| White-browed meadowlark | |
|---|---|
| male in breeding plumage in Colonia, Uruguay | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Icteridae |
| Genus: | Leistes |
| Species: | L. superciliaris |
| Binomial name | |
| Leistes superciliaris (Bonaparte, 1850) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
Sturnella superciliaris | |
The white-browed meadowlark (Leistes superciliaris) is a passerine bird in the New World family Icteridae. It was formerly named white-browed blackbird but is not closely related to the red-winged blackbird group. [2]
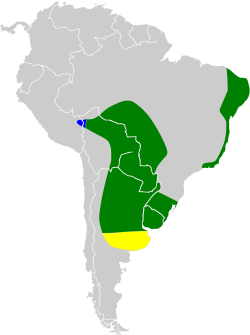
The white-browed meadowlark breeds in north-eastern Brazil and in southern South America from south-western Brazil through Paraguay, Uruguay and Argentina. Southern populations are partially migratory.
Like other meadowlarks, it is a bird associated with open country, including moist grasslands, pasture and cultivation, preferably with the odd bush or fence post for males to use as a songpost. In display the male flies up to 10 m in the air, then parachutes down on folded wings whilst singing an initially buzzing song, followed by a series of notes TZZZZZZ-teee-chu-chu-chak-chak. The call is a short chuck.
The white-browed meadowlark builds a deep grass-lined open cup nest on the ground amongst tall grasses, with several nests often close together. The normal clutch is three to five reddish brown-blotched greenish eggs. This species is often parasitised by the shiny cowbird, and on one occasion 19 cowbird eggs were found with one meadowlark egg in a nest.
The white-browed meadowlark is a small icterid. The male has mainly black plumage, apart from a bright red throat, belly and wing epaulets, and a white supercilium. The female has buff edged dark brown upperpart feathers, buff underparts, and pale streaks through the crown and eye. Juveniles resemble the female, but are paler.
This species is very closely related to the red-breasted meadowlark, L. militaris, which breeds further north, and was formerly considered to be subspecies of that bird. The male white-browed is easily distinguished by his bright white supercilium, but females of the two species are almost identical. The female red-breasted meadowlark is longer billed, smaller, and shorter winged than the white-browed, with more red and less streaking on the underparts.
This gregarious bird feeds mainly on insects and some seeds, including rice, and forages on the ground like a bobolink.
The white-browed meadowlark has benefited from the more open habitat created by forest clearance and ranching, and is extending its range.

