
The Marijuana Policy Project (MPP) is the largest organization working solely on marijuana policy reform in the United States in terms of its budget, number of members, and staff.
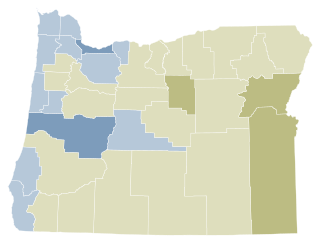
The Oregon Medical Marijuana Act, a law in the U.S. state of Oregon, was established by Oregon Ballot Measure 67 in 1998, passing with 54.6% support. It modified state law to allow the cultivation, possession, and use of marijuana by doctor recommendation for patients with certain medical conditions. The Act does not affect federal law, which still prohibits the cultivation and possession of marijuana.
Timothy Dean Garon was an American singer/songwriter who was denied a liver transplant by the University of Washington Medical Center due to his legal use of cannabis.
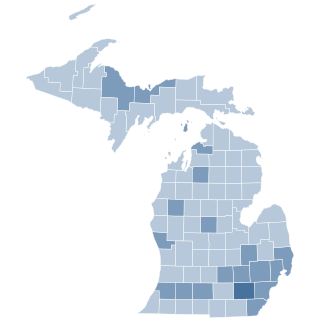
The Michigan Compassionate Care Initiative was an indirect initiated state statute that allowed the medical use of marijuana for seriously ill patients. It was approved by voters as Proposal 1 on November 6, 2008, 63 percent in favor to 37 percent opposed.

Initiative 1000 (I-1000) of 2008 established the U.S. state of Washington's Death with Dignity Act, which legalizes medical aid in dying with certain restrictions. Passage of this initiative made Washington the second U.S. state to permit some terminally ill patients to determine the time of their own death. The effort was headed by former Governor Booth Gardner.

Cannabis in Oregon is legal for both medical and recreational use. In recent decades, the U.S. state of Oregon has had a number of legislative, legal, and cultural events surrounding use of cannabis. Oregon was the first state to decriminalize the possession of small amounts of cannabis, and among the first to authorize its use for medical purposes. An attempt to recriminalize possession of small amounts of cannabis was turned down by Oregon voters in 1997.
Initiative 1068 was a proposed initiative for the November 2010 Washington state general election that would have removed criminal penalties from the adult use, possession, and cultivation of marijuana in Washington. Sponsored by Vivian McPeak, Douglass Hiatt, Jeffrey Steinborn, Philip Dawdy, initiative I-1068 sought to legalize marijuana by removing marijuana offenses from the state's controlled substances act, but failed to gather enough signatures to qualify for the ballot.

Proposition 203, or the Arizona Medical Marijuana Act, was an Arizona ballot measure to legalize the use of medical marijuana without the normal Food and Drug Administration testing for safety and efficacy. Proposition 203 passed by a narrow margin, with 50.13% of the vote.

Washington Initiative 502 (I-502) "on marijuana reform" was an initiative to the Washington State Legislature, which appeared on the November 2012 general ballot, passing by a margin of approximately 56 to 44 percent. Originally submitted to the Washington Secretary of State during the summer of 2011, enough signatures were collected and submitted by December to meet the required 241,153 signatures, sending it to the legislature. When the legislature adjourned without action in April, Initiative 502 automatically advanced to the November 2012 general ballot. It was approved by popular vote on November 6, and took effect over the course of a year, beginning with certification no later than December 6, 2012. Along with a similar Colorado measure, Initiative 502 was credited for encouraging voter turnout of 81%, the highest in the nation.
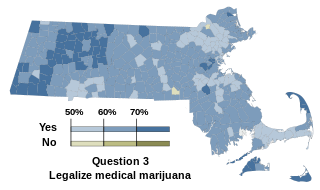
The Massachusetts Medical Marijuana Initiative, appeared as the third question on the state's 2012 ballot as an indirect initiated state statute. The measure allows cannabis to be used for medical purposes in the state. The initiative—backed by the American Civil Liberties Union, the Massachusetts Patient Advocacy Alliance, and the Committee for Compassionate Medicine—was filed with proponents turning in the required signatures to the Massachusetts Attorney General's office by the August 3, 2011 deadline. Those signatures were needed for the required ten qualified voters who submitted the original petition to put forward the full text of the law they want enacted. The initiative passed with support from 63% of state voters.

Florida Amendment 2, Use of Marijuana for Certain Medical Conditions, is an initiative that appeared on the November 4, 2014, ballot in the state of Florida as a citizen initiated state constitutional amendment.

Cannabis in Utah is illegal for recreational use. Possession of small amounts is punishable as a misdemeanor crime. Medical use was legalized by ballot measure in November 2018, after a CBD-only law was passed in 2014 and a limited "right to try" law was passed in March 2018.

Amendment 20 was an amendment to state statutes, submitted for referendum in the 2000 general elections in the U.S. state of Colorado. The amendment was adopted by 54% of participating voters. Under the law, patients may possess up to 2 ounces of medicinal marijuana and may cultivate no more than six marijuana plants at a time. Patients who are caught with more than this in their possession may argue "affirmative defense of medical necessity" but are not protected under state law with the rights of those who stay within the guidelines set forth by the state.[4]

Cannabis in Nevada became legal for recreational use on January 1, 2017, following the passage of Question 2 on the 2016 ballot with 54% of the vote. The first licensed sales of recreational cannabis began on July 1, 2017.

The Florida Medical Marijuana Legalization Initiative, also known as Amendment 2, was approved by voters in the Tuesday, November 8, 2016, general election in the State of Florida. The bill required a super-majority vote to pass, with at least 60% of voters voting for support of a state constitutional amendment. Florida already had a medical marijuana law in place, but only for those who are terminally ill and with less than a year left to live. The goal of Amendment 2 is to alleviate those suffering from these medical conditions: cancer, epilepsy, glaucoma, positive status for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Crohn's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, chronic nonmalignant pain caused by a qualifying medical condition or that originates from a qualified medical condition or other debilitating medical conditions comparable to those listed. Under Amendment 2, the medical marijuana will be given to the patient if the physician believes that the medical use of marijuana would likely outweigh the potential health risks for a patient. Smoking the medication was not allowed under a statute passed by the Florida State Legislature, however this ban was struck down by Leon County Circuit Court Judge Karen Gievers on May 25, 2018.

Cannabis in Arizona is legal for recreational use. A 2020 initiative to legalize recreational use passed with 60% of the vote. Possession and cultivation of recreational cannabis became legal on November 30, 2020, with the first state-licensed sales occurring on January 22, 2021.

Cannabis in Missouri is legal for recreational use. A ballot initiative to legalize recreational use passed by a 53–47 margin on November 8, 2022. Possession for adults 21 and over became legal on December 8, 2022, with the first licensed sales occurring on February 3, 2023.

Cannabis in Washington relates to a number of legislative, legal, and cultural events surrounding the use of cannabis. On December 6, 2012, Washington became the first U.S. state to legalize recreational use of marijuana and the first to allow recreational marijuana sales, alongside Colorado. The state had previously legalized medical marijuana in 1998. Under state law, cannabis is legal for medical purposes and for any purpose by adults over 21.

Initiative 182 was a 2016 ballot initiative that amended Montana law to legalize marijuana for medical use in the state. The initiative passed via public referendum on November 8, 2016 with 58% of voters supporting and 42% opposing.

Mississippi state elections in 2020 were held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. Its primaries were held on March 10, 2020, with runoffs taking place on June 23.

















