Lake Traverse Indian Reservation | |
|---|---|
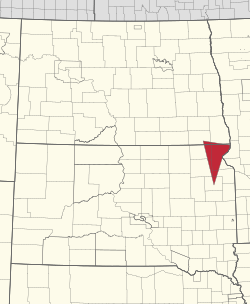 Location in North Dakota and South Dakota | |
| Tribe | Sisseton Wahpeton Oyate |
| Country | United States |
| States | North Dakota South Dakota |
| Counties | Richland Sargent Codington Day Grant Marshall Roberts |
| Headquarters | Agency Village |
| Government | |
| • Body | Tribal Council |
| • Chairman | J. Garret Renville |
| • Vice-Chairman | Lexie Fancher-Lincoln |
| • Secretary | Curtis Bissonette |
| Population (2024) [1] | |
• Total | 14,800 |
| Website | swo-nsn.gov |
The Lake Traverse Indian Reservation is the homeland of the federally recognized Sisseton Wahpeton Oyate, a branch of the Santee Dakota group of Native Americans. [2] Most of the reservation covers parts of five counties in northeastern South Dakota, while smaller parts are in two counties in southeastern North Dakota, United States. [3] [4] Its largest community is the city of Sisseton, South Dakota.
Contents
As of 2019, the reservation had an estimated population of 11,095. [5]