Aphantophryne minuta is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and is known from its type locality near Myola Guest House in the Owen Stanley Range, Northern Province, from another locality in the same province, Mount Tafa; only a single specimen is known from each locality. The specific name minuta refers to the very small size of this species. Common name Myola Guinea frog has been coined for it.
Aphantophryne sabini is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and is only known from the region of its type locality, Myola Guest House in the Owen Stanley Range, Northern Province. The specific name sabini honors Andrew E. Sabin, an American businessman, philanthropist, and environmentalist who joined the expedition during which the holotype of this species was collected. However, its vernacular name Guest House Guinea frog refers to the type locality instead.
Austrochaperina blumi is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and known from the northern slopes of the New Guinean Central Range in Western New Guinea (Indonesia), and from the Bewani, Torricelli, and Hunstein Mountains in Papua New Guinea. The specific name blumi honors J. Paul Blum, the herpetologist who collected the type series. Common name Kosarek land frog has been proposed for it.

Copiula guttata is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and known from around the head of the Gulf of Papua in the Gulf and Chimbu Provinces. The specific name is the Latin adjective guttata that means "spotted" and refers to the dorsal colour pattern of this species. Based on molecular evidence, it was transferred from Austrochaperina to Copiula in 2016.
Austrochaperina kosarek is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and only known from its type locality, Kosarek, in West Papua (Indonesia). It is only known from one specimen collected in 1979. It has not been well-studied but it might be widespread in suitable habitat.

Barygenys atra is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to eastern New Guinea and is known from the Morobe and Northern Provinces, Papua New Guinea. Common name Gunther's Papua frog has been proposed for it.
Barygenys cheesmanae is a species of frogs in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to eastern New Guinea and is only known from Mount Tafa in Central Province, Papua New Guinea. The specific name cheesmanae honors Lucy Evelyn Cheesman, an English entomologist, explorer, curator at London Zoo, and collector of the holotype. Common name Cheesman's Papua frog has been coined for this species.
Barygenys nana is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and is known from the mountains of Eastern Highlands and Western Highlands Provinces, Papua New Guinea. The specific name nana refers to the small size of this species. Common name highland Papua frog has been proposed for it.
Callulops boettgeri, also known as Boettger's Callulops frog, is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Halmahera in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. It is only known from the holotype collected from Galela in 1894. The genus-level placement of this little known frog has changed many times, and it is still unclear whether it should be placed in some other genus.

Callulops personatus is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to the northern lowlands of central New Guinea and occurs in both Western New Guinea (Indonesia) and Papua New Guinea. The specific name personatus is Latin adjective meaning "masked", in reference to the head coloration. Common name Maprik callulops frog has been proposed for it.

Callulops stictogaster is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and occurs in the central mountain ranges of Papua New Guinea in the Western Highlands, Eastern Highlands, Chimbu, and Morobe Provinces. The specific name stictogaster is derived from the Greek stictos (="spotted") and gaster (="belly"). Common name Irumbofoie callulops frog has been proposed for it.
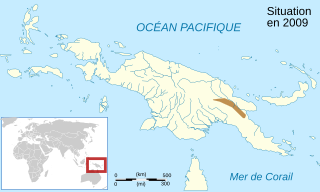
Cophixalus parkeri is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea where it occurs in the central mountainous region between Chimbu and Morobe Provinces. The specific name parkeri presumably honours Hampton Wildman Parker, an English zoologist and herpetologist to whose perusal Arthur Loveridge sent the holotype. Common name Papua rainforest frog has been coined for it.
Cophixalus riparius is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the New Guinea Highlands in Madang, Southern Highlands, and Western Highlands provinces southeastward to the Morobe Province. The specific name riparius refers to the creek-side habitat from which many specimens in the type series were collected. Common name Wilhelm rainforest frog has been coined for this species.
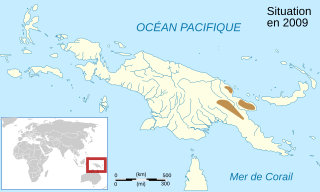
Cophixalus shellyi is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the New Guinea Highlands as well as in the Adelbert Range and on the Huon Peninsula. The specific name shellyi honors Father Otto Schellenberger ("Shelly"), an American missionary and former professor in mathematics who collected the type series.
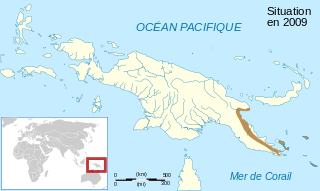
Sphenophryne thomsoni, sometimes known as Thomson's toothless frog, is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the southeastern peninsular New Guinea, Louisiade Archipelago, d'Entrecasteaux Islands, and Woodlark Island. It was formerly in its own monotypic genus Genyophryne. The specific name thomsoni honours Basil Thomson, a British intelligence officer, police officer, prison governor, colonial administrator, and writer.
Hylophorbus infulatus is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and known from its type locality, Arau in the Kratke Mountains, as well as from the Adelbert Range, both in Papua New Guinea. Common name Arau archipelago frog has been proposed for it.
Copiula alpestris is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and known from the Western Highlands, Chimbu, and Eastern Highlands Provinces at elevations of 1,800–2,800 m (5,900–9,200 ft) above sea level. The specific name is a Latin adjective meaning "living in high mountains", in reference to its relatively high-altitude habitats. Based on molecular evidence, the species was transferred from Oxydactyla to Copiula in 2016.

Xenorhina bidens is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and found between Lorentz River in the west and Fly River in the east, thus being present in both West Papua (Indonesia) and Papua New Guinea. Common name Digul River fanged frog has been coined for it, in reference to Digul River where the type series was collected in 1904 or 1905.
Xenorhina subcrocea is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and is known from the New Guinean north coast, including coastal ranges between Vanimo and Lae. Common name Lae fanged frog has been coined for it.
Xenorhina zweifeli is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and is only known from the Bewani and Hunstein Mountains in northern Papua New Guinea. The species is named for American herpetologist Richard G. Zweifel, a specialist in New Guinean herpetology and microhylid frogs; he is also said to share "characteristically terse vocalizations" with this frog.








