
Xenomystax is a genus of eels in the family Congridae. It currently contains the following species:
Chlopsis bidentatus is an eel in the family Chlopsidae. It was described by Kenneth A. Tighe and John E. McCosker in 2003. It is a deep-water, marine eel which is known from New Caledonia and Fiji, in the western central Pacific Ocean. It typically dwells at a depth range of 300–503 m. Males can reach a maximum total length of 16.7 cm.

Moringua edwardsi, the common spaghetti eel, is an eel in the family Moringuidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Harvey Bollman in 1889, originally under the genus Stilbiscus. It is a subtropical, marine eel known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including Antigua and Barbuda, Aruba, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, Cuba, Dominica, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Honduras, Jamaica, Martinique, Mexico, Montserrat, Nicaragua, Puerto Rico, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, Florida, Venezuela, the Virgin Islands, British, and the Virgin Islands of the United States. Males can reach a maximum total length of 15 cm, while females can reach a maximum of 50 cm. The eels feed primarily off of burrowing invertebrates.

Ariosoma selenops is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Earl Desmond Reid in 1934. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the northwestern, southwestern, and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Antigua and Barbuda, the Bahamas, Brazil, Dominica, the Dominican Republic, Canada, Haiti, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Saint Lucia, the United States, and Venezuela. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 348–549 metres.
The dubious conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Charles Marcus Breder Jr. in 1927, originally under the genus Pseudoxenomystax. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, the Gulf of Mexico, Caribbean Sea, and the Guianas. It dwells at a depth range of 128–886 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 44.3 centimetres (1.45 ft) centimeters.
The Conger eel is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Earl Desmond Reid in 1934, originally under the genus Congrina. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from Cuba and Venezuela, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 476–659 metres.

The yellow conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean in 1896. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Gulf of Mexico and the mouth of the Amazon River, in the western Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 26 to 183 meters, and inhabits soft sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 150 centimeters (59 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 30 centimeters (12 in).
Xenomystax austrinus is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David G. Smith and Robert H. Kanazawa in 1989. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 458 to 732 meters.
Xenomystax trucidans is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Alfred William Alcock in 1894. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from Maldives and Laccadives, in the western Indian Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 1,316 metres (4,318 ft), but is more commonly found at a depth range of 400 to 800 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 64.5 centimetres (25.4 in).
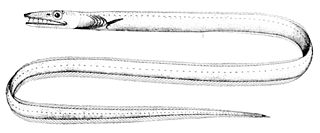
The blacktail pike-conger is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by George Brown Goode and Tarleton Hoffman Bean in 1896. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 203 meters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 36.6 centimeters.
The slender duckbill eel is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Charles Tate Regan in 1915. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Gulf of Guinea, in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It inhabits the continental shelf and slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 55.5 centimetres (21.9 in).

Aplatophis chauliodus, the fangtooth snake-eel, also known as the tusky eel in Cuba and the United States, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by James Erwin Böhlke in 1956. It is a marine, tropical eel known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the Gulf of Mexico and French Guiana. It is also known to occur on the northeastern coast of Brasil. It dwells at a depth range of 33–91 m (100–300 ft), and dwells in both marine waters and brackish estuaries. It inhabits burrows on a permanent or semipermanent basis, and leaves its eyes and snout exposed. Males can reach a maximum total length of 84 cm (33 in). The fangtooth snake-eel's diet consists of bony fish and crustaceans.

The goldspotted eel, also known as the goldspotted snake eel or the dark-spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1825, originally under the genus Muraenophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, southern Florida, USA; the Bahamas, Santa Catarina, and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 15 metres (49 ft), and inhabits rocky and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 110 centimetres (3.6 ft).

The dark-shouldered snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Pieter Bleeker in 1864. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Pacific Ocean, including the East Indies, the Society Islands, the Mariana Islands, Queensland, the Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Japan, and India. It dwells at a depth range of 2–15 metres, and inhabits reefs. It forms burrows in mud and sand, and forages during the night. Males can reach a maximum total length of 115 centimetres.
The Antillian snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John Roxborough Norman in 1922. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the western central Atlantic Ocean, including Cuba, Puerto Rico, Trinidad-Tobago, and Venezuela. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 300 meters, and inhabits coastal waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 107 centimeters, but more commonly reach a TL of 70 cm.

The manetail snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Coenraad Jacob Temminck and Hermann Schlegel in 1846, originally under the genus Conger. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. It inhabits deep waters, but is found in muddy sediments in shallow waters on rare occasions. Males can reach a maximum total length of 61.5 centimetres (24.2 in).

The Bean's sawtooth eel is an eel in the family Serrivomeridae. It was described by Theodore Gill and John Adam Ryder in 1883. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from throughout the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and the Western Pacific Ocean, including Iceland, South Africa, Réunion, and Australia. It dwells at a depth range of 0–5,998 metres (0–19,680 ft), and leads a solitary lifestyle. It migrates vertically at night. Males can reach a maximum total length of 78-80 centimetres, making it the largest sawtooth eel.
Dysomma brevirostre, the pignosed arrowtooth eel or batnose eel, is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Luigi Facciolà in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including Madeira Island, the Gulf of Guinea, the Ligurian Sea, Italy, and Florida and Hawaii, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 200 to 1,000 metres, and inhabits soft sediments on the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30 centimetres (12 in).
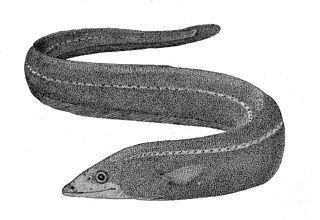
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).

The Kaup's arrowtooth eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by James Yate Johnson in 1862. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Cape Verde, the Western Sahara, Nigeria, Namibia, South Africa, Greenland, France, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Philippines, Portugal, Spain, the Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Cuba, Japan, Australia, Mauritania, Morocco, and Hawaii. It dwells at a depth range of 120 to 4,800 metres, most often between 400 and 2,200 metres, and inhabits the upper abyssal zone on the continental slope. It is intolerant of the temperatures of higher waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).











