This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2014) |
Western Division | |
|---|---|
Division | |
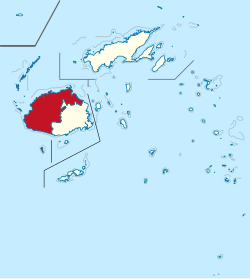 Map of Fiji showing Western division. | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Lautoka |
| Area | |
• Total | 6,360 km2 (2,460 sq mi) |
| Population (2017) [2] | |
• Total | 337,071 |
| • Density | 53/km2 (140/sq mi) |
The Western Division is one of Fiji's four divisions. [3] It consists of three provinces in western and northern Viti Levu, namely Ba Province, Nadroga-Navosa Province, and Ra Province. [4] The largest city and capital is Lautoka. [3]
It also includes a few outlying islands, including the Yasawa Islands, Viwa Island, and Mamanuca Islands. It has a land border with the Central Division on Viti Levu, and sea borders with the Northern Division and Eastern Division.