
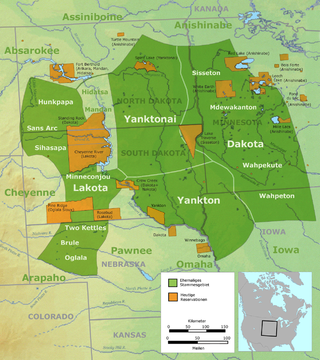
The Lakota are a Native American people. Also known as the Teton Sioux, they are one of the three prominent subcultures of the Sioux people, with the Eastern Dakota (Santee) and Western Dakota (Wičhíyena). Their current lands are in North and South Dakota. They speak Lakȟótiyapi—the Lakota language, the westernmost of three closely related languages that belong to the Siouan language family.

The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin are groups of Native American tribes and First Nations people from the Great Plains of North America. The Sioux have two major linguistic divisions: the Dakota and Lakota peoples. Collectively, they are the Očhéthi Šakówiŋ, or "Seven Council Fires". The term "Sioux", an exonym from a French transcription of the Ojibwe term Nadowessi, can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or to any of the nation's many language dialects.

Marty is a census-designated place (CDP) in southern Charles Mix County, South Dakota, United States. The population was 677 at the 2020 census.

The Treaty of Fort Laramie is an agreement between the United States and the Oglala, Miniconjou, and Brulé bands of Lakota people, Yanktonai Dakota, and Arapaho Nation, following the failure of the first Fort Laramie treaty, signed in 1851.

The Fort Laramie Treaty of 1851 was signed on September 17, 1851 between United States treaty commissioners and representatives of the Cheyenne, Sioux, Arapaho, Crow, Assiniboine, Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nations. Also known as Horse Creek Treaty, the treaty set forth traditional territorial claims of the tribes.
The Mdewakanton or Mdewakantonwan are one of the sub-tribes of the Isanti (Santee) Dakota (Sioux). Their historic home is Mille Lacs Lake in central Minnesota. Together with the Wahpekute, they form the so-called Upper Council of the Dakota or Santee Sioux. Today their descendants are members of federally recognized tribes in Minnesota, South Dakota and Nebraska of the United States, and First Nations in Manitoba, Canada.

The Great Sioux Reservation is an Indian reservation created by the United States through treaty with the Sioux, principally the Lakota, who dominated the territory before its establishment. In the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868, the reservation included lands west of the Missouri River in South Dakota and Nebraska, including all of present-day western South Dakota. The treaty also provided rights to roam and hunt in contiguous areas of North Dakota, Montana Wyoming, and northwest Colorado.

The Crow Creek Indian Reservation, home to Crow Creek Sioux Tribe is located in parts of Buffalo, Hughes, and Hyde counties on the east bank of the Missouri River in central South Dakota in the United States. It has a land area of 421.658 square miles (1,092.09 km2) and a 2000 census population of 2,225 persons. The major town and capital of the federally recognized Crow Creek Sioux Tribe is Fort Thompson.

Struck by the Ree, also known as Strikes the Ree and alternatively Palaneapape, Padani Apapi and Pa-Da-Ni-A-Ha-Hi in Sioux language was a chief of the Native American Yankton Sioux tribe.

The Spirit Lake Tribe is a federally recognized tribe based on the Spirit Lake Dakota Reservation located in east-central North Dakota on the southern shores of Devils Lake. It is made up of people of the Pabaksa (Iháŋkthuŋwaŋna), Sisseton (Sisíthuŋwaŋ) and Wahpeton (Waȟpéthuŋwaŋ) bands of the Dakota tribe. Established in 1867 in a treaty between Sisseton-Wahpeton Bands and the United States government, the reservation, at 47°54′38″N98°53′01″W, consists of 1,283.777 square kilometres (495.669 sq mi) of land area, primarily in Benson and Eddy counties. Smaller areas extend into Ramsey, Wells and Nelson counties.

The Dakota are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided into the Eastern Dakota and the Western Dakota.

The Sisseton Wahpeton Oyate of the Lake Traverse Reservation, formerly Sisseton-Wahpeton Sioux Tribe/Dakota Nation, is a federally recognized tribe comprising two bands and two subdivisions of the Isanti or Santee Dakota people. They are on the Lake Traverse Reservation in northeast South Dakota.

The Yankton Sioux Tribe of South Dakota is a federally recognized tribe of Yankton Western Dakota people, located in South Dakota. Their Dakota name is Ihaƞktoƞwaƞ Dakota Oyate, meaning "People of the End Village" which comes from the period when the tribe lived at the end of Spirit Lake just north of Mille Lacs Lake.
The Yankton Treaty was a treaty signed in 1858 between the United States Government and the Yankton Sioux Tribe, that ceded most of eastern South Dakota to the U.S. Government. The treaty was signed in April 1858, and ratified by the United States Congress on February 16, 1859.

The United States government illegally seized the Black Hills – a mountain range in the US states of South Dakota and Wyoming – from the Sioux Nation in 1876. The land was pledged to the Sioux Nation in the Treaty of Fort Laramie, but a few years later the United States illegally seized the land and nullified the treaty with the Indian Appropriations Bill of 1876, without the tribe's consent. That bill "denied the Sioux all further appropriation and treaty-guaranteed annuities" until they gave up the Black Hills. A Supreme Court case was ruled in favor of the Sioux in 1980. As of 2011, the court's award was worth over $1 billion, but the Sioux have outstanding issues with the ruling and have not collected the funds.

Solomon Iron Nation, often just referred to as Iron Nation, was a principal chief—and the last Head Chief—of the Lower Brule Lakota. He signed multiple treaties with the United States government, including the Fort Laramie Treaties of 1851 and 1868. His leadership oversaw the creation of the Lower Brule Indian Reservation.
This timeline of South Dakota is a list of events in the history of South Dakota by year.

Native Americans from various tribes lived in North Dakota before the arrival of settlers. With time, a number of treaties and agreements were signed between the Indians and the newcomers. Many of the treaties defined the domain of a specific group of Indians. The three maps below show the treaty territories of different Indians living in North Dakota and how the territories changed and diminished over time in the 19th century.
Marty Indian School is a K-12 tribal boarding school in Marty, South Dakota. It is affiliated with the Bureau of Indian Education (BIE). It is on the Yankton Indian Reservation. The Yankton Sioux Tribe owns the facilities and directly manages the school.
The Treaty with the Sioux, 1858 was signed on June 19, 1858, between the United States government and representatives of the Sisseton and Wahpeton bands of Dakota. This treaty defined the boundaries of the Lower Sioux reservation as that portion of the strip defined in the Treaty of Traverse des Sioux lying south of the Minnesota River. Notably, this excluded the northern half of the land previously allotted to the Indians. Additional provisions for surveying the land, allotting land to individual families, law enforcement, compensation payments, and economic development were also included.


















