.6′N37°54.8′E to the confluence of the Balasa with the Mareb at 14°38′N39°1.3′E.
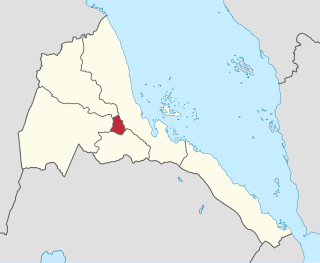
Central Region, also known as the Ma'ekel or Maakel Region, is an administrative region of Eritrea, located in central Eritrea. The region was formed on 15 April 1996, from the historical province of Hamasien. The region is located on the central plateau, and sits at an average of about 2,250 metres (7,380 ft) above sea level. It contains Asmara, the capital and largest city of Eritrea.

The Eritrean–Ethiopian War, also known as the Badme War, was a major armed conflict between Ethiopia and Eritrea that took place from May 1998 to June 2000.

The Kunama are an ethnic group native to Eritrea. They are one of the smallest ethnic communities in Eritrea, constituting only 4% of the population. Most of the estimated 260,000 Kunama live in the remote and isolated area between the Gash and Setit rivers near the border with Ethiopia. The Kunama people have ancient ancestry in the land of Eritrea. In the 2007 Ethiopian census, however, the number of Kunama in Tigray has dropped to 2,976 as the remaining 2,000 or so members of this ethnic group have migrated into the other regions of Ethiopia.
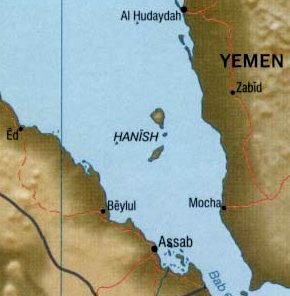
The Hanish Islands conflict was a dispute between Yemen and Eritrea over the island of Greater Hanish in the Red Sea, one of the largest in the then disputed Zukur-Hanish archipelago. Fighting took place over three days from 15 December to 17 December 1995. In 1998 the Permanent Court of Arbitration determined that the territory belonged to Yemen.

Tahtay Adiyabo is a woreda in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Part of the North Western Zone, Tahtay Adiyabo is bordered on the south by Asigede Tsimbela, on the southwest by the Tekezé River on the north by Eritrea, and on the east by La'ilay Adiyabo; part of the northern border with Eritrea is delineated by the Mareb River. The northernmost point of this woreda is the northernmost point of Ethiopia. Towns in this woreda include Addi Awuala and Addi Hageray. The town of Sheraro is surrounded by Tahtay Adiyabo.
The Wokiro River is a seasonal watercourse in Eritrea. It ends north of Massawa, at the Red Sea. Prior to its terminus, the Wokiro merges with the Wadi Laba River.
The Haddas River is a seasonal river in Eritrea. Outside of the small town of Foro in the central part of the nation, the watercourse merges with the Comaile and Aligide rivers. The combined river flows south of Massawa, emptying into the Red Sea. Silt carried down in the river has led to the burial of the ancient town of Adulis.
The Damas River is a seasonal river in Eritrea. It passes outside the town of Ghinda.
The Comaile River has its source between the towns of Adi Keyh and Senafe. It flows down the Eastern Escarpment of Eritrea until the small town of Foro near the Red Sea coast. At this point it merges with two other rivers, the Aligide River and the Haddas River. From this point it continues until it empties into the Red Sea.
The Aligide River is a watercourse in Eritrea. It has its source a short distance outside of the national capital, Asmara. The river flows down the Eastern Escarpment of Eritrea until the small town of Foro near the Red Sea coast. At this point, the Aligide merges with two other rivers, the Comaile River and the Haddas River. It continues from there until it empties into the Red Sea.
Foro is a town in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea.

The Obel River is a right tributary of the Mareb (Gash) river. The latter watercourse forms part of the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia, with its headwaters in the Eritrean Highlands.
Foro Subregion is a subregion in the Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea. Its capital lies at Foro.

Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the south, Sudan in the west, and Djibouti in the southeast. The northeastern and eastern parts of Eritrea have an extensive coastline along the Red Sea. The nation has a total area of approximately 117,600 km2 (45,406 sq mi), and includes the Dahlak Archipelago and several of the Hanish Islands.












