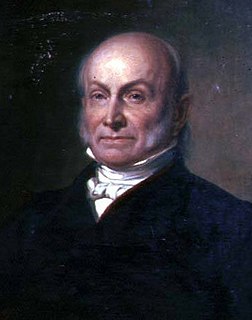The 1824 United States presidential election was the tenth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Tuesday, October 26 to Wednesday, December 1, 1824. Andrew Jackson, John Quincy Adams, Henry Clay and William Crawford were the primary contenders for the presidency. The result of the election was inconclusive, as no candidate won a majority of the electoral vote. In the election for vice president, John C. Calhoun was elected with a comfortable majority of the vote. Because none of the candidates for president garnered an electoral vote majority, the U.S. House of Representatives, under the provisions of the Twelfth Amendment, held a contingent election. On February 9, 1825, John Quincy Adams was elected as president without getting the majority of the electoral vote or the popular vote, being the only president to do so.

The 1828 United States presidential election was the 11th quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, October 31 to Tuesday, December 2, 1828. It featured a rematch of the 1824 election, as President John Quincy Adams of the National Republican Party faced Andrew Jackson of the Democratic-Republican Party. Both parties were new organizations, and this was the first presidential election their nominees contested. Jackson's victory over Adams marked the start of Democratic dominance in federal politics.

The 18th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, consisting of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from March 4, 1823, to March 4, 1825, during the seventh and eighth years of James Monroe's presidency. The apportionment of seats in the House of Representatives was based on the Fourth Census of the United States in 1820. Both chambers had a Democratic-Republican majority.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 19th Congress were held at various dates in different states between July 1824 and August 1825, coinciding with the contentious 1824 Presidential election. After no Presidential candidate won an electoral majority, in February 1825 the House of the outgoing 18th Congress chose the President in a contingent election.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 18th Congress were held at various dates in different states between July 1822 and August 1823 during President James Monroe's second term.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 14th Congress were held at various dates in different states between April 1814 and August 1815 during President James Madison's second term.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 12th Congress were held at various dates in different states between April 1810 and August 1811 during President James Madison's first term.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 11th Congress were held at various dates in different states between April 1808 and May 1809 as James Madison was elected president.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 8th Congress were held at various dates in each state, from April 26, 1802 to December 14, 1803 during Thomas Jefferson's first term in office. It was common in the early years of the United Congress for some states to elect representatives to a Congress after it had already convened. In the case of the 8th Congress, the representatives from New Jersey were only elected after its first meeting on October 17, 1803.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 5th Congress took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. The first session was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 4th Congress were held on various dates in each state between August 25, 1794, and September 5, 1795 (Kentucky). The election was held during President George Washington's second term.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 3rd Congress were held in 1792 and 1793, coinciding with the re-election of George Washington as President. While Washington ran for president as an independent, his followers formed the nation's first organized political party, the Federalist Party, whose members and sympathizers are identified as pro-Administration on this page. In response, followers of Thomas Jefferson and James Madison created the opposition Democratic-Republican Party, who are identified as anti-Administration on this page. The Federalists promoted urbanization, industrialization, mercantilism, centralized government, and a broad interpretation of the United States Constitution. In contrast, Democratic-Republicans supported the ideal of an agrarian republic made up of self-sufficient farmers and small, localized governments with limited power.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives for the 1st Congress were held in 1788 and 1789, coinciding with the election of George Washington as first President of the United States. The dates and methods of election were set by the states. Actual political parties did not yet exist, but new members of Congress were informally categorized as either "pro-Administration" or "anti-Administration".
The United States Senate elections of 1814 and 1815 were elections that had the Democratic-Republican Party lose a seat but still retain an overwhelming majority in the United States Senate. Unlike in recent elections, the minority Federalists had gone into the elections with a chance of regaining their long-lost majority had they swept almost all the seats. However, only one seat switched parties. Two seats held by Democratic-Republicans were left unfilled until long after the next Congress began.

The 1824 United States House of Representatives elections in New York were held from November 1 to 3, 1824, to elect 34 U.S. Representatives to represent the State of New York in the United States House of Representatives of the 19th United States Congress.
The United States Senate elections of 1824 and 1825 were elections for the United States Senate that saw the Jacksonians gain a majority over the Anti-Jacksonian National Republican Party.
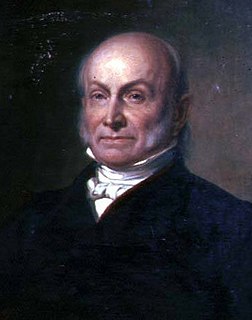
The 1824 United States presidential election in New Hampshire took place between October 26 and December 2, 1824, as part of the 1824 United States presidential election. Voters chose eight representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for President and Vice President.

The 1824 United States elections elected the members of the 19th United States Congress. It marked the end of the Era of Good Feelings and the First Party System. Members of the Democratic-Republican Party continued to maintain a dominant role in federal politics, but the party became factionalized between supporters of Andrew Jackson and supporters of John Quincy Adams. The Federalist Party ceased to function as a national party, having fallen into irrelevance following a relatively strong performance in 1812.

Following is a table of United States presidential elections in New Hampshire, ordered by year. Since its admission to statehood in 1788, New Hampshire has participated in every U.S. presidential election.

Rhode Island elected its members August 30, 1825 after the term began but before the new Congress convened. Rhode Island law required a candidate receive votes from a majority of voters for election, as only one candidate received a majority in this election, a second election was held for the remaining seat.