
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family, including the carps, the true minnows, and their relatives the barbs and barbels, among others. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family, and the largest vertebrate animal family overall, with about 3,000 species; only 1,270 of these remain extant, divided into about 200 valid genera. Cyprinids range from about 12 mm (0.5 in) in size to the 3 m (9.8 ft) giant barb. By genus and species count, the family makes up more than two-thirds of the ostariophysian order Cypriniformes. The family name is derived from the Greek word kyprînos.

Trout is a generic common name for numerous species of carnivorous freshwater ray-finned fishes belonging to the genera Oncorhynchus, Salmo and Salvelinus, all of which are members of the subfamily Salmoninae in the family Salmonidae. The word trout is also used for some similar-shaped but non-salmonid fish, such as the spotted seatrout/speckled trout.

Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.

Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

Herring are various species of forage fish, belonging to the order Clupeiformes.

The term carp is a generic common name for numerous species of freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large clade of ray-finned fish mostly native to Eurasia. While carp are prized quarries and are valued as both food and ornamental fish in many parts of the Old World, they are considered trash fish and invasive pests in many parts of Africa, Australia and most of the United States.

Tilapia is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the coelotilapine, coptodonine, heterotilapine, oreochromine, pelmatolapiine, and tilapiine tribes, with the economically most important species placed in the Coptodonini and Oreochromini. Tilapia are mainly freshwater fish inhabiting shallow streams, ponds, rivers, and lakes, and less commonly found living in brackish water. Historically, they have been of major importance in artisanal fishing in Africa, and they are of increasing importance in aquaculture and aquaponics. Tilapia can become a problematic invasive species in new warm-water habitats such as Australia, whether deliberately or accidentally introduced, but generally not in temperate climates due to their inability to survive in cold water.

Teleostei, members of which are known as teleosts, is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes, with 96% of all extant species of fish. The Teleostei, which is variously considered a division or an infraclass in different taxonomic systems, include over 26,000 species that are arranged in about 40 orders and 448 families. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring 7.6 m (25 ft) or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over 2 t, to the minute male anglerfish Photocorynus spiniceps, just 6.2 mm (0.24 in) long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses.
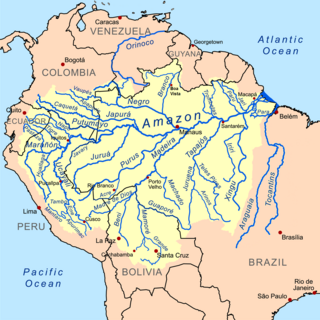
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana.

A fish is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), contemporary phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group.

The Zhelin Reservoir, also named Mount Lu West Sea, is a reservoir located in the counties of Yongxiu, Wuning, and Xiushui in Jiujiang, China. It is 90 kilometers to the south of Mount Lu, with a total area of 308 square kilometers. The reservoir is the largest in Jiangxi province, with a storage capacity of 7,920,000,000 cubic metres.
Xenocypris is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. In addition to the extant species, X. yushensis, being known only from fossils, and one, X. yunnanensis, which is critically endangered or recently extinct.
Xenocypris yunnanensis, the Kunming nase, is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Xenocypris. It is endemic to Lake Dianchi in Yunnan Province, China. The species started to decline in the 1970s and has not been caught in the lake after two specimens were collected in 1985; it may be extinct. Its demise is likely due to introduced fish species, grass carp. It was also impacted by over-fishing and pollution. They grow to a maximum length of 23 cm (9.1 in). They are dark grayish with a silvery white belly, gray dorsal fin, reddish anal fin and orange red caudal fin. They have a rounded belly, blunt snout, eyes on the lateral part of their heads, and a small transverse mouth.
Canna Maria Louise Popta was a Dutch biologist.

Xenocyprididae, is a family of freshwater ray-finned fishes with a natural distribution in Asia. This taxon, sometimes spelt Xenocypridae, was previoulsy regarded to be a subfamily, Xenocyprinae, of the family Cyprinidae. Cyprinidae sensu lato is now divided into a number of smaller families within the suborder Cyprinoidei, in the order Cypriniformes.
Xenocypris davidi is a freshwater fish native to the Pearl River, Hainan Island, the Yangtze River, the Yellow River and the southeast coast of China. It is the subject of artisanal fishing, sport fishing, and a nascent aquaculture attempt.
Xenocypris fangi is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. It has a maximum total length of 20.0 centimetres (7.9 in) and a common standard length of 17.0 centimetres (6.7 in). It inhabits the upper Yangtze and is considered harmless to humans.
Xenocypris hupeinensis is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. It inhabits the upper and middle Changjiang River of China and has a maximum length among unsexed males of 25.6 centimetres (10.1 in). It is classified as "data deficient" by the IUCN.
Xenocypris macrolepis, also known as the yellowfin, is a species of is a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. The fish is found in the Amur River and Vietnam. The fish is usually 10 cm (3.9 in) long (SL), the largest specimen of the fish ever recorded was 34.6 cm (13.6 in) long (SL).











