
The 2001 Nisqually earthquake occurred at on February 28, 2001, and lasted nearly a minute. The intraslab earthquake had a moment magnitude of 6.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The epicenter was in the southern Puget Sound, northeast of Olympia, but the shock was felt in Oregon, British Columbia, eastern Washington, and Idaho. This was the most recent of several large earthquakes that occurred in the Puget Sound region over a 52-year period and caused property damage valued at $1–4 billion. One person died of a heart attack and several hundred were injured.

The Seattle Fault is a zone of multiple shallow east–west thrust faults that cross the Puget Sound Lowland and through Seattle in the vicinity of Interstate Highway 90. The Seattle Fault was first recognized as a significant seismic hazard in 1992, when a set of reports showed that about 1,100 years ago it was the scene of a major earthquake of about magnitude 7 – an event that entered Native American oral traditions. Extensive research has since shown the Seattle Fault to be part of a regional system of faults.

The 1970 Ancash earthquake occurred on 31 May off the coast of Peru in the Pacific Ocean at . Combined with a resultant landslide, it is the most catastrophic natural disaster in the history of Peru. Due to the large amounts of snow and ice included in the landslide that caused an estimated 66,000-70,000 casualties, it is also considered to be the world's deadliest avalanche.
The 1918 San Fermín earthquake, also known as the Puerto Rico earthquake of 1918, struck the island of Puerto Rico at on October 11. The earthquake measured 7.1 on the moment magnitude scale and IX (Violent) on the Mercalli intensity scale. The mainshock epicenter occurred off the northwestern coast of the island, somewhere along the Puerto Rico Trench.
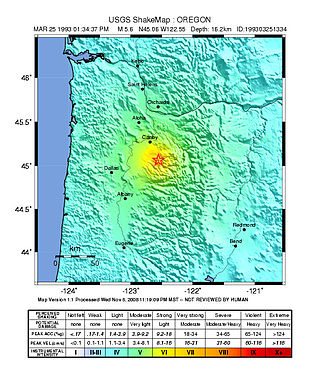
The 1993 Scotts Mills earthquake, also known as the "Spring break quake", occurred in the U.S. state of Oregon on March 25 at 5:34 AM Pacific Standard Time. With a moment magnitude of 5.6 and a maximum perceived intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale, it was the largest earthquake in the Pacific Northwest since the Elk Lake and Goat Rocks earthquakes of 1981. Ground motion was widely felt in Oregon's Willamette Valley, the Portland metropolitan area, and as far north as the Puget Sound area near Seattle, Washington.
The 1946 Vancouver Island earthquake struck Vancouver Island on the coast of British Columbia, Canada, on June 23 at 10:15 a.m. with a magnitude estimated at 7.0 and 7.5 . The main shock epicenter occurred in the Forbidden Plateau area northwest of Courtenay. While most of the large earthquakes in the Vancouver area occur at tectonic plate boundaries, the 1946 Vancouver Island earthquake was a crustal event. Shaking was felt from Portland, Oregon, to Prince Rupert, British Columbia. This is one of the most damaging earthquakes in the history of British Columbia, but damage was restricted because there were no heavily populated areas near the epicentre, where severe shaking occurred.
The 1970 Tonghai earthquake occurred at with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (Extreme). The strike-slip rupture originated on the Red River Fault, which had not experienced an earthquake above magnitude 7 since 1700, and affected Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China. At least 10,000 people were killed, making it one of the deadliest in its decade. The tremor caused between US$5 and $25 million in damage, felt over an area of 8,781 km2 (3,390 sq mi). In Hanoi, North Vietnam, almost 483 km (300 mi) from the epicenter, victims left their homes as the rupture rumbled through the city.
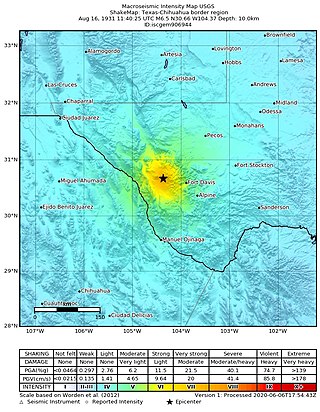
In the early morning hours of August 16, 1931, a powerful earthquake occurred in West Texas with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). Estimates of its magnitude range between 5.8–6.4 mb, making it the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Texas history. Its epicenter was near the town of Valentine, Texas; there, the earthquake caused damage to many homes and buildings. The earthquake may have been caused by movement along oblique-slip faulting in West Texas, the most seismically-active region in the state. Shaking from the earthquake was perceptible within a 400 mi (640 km) radius of the epicenter, affecting four U.S. states and northern Mexico. Several foreshocks and aftershocks accompanied the primary temblor, with the aftershocks continuing until at least November 3, 1931. The main earthquake caused no fatalities, though several people sustained minor injuries; the damage in Valentine amounted to $50,000–$75,000.
The 1965 Puget Sound earthquake occurred at 08:28 AM PDT on April 29 within the Puget Sound region of Washington state. It had a magnitude of 6.7 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It caused the deaths of seven people and about $12.5–28 million in damage. There were no recorded aftershocks.
The 1995 Neftegorsk earthquake occurred on 28 May at on northern Sakhalin Island in the Russian Far East. It was the most destructive earthquake known within the current territory of Russia, with a magnitude of 7.1 and maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent) that devastated the oil town of Neftegorsk, where 1,989 of its 3,977 citizens were killed, and another 750 injured.

The 1940 New Hampshire earthquakes struck on December 20 and again on December 24. Both shocks had an estimated magnitude of 5.6, and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. These doublet earthquakes were the largest to hit the state in several hundred years. Damage included minor fractures or knocked over chimneys in a zone extending through New Hampshire and four other states: Maine, New York, Vermont and Massachusetts.
The 1982 North Yemen earthquake hit near the city of Dhamar, North Yemen on December 13. Measuring 6.2 on the moment magnitude scale, with a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale, as many as 2,800 people were killed and another 1,500 injured. The shock occurred within several hundred kilometers of a plate boundary in a geologically complex region that includes active volcanoes and seafloor spreading ridges. Yemen has a history of destructive earthquakes, though this was the first instrumentally recorded event to be detected on global seismograph networks.
The 1986 Chalfant Valley earthquake struck southern Mono County near Bishop and Chalfant, California at Pacific Daylight Time on July 21. With a moment magnitude of 6.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong), the shock injured two people and caused property damage estimated at $2.7 million in the affected areas. There was a significant foreshock and aftershock sequence that included a few moderate events, and was the last in a series of three earthquakes that affected southern California and the northern Owens Valley in July 1986.

The Tacoma Fault, just north of the city of Tacoma, Washington, is an active east–west striking north dipping reverse fault with approximately 35 miles (56 km) of identified surface rupture. It is believed capable of generating earthquakes of at least magnitude Mw 7, and there is evidence of such a quake approximately 1,000 years ago, possibly the same earthquake documented on the Seattle Fault 24 miles (38 km) to the north.
The 1872 North Cascades earthquake occurred at in central Washington Territory. A maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe) was assessed for several locations, though less intense shaking was observed at many other locations in Washington, Oregon, and British Columbia. Some of these intermediate outlying areas reported V (Moderate) to VII shaking, but intensities as high as IV (Light) were reported as far distant as Idaho and Montana. Due to the remote location of the mainshock and a series of strong aftershocks, damage to structures was limited to a few cabins close to the areas of the highest intensity.

The 1918 San Jacinto earthquake occurred in extreme eastern San Diego County in Southern California on April 21 at . The shock had a moment magnitude of 6.7 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). Several injuries and one death occurred with total losses estimated to be $200,000.
The 1932 Eureka earthquake occurred on June 6 at along the northern coastal area of California in the United States. With a moment magnitude of 6.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), this earthquake left one person dead from a falling chimney and several injured. The shock was the largest in the area since 1923 and was felt in southern Oregon and northern California.
The 1912 Maymyo earthquake or Burma earthquake struck Burma on the morning of May 23, with an epicentre near Taunggyi and Pyin Oo Lwin in Shan State. The earthquake was initially calculated at 8.0 on the surface wave magnitude scale (Ms ) by Beno Gutenberg and Charles Francis Richter, and described by them as being one of the most remarkable seismic events in the early 1900s. Recent re-evaluation of the earthquake, however, have revised the magnitude to 7.6–7.9. It was preceded by two foreshocks on May 18 and 21 with respective intensities V and VII on the Rossi–Forel scale, while the mainshock was assigned IX. Shaking was felt throughout most of Burma, parts of Siam and Yunnan; an area covering approximately 375,000 square miles. It was one of the largest earthquakes in the country.
On January 30, 1973, at 15:01 (UTC–6), a magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck 35.3 km (21.9 mi) beneath the Sierra Madre del Sur range in the Mexican states of Colima, Jalisco and Michoacán. On the Mercalli intensity scale, the earthquake reached a maximum intensity of X (Extreme), causing serious damage in the region. At least 56 people were killed and about 390 were injured. The event is commonly referred to as the Colima earthquake.

The 1995 Kerinci earthquake struck near Sungai Penuh in Jambi Province on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia. It earthquake occurred at 01:18 WIB local time on October 7. The earthquake measured 6.7 on the moment magnitude scale, and 6.9–7.0 on the surface wave magnitude scale. Between 84 and possibly even 100 people were killed in the earthquake. An extimated 4,000 buildings collapsed or were seriously damaged while a further 5,000 suffered some damage.









