
The following four classifications of wine constitute the Italian system of labelling and legally protecting Italian wine:

In France, the appellation d'origine contrôlée(AOC) is a label that identifies an agricultural product whose stages of production and processing are carried out in a defined geographical area – the terroir – and using recognized and traditional know-how. The specificity of an AOC product is determined by the combination of a physical and biological environment with established production techniques transmitted within a human community. Together, these give the product its distinctive qualities.

Qormi, also known by its title Città Pinto, is a city in the Southern Region of Malta, southwest of Valletta in the centre of the island. It has a population of 16,324, making it Malta's fifth-largest city.

Italian wine is produced in every region of Italy. Italy is the world's largest wine producer, as well as the country with the widest variety of indigenous grapevine in the world, with an area of 702,000 hectares under vineyard cultivation, and contributing a 2013–2017 annual average of 48.3 million hl of wine. In 2018 Italy accounted for 19 per cent of global production, ahead of France and Spain. Italian wine is both exported around the world and popular domestically among Italians, who consume an average of 42 litres per capita, ranking fifth in world wine consumption.

Greece is one of the oldest wine-producing regions in the world and among the first wine-producing territories in Europe. The earliest evidence of Greek wine has been dated to 6,500 years ago where wine was produced on a household or communal basis. In ancient times, as trade in wine became extensive, it was transported from end to end of the Mediterranean; Greek wine had especially high prestige in Italy under the Roman Empire. In the medieval period, wines exported from Crete, Monemvasia and other Greek ports fetched high prices in northern Europe.

Fontana is an administrative unit of Malta, on the island of Gozo, with a population of 985 people.

Wine has been produced in the United States since the 1500s, with the first widespread production beginning in New Mexico in 1628. Today, wine production is undertaken in all fifty states, with California producing 84 percent of all US wine. The North American continent is home to several native species of grape, including Vitis labrusca, Vitis riparia, Vitis rotundifolia, and Vitis vulpina, but the wine-making industry is based almost entirely on the cultivation of the European Vitis vinifera, which was introduced by European settlers. With more than 1,100,000 acres (4,500 km2) under vine, the United States is the fourth-largest wine producing country in the world, after Italy, Spain, and France.
The glossary of wine terms lists the definitions of many general terms used within the wine industry. For terms specific to viticulture, winemaking, grape varieties, and wine tasting, see the topic specific list in the "See also" section below.
Malta is the country with the most holidays in the European Union. Since 2020, any holidays falling on Saturdays or Sundays add an extra day to the workers' leave pool, reverting to the pre 2005 system.

The United Kingdom is a major consumer of wine, although a minor grower and producer. Wine production in the UK has historically been perceived as less than ideal due to the cold climate, but warmer summers and grapes adapted to these conditions have played a role in increasing investment and sale of wines. Most is English sparkling wine, from vineyards across Southern England and sparkling wine from Wales where the climate is warmer than that of northern areas. Vineyards are becoming more commonplace in counties such as Essex, Sussex and Kent, where more varieties of wine can be produced due to the drier and warmer climate.
Easter is one of the most significant events in the religious and social calendar, celebrated heavily in the European country of Malta.

Malta is for non-local government purposes divided into districts as opposed to the local government localities. The three main types of such districts – statistical, electoral at national level, and policing – have no mainstream administrative effect as the local councils form the first-tier – moreover only administrative tier – divisions of the country.

Priorat is a Denominació d'Origen Qualificada (DOQ) for Catalan wines produced in the Priorat county, in the province of Tarragona, in the southwest of Catalonia.

Tuscan wine is Italian wine from the Tuscany region. Located in central Italy along the Tyrrhenian coast, Tuscany is home to some of the world's most notable wine regions. Chianti, Brunello di Montalcino and Vino Nobile di Montepulciano are primarily made with Sangiovese grape whereas the Vernaccia grape is the basis of the white Vernaccia di San Gimignano. Tuscany is also known for the dessert wine Vin Santo, made from a variety of the region's grapes. Tuscany has forty-one Denominazioni di origine controllata (DOC) and eleven Denominazioni di Origine Controllata e Garantita (DOCG). In the 1970s a new class of wines known in the trade as "Super Tuscans" emerged. These wines were made outside DOC/DOCG regulations but were considered of high quality and commanded high prices. Many of these wines became cult wines. In the reformation of the Italian classification system many of the original Super Tuscans now qualify as DOC or DOCG wines but some producers still prefer the declassified rankings or to use the Indicazione Geografica Tipica (IGT) classification of Toscana. Tuscany has six sub-categories of IGT wines today.

Luxembourgish wine is primarily produced in the southeastern part of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, with vineyards overlooking the river Moselle. Along this river, which for 42 km makes up part of the border between Luxembourg and Germany, wine is made in three countries. There is a continuous history of winemaking along Moselle and in Luxembourg going back to Ancient Roman times. Wine production in 2006/07 was 123,652 hectoliter from 1,237 hectares of vineyards. Out of total wine exports of 87,776 hectoliter in 2005/06, 71,726 hectoliter or 82% was exported to nearby Belgium. Exports to Germany were the second largest at 8,168 hectoliter, or 9%, and is to a large extent made up of base wine in bulk for the production of blended Sekt rather than being sold bottled with "Luxembourg" anywhere on the label. Therefore, very little Luxembourgish wine is seen outside Luxembourg and Belgium.
Emmanuel Delicata is a Maltese wine producer.
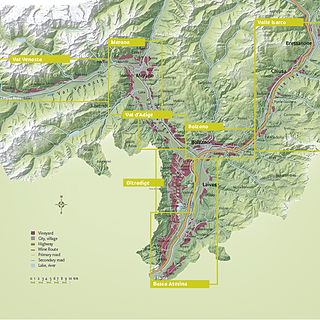
South Tyrol is an autonomous province located in northeast Italy producing wine. This Austro-Italian wine region is noted for the distinct Austrian influences on the wine industry, due to the region's long history under the rule of Austria-Hungary and Holy Roman Empires.

In Malta most of the main roads are in the outskirts of the localities to connect one urban area with another urban area. The most important roads are those that connect the south of the island with the northern part, like Tal-Barrani Road, Aldo Moro Street in Marsa and Birkirkara Bypass.

The 1813–1814 Malta plague epidemic was the last major outbreak of plague on the islands of Malta and Gozo. It occurred between March 1813 and January 1814 on Malta and between February and May 1814 on Gozo, and the epidemic was officially declared to be over in September 1814. It resulted in approximately 4500 deaths, which was about 5% of the islands' population.
















