Related Research Articles

Guinea is a country on the coast of West Africa and is bordered by Guinea-Bissau, Senegal, Mali, Ivory Coast, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.

Sierra Leone is a country in West Africa with a North Atlantic Ocean coastline to the west. It lies on the African Plate. The island's main geographical features include wooded hill country, an upland plateau, and mountains in the east. The highest peak is Mount Bintumani, which is 1,948 meters (6,391 ft) above sea level. The coastline has a belt of mangrove swamps. Freetown, the nation's capital city, has one of the world's largest natural harbours. The Rokel River is the largest river in Sierra Leone. It is 400 kilometres (250 mi) long and has a basin with a total area of 10,622 square kilometres (4,101 sq mi).

West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. The population of West Africa is estimated at 419 million people as of 2021, and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 were female and 192,309,000 male. The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent.
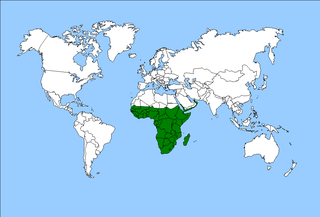
The Afrotropical realm is one of Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the southern Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region.

Taï National Park is a national park in Côte d'Ivoire that contains one of the last areas of primary rainforest in West Africa. It was inscribed as a World Heritage Site in 1982 due to the diversity of its flora and fauna. Five mammal species of the Taï National Park are on the Red List of Threatened Species: pygmy hippopotamus, olive colobus monkeys, leopards, chimpanzees, and Jentink's duiker.


In West Africa, the Dahomey Gap refers to the portion of the Guinean forest-savanna mosaic that extends all the way to the coast in Benin, Togo, and Ghana, thus separating the forest zone that covers much of the south of the region into two separate parts. The forest region west of the gap is called the Upper Guinean forests or Guinean forest zone, and the portion east of the gap is called the Lower Guinean forests, Lower Guinean-Congolian forests, or Congolian Forest Zone.

The unofficial geographic term Northern Australia includes those parts of Queensland and Western Australia north of latitude 26° and all of the Northern Territory. Those local government areas of Western Australia and Queensland that lie partially in the north are included.

The Guinean forests of West Africa is a biodiversity hotspot designated by Conservation International, which includes the belt of tropical moist broadleaf forests along the coast of West Africa, running from Sierra Leone and Guinea in the west to the Sanaga River of Cameroon in the east. The Dahomey Gap, a region of savanna and dry forest in Togo and Benin, divides the Guinean forests into the Upper Guinean forests and Lower Guinean forests.

The Upper Guinean forests is a tropical seasonal forest region of West Africa. The Upper Guinean forests extend from Guinea and Sierra Leone in the west through Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana to Togo in the east, and a few hundred kilometers inland from the Atlantic coast. A few enclaves of montane forest lie further inland in the mountains of central Guinea and central Togo and Benin.

The Guinean forest–savanna mosaic is an ecoregion of West Africa, a band of interlaced forest, savanna, and grassland running east to west and dividing the tropical moist forests near the coast from the West Sudanian savanna of the interior.

The Cameroon line is a 1,600 km (1,000 mi) long chain of volcanoes that includes islands in the Gulf of Guinea and mountains on the African mainland, from Mount Cameroon on the coast towards Lake Chad on the northeast. They form a natural border between eastern Nigeria and the West Region of Cameroon. The islands, which span the equator, have tropical climates and are home to many unique plant and bird species. The mainland mountain regions are much cooler than the surrounding lowlands, and also contain unique and ecologically important environments.

Papilio antimachus, the African giant swallowtail, is a butterfly in the family Papilionidae. With a wingspan between 18 and 23 centimetres, it is the largest butterfly in Africa and among the largest butterflies in the world. The wings are long and narrow and the ground colour is orange brown with black markings. P. antimachus live in the tropical rainforests of west and central Africa. The distribution area (range) stretches from Angola, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, and Uganda. It is much rarer in the west of its range than in the eastern parts of its range. It probably stays in forest canopy but males come down to mud-puddle. The male is larger than the female and can be seen in groups at nectar. The females show themselves less, continually flying high above the treetops. It has been seen hill-topping in Liberia. The butterfly may have no natural enemies because it is very toxic. The larval foodplant is unknown and nothing is published on the early stages. Cardiac glycosides found in the Imago by Miriam Rothschild indicate that the so-far unidentified larva, most probably, sequesters foodplant toxins which persist through pupation into the imago as an aposematic protection against predation, and therefore that the larval foodplant is probably an asclepiad vine.
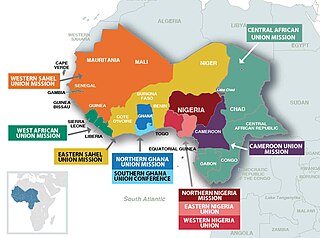
The West-Central Africa Division (WAD) of Seventh-day Adventists is a sub-entity of the General Conference of Seventh-day Adventists, which coordinates the Church's operations in 22 African countries, which include Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo. Its headquarters is in Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire. Founded in 2003, the division membership as of June 30, 2021 is 889,196

Euxanthe eurinome, the common forest queen, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Senegal, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Gabon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Central African Republic, Uganda, Kenya and Ethiopia. The habitat consists of lowland evergreen forests and dry and degraded forests.

Amauris damocles, the small monk, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Senegal, Gambia, Guinea, Burkina Faso, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Cameroon and Tanzania. The habitat consists of dry forests, Guinea savanna and disturbed areas in the rainforest zone.

The Guinean montane forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa.
Maritime Guinea, also known as Lower Guinea, is one of the four natural regions of Guinea. It is located in the west of the country, between the Atlantic Ocean and the Fouta Djallon plateau. Conakry, Guinea's capital and largest city, is located in the region.

Seasonal tropical forest, also known as moist deciduous, semi-evergreen seasonal, tropical mixed or monsoon forests, typically contain a range of tree species: only some of which drop some or all of their leaves during the dry season. This tropical forest is classified under the Walter system as (i) tropical climate with high overall rainfall and (ii) having a very distinct wet season with dry season. These forests represent a range of habitats influenced by monsoon (Am) or tropical wet savannah (Aw) climates. Drier forests in the Aw climate zone are typically deciduous and placed in the Tropical dry forest biome: with further transitional zones (ecotones) of savannah woodland then tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands.

The Guineo-Congolian region is a biogeographical region in Africa straddling the Equator and stretching from the Atlantic Ocean through the Congo Basin to the Congo / Nile divide in Rwanda and Burundi. Formerly, this region was largely covered in rain forest, on both well-drained sites and in swamp forests, but little undisturbed primary forest now remains, having been replaced in many areas by savanna and secondary-growth forest.
References
Davis, Stephen D. (Editor), Heywood, V. H. (Editor), Hamilton, A. C. (Editor) Centres of Plant Diversity : A Guide and Strategy for Their Conservation: Volume 1 (Europe, Africa, South West Asia, and the Middle East) published 1993 by World Wide Fund For Nature and International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources.