
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino and also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino, is a European microstate and country enclaved by Italy. Located on the northeastern side of the Apennine Mountains, San Marino is the fifth-smallest country in the world and covers a land area of just over 61 km2, with a population of 33,562.

Vermouth is an aromatized fortified wine, flavoured with various botanicals and sometimes colored. The modern versions of the beverage were first produced in the mid to late 18th century in Turin, Italy. While vermouth was traditionally used for medicinal purposes, it was later served as an apéritif, with fashionable cafés in Turin serving it to guests around the clock. In the late 19th century, it became popular with bartenders as a key ingredient for cocktails, such as the martini, the Manhattan, the Rob Roy, and the Negroni. In addition to being consumed as an aperitif or cocktail ingredient, vermouth is sometimes used as an alternative to white wine in cooking.

Zinfandel is a variety of black-skinned wine grape. The variety is grown in over 10 percent of California vineyards. DNA analysis has revealed that it is genetically equivalent to the Croatian grapes Crljenak Kaštelanski and Tribidrag, as well as to the Primitivo variety traditionally grown in Apulia, Italy, where it was introduced in the 18th century, and Kratošija in Montenegro. The grape found its way to the United States in the mid-19th century, where it became known by variations of a name applied to a different grape, likely "Zierfandler" from Austria.

German wine is primarily produced in the west of Germany, along the river Rhine and its tributaries, with the oldest plantations going back to the Roman era. Approximately 60 percent of German wine is produced in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, where 6 of the 13 regions (Anbaugebiete) for quality wine are situated. Germany has about 103,000 hectares of vineyard, which is around one tenth of the vineyard surface in Spain, France or Italy. The total wine production is usually around 10 million hectoliters annually, corresponding to 1.3 billion bottles, which places Germany as the eighth-largest wine-producing country in the world. White wine accounts for almost two thirds of the total production.

A rosé is a type of wine that incorporates some of the color from the grape skins, but not enough to qualify it as a red wine. It may be the oldest known type of wine, as it is the most straightforward to make with the skin contact method. The pink color can range from a pale "onionskin" orange to a vivid near-purple, depending on the grape varieties used and winemaking techniques. Usually, the wine is labelled rosé in French, Portuguese, and English-speaking countries, rosado in Spanish, or rosato in Italian.

New World wines are those wines produced outside the traditional winegrowing areas of Europe and the Middle East, in particular from Argentina, Australia, Canada, Chile, Mexico, New Zealand, South Africa and the United States. The phrase connotes a distinction between these "New World" wines and those wines produced in "Old World" countries with a long-established history of wine production, essentially in Europe, most notably: France, Italy, Germany, Spain and Portugal.

Italian wine is produced in every region of Italy. Italy is the world's largest producer of wine, with an area of 702,000 hectares under vineyard cultivation, and contributing a 2013–2017 annual average of 48.3 million hl of wine. In 2018 Italy accounted for 19 per cent of global production, ahead of France and Spain. Italian wine is both exported around the world and popular domestically among Italians, who consume an average of 42 litres per capita, ranking fifth in world wine consumption.

French wine is produced all throughout France, in quantities between 50 and 60 million hectolitres per year, or 7–8 billion bottles. France is one of the largest wine producers in the world, along with Italian, Spanish, and American wine-producing regions. French wine traces its history to the 6th century BCE, with many of France's regions dating their wine-making history to Roman times. The wines produced range from expensive wines sold internationally to modest wines usually only seen within France such as the Margnat wines of the post war period.

Argentina is the fifth largest producer of wine in the world. Argentine wine, as with some aspects of Argentine cuisine, has its roots in Spain. During the Spanish colonization of the Americas, vine cuttings were brought to Santiago del Estero in 1557, and the cultivation of the grape and wine production stretched first to neighboring regions, and then to other parts of the country.

Spanish wine includes red, white, and sparkling wines produced throughout the country. Located on the Iberian Peninsula, Spain has over 1.2 million hectares planted in wine grapes, making it the most widely planted wine-producing nation, but the second largest producer of wine in the world, behind Italy and ahead of France and the United States. This is due, in part, to the very low yields and wide spacing of the old vines planted on the dry soils found in some of the Spanish wine regions. The country is ninth in worldwide consumption with Spaniards drinking, on average, 21.6 litres per person a year. The country has an abundance of native grape varieties, with over 400 varieties planted throughout Spain, though 88 percent of the country's wine production is from only 20 grapes — including the reds Tempranillo, Bobal, Garnacha, and Monastrell; the whites Albariño, Airén, Verdejo, Palomino, and Macabeo; and the three Cava grapes Parellada, Xarel·lo, and Macabeo.

Tourism in San Marino, known also as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino is an integral element of the economy within the microstate. The tourism sector contributes a large part of San Marino's GDP, with approximately 2 million tourists visiting per year.

As San Marino is a microstate completely landlocked by Italy, Sammarinese cuisine is strongly similar to Italian cuisine, especially that of the adjoining Emilia-Romagna and Marche regions. San Marino's primary agricultural products are cheese, wine and livestock, and cheesemaking is a primary economic activity in San Marino. San Marino participated in The Exposition Universelle of 1889, a world's fair held in Paris, France, with three exhibits of oils and cheese.

Piemonte wine is the range of Italian wines made in the region of Piedmont in the northwestern corner of Italy. The best-known wines from the region include Barolo and Barbaresco. They are made from the Nebbiolo grape. These wines are ideal for storage and a well-aged Barolo for instance may leave a feeling of drinking velvet because the tannins are polished and integrated more and more into the wine. As the wine matures the colour becomes more brownish and rust-red.

Friuli-Venezia Giulia wine is wine made in the northeastern Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. There are 11 Denominazione di origine controllata (DOC) and 3 Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita (DOCG) in the Friuli-Venezia Giulia area. The region has 3 Indicazione Geografica Tipica (IGT) designations Alto Livenza, delle Venezie and Venezia Giulia. Nearly 62% of the wine produced in the region falls under a DOC designation. The area is known predominantly for its white wines which are considered some of the best examples of Italian wine in that style. Along with the Veneto and Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, the Friuli-Venezia Giulia forms the Tre Venezie wine region which ranks with Tuscany and Piedmont as Italy's world class wine regions.

Fiano is a white Italian wine grape variety that is grown primarily in the Campania region of southern Italy and on the island of Sicily. In Campania, this fairly strong flavored white wine grape is particularly noted around Avellino where the Denominazione di origine controllata e Garantita (DOCG) wine of Fiano di Avellino is produced. The grape has a long history in the Campanian region and is believed to have been the grape behind the ancient Roman wine Apianum. Even today, the name Apianum is permitted to appear on wine labels of the DOCG wine Fiano di Avellino.

Slovenia has more than 28,000 wineries making between 80 and 90 million litres annually from the country's 22,300 ha of vineyards. About 75% of the country's production is white wine. Almost all of the wine is consumed domestically with only 6.1 million L a year being exported—mostly to the United States, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, and lately the Czech Republic. Most of the country's wine production falls under the classification of premium (vrhunsko) wine with less than 30% classified as basic table wine (namizno vino). Slovenia has three principal wine regions: the Drava Wine-Growing Region, the Lower Sava Wine-Growing Region, and the Littoral Wine-Growing Region.

The Gorizia Hills is a hilly microregion in western Slovenia and northeastern Italy. It lies on the right bank of the Soča (Isonzo) river, north of the Italian town of Gorizia, after which it is named. The region has around 120 square kilometres and 7,000 inhabitants, mostly ethnic Slovenes, with a small number of Friulian speakers in its westernmost part.

The history of Chianti dates back to at least the 13th century with the earliest incarnations of Chianti as a white wine. Today this Tuscan wine is one of Italy's most well known and recognizable wines. In the Middle Ages, the villages of Gaiole, Castellina and Radda located near Florence formed as a Lega del Chianti creating an area that would become the spiritual and historical "heart" of the Chianti region and today is located within the Chianti Classico Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita (DOCG). As the wines of Chianti grew in popularity other villages in Tuscany wanted their lands to be called Chianti. The boundaries of the region have seen many expansions and sub-divisions over the centuries. The variable terroir of these different macroclimates contributed to diverging range of quality on the market and by the late 20th century consumer perception of Chianti was often associated with basic mass-market Chianti sold in a squat bottle enclosed in a straw basket, called fiasco.

Winemaking has a long tradition in Egypt dating back to the 3rd millennium BC. The modern wine industry is relatively small scale but there have been significant strides towards reviving the industry. In the late nineties the industry invited international expertise in a bid to improve the quality of Egyptian wine, which used to be known for its poor quality. In recent years Egyptian wines have received some recognition, having won several international awards. In 2013 Egypt produced 4,500 tonnes of wine, ranking 54th globally, ahead of Belgium and the United Kingdom.
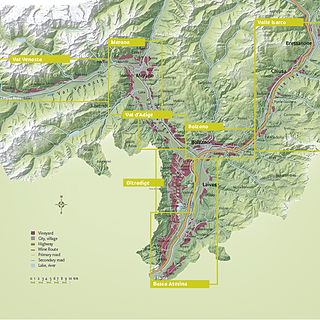
South Tyrol is an autonomous province located in north-east Italy producing wine. This Austro-Italian wine region is noted for the distinct Austrian influences on the wine industry due to the region's long history under the rule of Austria-Hungary and Holy Roman Empires.





















