Malbec is a purple grape variety used in making red wine. The grapes tend to have an inky dark color and robust tannins, and are known as one of the six grapes allowed in the blend of red Bordeaux wine. In France, plantations of Malbec are now found primarily in Cahors in South West France, though the grape is grown worldwide. It is also available as an Argentine varietal.

Mosel is one of 13 German wine regions (Weinbaugebiete) for quality wines , and takes its name from the Mosel River. Before 1 August 2007 the region was called Mosel-Saar-Ruwer, but changed to a name that was considered more consumer-friendly. The wine region is Germany's third largest in terms of production but some consider it the leading region in terms of international prestige.

Chenin blanc is a white wine grape variety from the Loire Valley of France. Its high acidity means it can be used to make varieties from sparkling wines to well-balanced dessert wines, although it can produce very bland, neutral wines if the vine's natural vigor is not controlled. Outside the Loire, it is found in most of the New World wine regions; it is the most widely planted variety in South Africa, where it was historically also known as Steen. The grape may have been one of the first to be grown in South Africa by Jan van Riebeeck in 1655, or it may have come to that country with Huguenots fleeing France after the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685. Chenin blanc was often misidentified in Australia, as well, so tracing its early history in the country is not easy. It may have been introduced in James Busby's collection of 1832, but C. Waterhouse was growing Steen at Highercombe in Houghton, South Australia, by 1862.

Burgundy wine is made in the Burgundy region of eastern France, in the valleys and slopes west of the Saône, a tributary of the Rhône. The most famous wines produced here, and those commonly referred to as "Burgundies", are dry red wines made from pinot noir grapes and white wines made from chardonnay grapes.

Blaufränkisch is a dark-skinned variety of grape used for red wine. Blaufränkisch, which is a late-ripening variety, produces red wines which are typically rich in tannin and may exhibit a pronounced spicy character.

German wine is primarily produced in the west of Germany, along the river Rhine and its tributaries, with the oldest plantations going back to the Roman era. Approximately 60 percent of German wine is produced in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, where 6 of the 13 regions (Anbaugebiete) for quality wine are situated. Germany has about 103,000 hectares of vineyard, which is around one tenth of the vineyard surface in Spain, France or Italy. The total wine production is usually around 10 million hectoliters annually, corresponding to 1.3 billion bottles, which places Germany as the eighth-largest wine-producing country in the world. White wine accounts for almost two thirds of the total production.

Alsace wine or Alsatian wine is produced in the Alsace region in France and is primarily white wine. Because of its Germanic influence, it is the only Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée region in France to produce mostly varietal wines, typically from similar grape varieties to those used in German wine. Along with Austria and Germany, it produces some of the most noted dry Rieslings in the world as well as highly aromatic Gewürztraminer wines. Wines are produced under three different AOCs: Alsace AOC for white, rosé and red wines, Alsace Grand Cru AOC for white wines from certain classified vineyards and Crémant d'Alsace AOC for sparkling wines. Both dry and sweet white wines are produced.

Müller-Thurgau is a white grape variety which was created by Hermann Müller from the Swiss Canton of Thurgau in 1882 at the Geisenheim Grape Breeding Institute in Germany. It is a crossing of Riesling with Madeleine Royale. It is used to make white wine in Germany, Austria, Northern Italy, Hungary, England, Australia, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, New Zealand, Canada, the United States, Belgium and Japan. There are around 22,201 hectares ) cultivated worldwide, which makes Müller-Thurgau the most widely planted of the so-called "new breeds" of grape varieties created since the late 19th century. Although plantings have decreased significantly since the 1980s, as of 2019 it was still Germany's second most planted variety at 11,400 hectares and 11.4% of the total vineyard surface. In 2007, the 125th anniversary was celebrated at the Geisenheim Grape Breeding Institute. Müller-Thurgau is also known as Rivaner, Riesling x Sylvaner, Riesling-Sylvaner, Rizvanec (Slovenia) and Rizlingszilváni (Hungary).

Moldova has a well-established wine industry. With a production of around 2 million hectolitres of wine, it is the 11th largest European wine-producing country. Moldova has a vineyard area of 148,500 hectares of which 107,800 hectares are used for commercial production. The remaining 40,700 hectares are vineyards planted in villages around the houses used to make home-made wine. Many families have their own recipes and strands of grapes that have been passed down through the generations. There are 3 historical wine regions: Valul lui Traian, Stefan Voda and Codru (center), destined for the production of wines with protected geographic indication.

French wine is produced all throughout France, in quantities between 50 and 60 million hectolitres per year, or 7–8 billion bottles. France is one of the largest wine producers in the world, along with Italian, Spanish, and American wine-producing regions. French wine traces its history to the 6th century BCE, with many of France's regions dating their wine-making history to Roman times. The wines produced range from expensive wines sold internationally to modest wines usually only seen within France such as the Margnat wines of the post-war period.

Corton-Charlemagne is an Appellation d'origine contrôlée (AOC) and Grand Cru vineyard for white wine in the Côte de Beaune subregion of Burgundy. It is located in the communes of Aloxe-Corton, Pernand-Vergelesses and Ladoix-Serrigny with Chardonnay, and Pinot Blanc being the only permitted grape varieties. Around 300,000 bottles of white wine are produced each year in the appellation.
South African wine has a history dating back to 1659 with the first bottle being produced in Cape Town by its founder and governor Jan van Riebeeck. Access to international markets led to new investment in the South African wine market. Production is concentrated around Cape Town and almost exclusively located within the Western Cape province, with major vineyard and production centres at Constantia, Paarl, Stellenbosch and Worcester.

Wine in the Czech Republic is produced mainly in southern Moravia, although a few vineyards are located in Bohemia. However, Moravia accounts for around 96% of the country's vineyards, which is why Czech wine is more often referred to as Moravian wine. Production centers on local grape varieties, but there has been an increase in the production of established international strains such as Cabernet Sauvignon.

Austrian wines are mostly dry white wines, though some sweeter white wines are also produced. About 30% of the wines are red, made from Blaufränkisch, Pinot noir and locally bred varieties such as Zweigelt. Four thousand years of winemaking history counted for little after the "antifreeze scandal" of 1985, when it was revealed that some wine brokers had been adulterating their wines with diethylene glycol. The scandal destroyed the market for Austrian wine and compelled Austria to tackle low standards of bulk wine production, and reposition itself as a producer of quality wines. The country is also home to Riedel, makers of some of the most expensive wine glasses in the world. Some of the best producers of Austria include Weingut Bründlmayer, Weingut F.X. Pichler and Weingut Franz Hirtzberger, Weingut Hutter, Weingut Eigl and Wellanschitz.

Ontario wine is Canadian wine produced in the province of Ontario. The province has three official wine-growing regions, the Niagara Peninsula, the north shore of Lake Erie, and Prince Edward County, although wineries also exist in other regions in Ontario. Approximately two-thirds of Canada's vineyard acreage is situated in Ontario, with over 150 vineyards spread across 6,900 hectares. As a result, the province is the country's largest producer of wine, accounting for 62 per cent of Canadian wine production, and 68 per cent of all Canadian wine exports.

Palatinate is a German wine-growing region (Weinbaugebiet) in the area of Bad Dürkheim, Neustadt an der Weinstraße, and Landau in Rhineland-Palatinate. Before 1993, it was known as Rhine Palatinate (Rheinpfalz). With 23,698 hectares under cultivation in 2022, the region is the second largest wine region in Germany after Rheinhessen. There are about 6,800 vintners producing around 2.3 million hectolitres of wine annually.
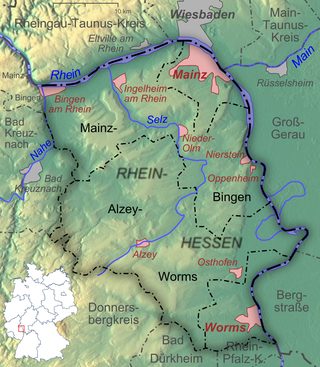
Rheinhessen is the largest of 13 German wine regions (Weinanbaugebiete) for quality wines with 26,758 hectares under cultivation in 2018. Named for the traditional region of Rhenish Hesse, it lies on the left bank of the Rhine between Worms and Bingen in the federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate. Despite its historic name it is currently no longer part of the federal-state of Hesse, this being the case since the end of World War II. There have been several unsuccessful attempts to legally reunite the former wine growing districts of Mainz on the Hessian side during the post-war area. Rheinhessen produces mostly white wine from a variety of grapes, particularly Riesling, Müller-Thurgau and Silvaner, and is best known as the home of Liebfraumilch, although some previously underrated Rieslings are also made, increasingly in a powerful dry style.

Nahe is a region (Anbaugebiet) for quality wine in Germany, along the River Nahe in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate. On the region's 4,155 hectares of vineyards in 2008, white wine grapes dominate with 75% and Riesling is the most common variety with 27.2%. A characteristic of the Nahe region is that the soils are very varied owing to the region's volcanic origins.

Belgian wine is produced in several parts of Belgium and production, although still modest at 1,400 hectoliters in 2004, has expanded in recent decades.

Wachau is one of Austria's most established and notable wine regions, specializing in dry wines made from Riesling and Grüner Veltliner. Located in Lower Austria along the Danube, west of Vienna and Krems an der Donau, it is one of the westernmost wine producing regions in Austria with only a few scattered plantings in Tyrol being further west. While most of Austria follows a wine classification systems based on ripeness and harvest must weight that parallels the German wine classification system, Wachau wines have a unique classification system. The three classification levels for Wachau wine include Steinfeder for wines up to 11.5% alcohol level, Federspiel for wines between 11.5–12.5% and Smaragd that must have a minimum of 12.5% alcohol level. Despite its renown, the Wachau is a small wine region that usually accounts for only around 3% of Austria's wine production.