
Sumbawa is an Indonesian island, located in the middle of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain, with Lombok to the west, Flores to the east, and Sumba further to the southeast. Along with Lombok, it forms the province of West Nusa Tenggara, but there have been plans by the Indonesian government to split the island off into a separate province. Traditionally, the island is known as the source of sappanwood, as well as honey and sandalwood. Its savanna-like climate and vast grasslands are used to breed horses and cattle, as well as to hunt deer.

Alor is the largest island in the Alor Archipelago and is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indonesia. It is located at the eastern end of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain that runs through southeastern Indonesia, which from the west include such islands as Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Komodo, and Flores.

West Nusa Tenggara is a province of Indonesia. It comprises the western portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, with the exception of Bali which is its own province. The area of this province is 19,675.89 km2 (7,596.90 sq mi) which consists of two main islands, namely Lombok Island and Sumbawa Island as well as several other small islands. The two largest islands in this province are the smaller but much more populated Lombok in the west and the much larger in area but much less densely populated Sumbawa island in the east. Mataram, on Lombok, is the capital and largest city of the province. It shares maritime borders with Bali to the west and East Nusa Tenggara to the east.

Adonara is an island in the Lesser Sunda Islands of Indonesia, located east of the larger island of Flores in the Solor Archipelago. To the east lies Lembata, formerly known as Lomblen. Adonara is the highest of the islands of the archipelago, reaching an altitude of 1,659 metres, and it has an area of 529.75 km2. It is situated administratively in the East Flores Regency of East Nusa Tenggara province.

Sangeang Api is an active complex volcano on the island of Sangeang in Indonesia. It consists of two volcanic cones, 1,949 metres (6,394 ft) Doro Api and 1,795 m (5,889 ft) Doro Mantoi. Sangeang Api is one of the most active volcanoes in the Lesser Sunda Islands. Administratively the island forms one village (desa) within Wera District (kecamatan) of Bima Regency; it covers a land area of 165.76 km2 and had a population of 4,739 in mid 2023.
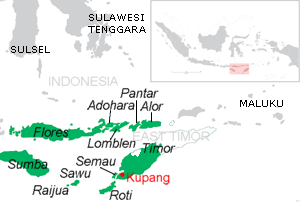
Pantar is the second largest island in the Indonesian Alor Archipelago, after Alor. To the east is the island of Alor and other small islands in the archipelago; to the west is the Alor Strait, which separates it from the Solor Archipelago. To the south is the Ombai Strait, and 72 kilometres (45 mi) away, the island of Timor. To the north is the Banda Sea. Pantar is about 50 kilometres (31 mi) north-to-south, and varies from 11 to 29 kilometres in east–west width. It has an area of 776.12 square kilometres (299.66 sq mi). The main towns on the island are Baranusa and Kabir. Administratively, the island is part of the Alor Regency.

Waingapu is the largest town in the eastern half of Sumba island, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It is the capital town of the East Sumba Regency.
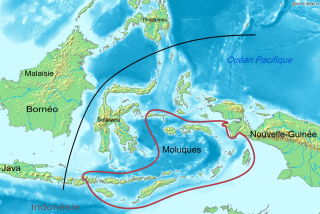
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages (CMP) are a proposed branch in the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor, but with the Bima language extending to the eastern half of Sumbawa Island in the province of West Nusa Tenggara and the Sula languages of the Sula archipelago in the southwest corner of the province of North Maluku. The principal islands in this region are Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor, Buru, and Seram. The numerically most important languages are Bima, Manggarai of western Flores, Uab Meto of West Timor, and Tetum, the national language of East Timor.

Klungkung Regency is the smallest regency (kabupaten) in the island province of Bali, Indonesia. It has an area of 315 km2 and had a population at the 2010 Census of 170,543 which increased to 206,925 at the Census of 2020; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 214,012. The administrative centre for the regency is in the town of Semarapura.

Bima city is a coastal city on the east of the island of Sumbawa in Indonesia's province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is the largest city on the island of Sumbawa, with a population of 142,443 at the 2010 census and 155,140 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid-2023 was 161,362. It is separate from the adjoining Bima Regency which had a population of 535,530 according to the mid-2023 official estimates.

Bima Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Sumbawa and the capital is Woha. The Regency covers an area of 4,389.40 km2, and had a population of 438,522 at the 2010 Census and 514,105 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 535,530. It administratively excludes but geographically completely surrounds Bima City on the landward side.

Dompu Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Sumbawa and the capital is Dompu. It is bordered to the north and to the east by two non-contiguous parts of Bima Regency, and to the west by Sumbawa Regency, as well as on its coasts by Saleh Bay, Sanggar Bay, and Cempi Bay. It covers an area of 2,324.55 km2, and the population at the 2010 Census was 218,984 and at the 2020 Census was 236,665; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 247,188.

Sumbawa Regency is a Regency (Kabupaten) of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Sumbawa and covers an area of 6,643.99 km2, following the separation on 18 December 2003 of what were until then its westernmost five districts to form the newly created West Sumbawa Regency. It includes the substantial island of Moyo, lying off the north coast of Sumbawa. The population of the Regency at the 2010 Census was 415,789, which rose at the 2020 Census to 509,753; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 529,487. The capital is the town of Sumbawa Besar on the north coast of Sumbawa Island.

West Sumbawa Regency is a Regency (Kabupaten) of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Sumbawa and has an area of 1,743.58 km2. The regency was created on 18 December 2003 from what were at that time the westernmost five districts (kecamatan) of Sumbawa Regency. The population at the 2010 Census was 114,754, and at the 2020 Census was 145,798; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 152,950 comprising 77,030 males and 75,920 females. The capital is the town of Taliwang.

Raba is a town in the Bima Regency, on the eastern part of the island of Sumbawa, in central Indonesia's province West Nusa Tenggara. Though not the capital, it is the largest city on the island of Sumbawa, with a population of approximately 440,000 in 2010. It is connected by provincial road to Bima and Sape.

Dompu is a town and the administrative centre of the Dompu Regency, located in the eastern part of the island of Sumbawa, in central Indonesia's province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is the third largest town on the island of Sumbawa, with a district population of 49,854 at the 2010 Census, which by the 2020 Census had grown to 54,987; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 57,680. It is connected by provincial road to Bima and Sape.
Bima Bay is a major waterway on the north side of the island of Sumbawa, and is adjacent to Bima City and Bima Regency. It contains the island Kambing Island (Bima), as well as the Bima harbor.
The Bima language, or Bimanese, is an Austronesian language spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of the Sumbawa language. Bima territory includes the Sanggar Peninsula, where the extinct Papuan language Tambora was once spoken. Bima is an exonym; the autochthonous name for the territory is Mbojo and the language is referred to as Nggahi Mbojo. There are over half a million Bima speakers. Neither the Bima nor the Sumbawa people have alphabets of their own for they use the alphabets of the Bugis and the Malay language indifferently.

Sumbawa or Sumbawarese is a Malayo-Polynesian language of the western half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of Bima. It is closely related to the languages of adjacent Lombok and Bali; indeed, it is the easternmost Austronesian language in the south of Indonesia that is not part of the Central Malayo-Polynesian Sprachbund. The Sumbawa write their language with their own native script commonly known in their homeland as Satera Jontal and they also use the Latin script.

The Sultanate of Bima, officially known as The Settlements and Lands of Mbojo, alternatively the Kingdom of Bima was a Muslim state in the eastern part of Sumbawa in Indonesia, at the site of the present-day regency of Bima. It was a regionally important polity which formed the eastern limit of Islam in this part of Indonesia and developed an elite culture inspired by Makassarese and Malay models. Bima was subjected to indirect colonial rule from 1908 to 1949 and ceased to be a sultanate in 1958.

















