| Microhylidae | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Eastern narrowmouth toad ( Gastrophryne carolinensis ) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Clade: | Ranoidea |
| Family: | Microhylidae Günther, 1858 |
| Subfamilies | |
Adelastinae Contents | |
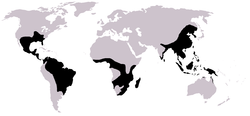 | |
| Distribution of Microhylidae (in black) | |
The Microhylidae, commonly known as narrow-mouthed frogs, are a geographically widespread family of frogs. The 683 species are in 57 genera and 11 subfamilies. [2]






