This article was imported from the CIA World Factbook . |
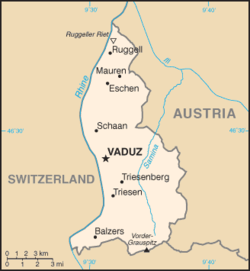


The principality of Liechtenstein encompasses most of the eastern half of the Rhine Valley, wedged between Austria and Switzerland. The majority of the country's population is found in the western half along the Rhine River. [1] Along with Uzbekistan, Liechtenstein is one of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world.