Related Research Articles

Merlot is a dark blue–colored wine grape variety, that is used as both a blending grape and for varietal wines. The name Merlot is thought to be a diminutive of merle, the French name for the blackbird, probably a reference to the color of the grape. Its softness and "fleshiness", combined with its earlier ripening, makes Merlot a popular grape for blending with the sterner, later-ripening Cabernet Sauvignon, which tends to be higher in tannin.

Riesling is a white grape variety which originated in the Rhine region. Riesling is an aromatic grape variety displaying flowery, almost perfumed, aromas as well as high acidity. It is used to make dry, semi-sweet, sweet, and sparkling white wines. Riesling wines are usually varietally pure and are seldom oaked. As of 2004, Riesling was estimated to be the world's 20th most grown variety at 48,700 hectares, but in terms of importance for quality wines, it is usually included in the "top three" white wine varieties together with Chardonnay and Sauvignon blanc. Riesling is a variety which is highly "terroir-expressive", meaning that the character of Riesling wines is greatly influenced by the wine's place of origin.

Pinot blanc is a white wine grape. It is a point genetic mutation of Pinot noir. Pinot noir is genetically unstable and will occasionally experience a point mutation in which a vine bears all black fruit except for one cane which produces white fruit.

Barbera is a red Italian wine grape variety that, as of 2000, was the third most-planted red grape variety in Italy. It produces good yields and is known for deep color, full body, low tannins and high levels of acidity.

Furmint is a white Hungarian wine grape variety that is most noted widely grown in the Tokaj-Hegyalja wine region where it is used to produce single-varietal dry wines as well as being the principal grape in the better known Tokaji dessert wines. It is also grown in the tiny Hungarian wine region of Somló. Furmint plays a similar role in the Slovakian wine region of Tokaj. It is also grown in Austria where it is known as Mosler. Smaller plantings are found in Slovenia where it is known as Šipon. The grape is also planted in Croatia, where it is known as Moslavac. It is also found in Romania and in former republics of the Soviet Union. Furmint is a late ripening variety. For dry wines the harvest starts usually in September, however sweet wine specific harvest can start in the second half of October or even later, and is often affected by Botrytis.

Austrian cuisine is a style of cuisine native to Austria and composed of influences from Central Europe and throughout the former Austro-Hungarian Empire. Austrian cuisine is most often associated with Viennese cuisine, but there are significant regional variations.

Grüner Veltliner is a white wine grape variety grown primarily in Austria, Hungary, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic. The leaves of the grape vine are five-lobed with bunches that are long but compact, and deep green grapes that ripen in mid-late October in the Northern Hemisphere.

Blaufränkisch is a dark-skinned variety of grape used for red wine. Blaufränkisch, which is a late-ripening variety, produces red wines which are typically rich in tannin and may exhibit a pronounced spicy character.

A rosé is a type of wine that incorporates some of the color from the grape skins, but not enough to qualify it as a red wine. It may be the oldest known type of wine, as it is the most straightforward to make with the skin contact method. The pink color can range from a pale "onion-skin" orange to a vivid near-purple, depending on the grape varieties used and winemaking techniques. Usually, the wine is labelled rosé in French, Portuguese, and English-speaking countries, rosado in Spanish, or rosato in Italian.
Hungarian wine has a history dating back to the Kingdom of Hungary. Outside Hungary, the best-known wines are the white dessert wine Tokaji aszú and the red wine Bull's Blood of Eger.
Schilcher is a wine produced solely in the Austrian region of Western Styria (Weststeiermark), in the districts of Deutschlandsberg and Voitsberg, sharing a border with Slovenia and Carinthia to the south and west. The Schilcher wine itself is a distinct rosé made from the indigenous Blauer Wildbacher grape. The colour ranges from a light onion tinge to a deep ruby. The grape was once a wild variety which was said to contain alcohol compounds which, in turn, allegedly would induce wild inebriation, hence its colloquial name Rabiatperle - rabid pearl. The name Schilcher originates from the Middle High German word schillern meaning to radiate with colour.

Blauer Portugieser is a red Austrian, Slovenian wine and German wine grape found primarily in the Rheinhessen, Pfalz and wine regions of Lower Austria and Slovenia. It is also one of the permitted grapes in the Hungarian wine Egri Bikavér. In Germany, the cultivated area covered 4,551 hectares or 4.5% of the total vineyard area in 2007. Wine cellars usually vinify a simple light red wine, which is characterized by a fresh, tart and light body. It is also frequently vinified as a rosé. Blauer Portugieser is also very well suited as table grapes; however, it is not sold as such because the selling of wine grapes as table grapes is not permitted in the European Union. Since 2000, higher quality wines have been vinified from Portugieser grapes. The use of oak provides additional aromas in order to compete with Bordeaux varieties. DNA profiling has shown that Blauer Portugieser is a cross between Grüner Silvaner and Blaue Zimmettraube. Historical ampelographic sources have provided very solid evidence that the geographic area of origin of the variety is Lower Styria.

Marzemino is a red Italian wine grape variety that is primarily grown around Isera, south of Trentino. The wine is most noted for its mention in the opera Don Giovanni of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. The vine ripens late and is susceptible to many grape diseases including oidium. Wine produced from the grape has a characteristic dark tint and light plummy taste.

Austrian wines are mostly dry white wines, though some sweeter white wines are also produced. About 30% of the wines are red, made from Blaufränkisch, Pinot noir and locally bred varieties such as Zweigelt. Four thousand years of winemaking history counted for little after the "antifreeze scandal" of 1985, when it was revealed that some wine brokers had been adulterating their wines with diethylene glycol. The scandal destroyed the market for Austrian wine and compelled Austria to tackle low standards of bulk wine production, and reposition itself as a producer of quality wines. The country is also home to Riedel, makers of some of the most expensive wine glasses in the world. Some of the best producers of Austria include Weingut Bründlmayer, Weingut F.X. Pichler and Weingut Franz Hirtzberger, Weingut Hutter, Weingut Eigl and Wellanschitz.

Piemonte wine is the range of Italian wines made in the region of Piedmont in the northwestern corner of Italy. The best-known wines from the region include Barolo and Barbaresco. They are made from the Nebbiolo grape. These wines are ideal for storage and a well-aged Barolo for instance may leave a feeling of drinking velvet because the tannins are polished and integrated more and more into the wine. As the wine matures the colour becomes more brownish and rust-red.

Friuli-Venezia Giulia wine is wine made in the northeastern Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. Once part of the Venetian Republic and with sections under the influence of the Austro-Hungarian Empire for some time, the wines of the region have noticeable Slavic and Germanic influences. There are 11 Denominazione di origine controllata (DOC) and 3 Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita (DOCG) in the Friuli-Venezia Giulia area. The region has 3 Indicazione Geografica Tipica (IGT) designations Alto Livenza, delle Venezie and Venezia Giulia. Nearly 62% of the wine produced in the region falls under a DOC designation. The area is known predominantly for its white wines which are considered some of the best examples of Italian wine in that style. Along with the Veneto and Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, the Friuli-Venezia Giulia forms the Tre Venezie wine region which ranks with Tuscany and Piedmont as Italy's world class wine regions.
Ribolla Gialla is a white wine grape grown most prominently in the Friuli region of northeast Italy. The grape is also found in Slovenia where it is known as Rebula. In Friuli, the grape thrives in the region around Rosazzo and Gorizia. In Slovenia, the grape is grown prominently in the Brda region. The grape is not related to the Friuli red wine grape Schioppettino, which is also known as Ribolla Nera. The obscure, lower quality Ribola Verde grape is a mutated version that is not widely used.
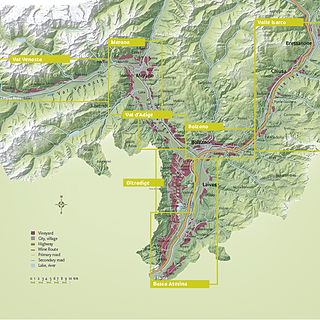
South Tyrol is an autonomous province located in north-east Italy producing wine. This Austro-Italian wine region is noted for the distinct Austrian influences on the wine industry due to the region's long history under the rule of Austria-Hungary and Holy Roman Empires.

Abruzzo (Abruzzi) is an Italian wine region located in the mountainous central Italian region of Abruzzo along the Adriatic Sea. It is bordered by the Molise wine region to the south, Marche to the north and Lazio to the west. Abruzzo's rugged terrain, 65% of which is mountainous, help to isolate the region from the winemaking influence of the ancient Romans and Etruscans in Tuscany but the area has had a long history of wine production.
Bianco d'Alessano is a white Italian wine grape variety that is grown in the Apulia region of southern Italy, where it is often blended with Verdeca. In the early 21st century, the grape was planted in the South Australian wine region of Riverland where varietal examples of Bianco d'Alessano has won wine competition awards as an "Alternative Variety". In Italy, the grape has also been historically used in the production of vermouth.
References
- ↑ Moser, Peter The Ultimate Austrian Wine Guide Falstaff Productions Ltd. (Falstaff Verlags GmbH) 2008 ISBN 978-3-902660-00-8
- ↑ Stevenson, Tom The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia Dorling Kindersley Limited 2007 ISBN 978-0-7566-3164-2