Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle, or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.

Choriocarcinoma is a malignant, trophoblastic cancer, usually of the placenta. It is characterized by early hematogenous spread to the lungs. It belongs to the malignant end of the spectrum in gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). It is also classified as a germ cell tumor and may arise in the testis or ovary.

Sertoli–Leydig cell tumour is a group of tumors composed of variable proportions of Sertoli cells, Leydig cells, and in the case of intermediate and poorly differentiated neoplasms, primitive gonadal stroma and sometimes heterologous elements.

A dysgerminoma is a type of germ cell tumor; it usually is malignant and usually occurs in the ovary.

A germ-cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ-cell tumors can be cancerous or benign. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads. GCTs that originate outside the gonads may be birth defects resulting from errors during development of the embryo.

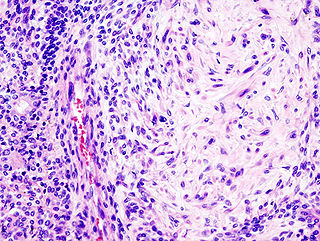
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP) is a rare tumor of the dermis layer of the skin, and is classified as a sarcoma. There is only about one case per million per year. DFSP is a fibrosarcoma, more precisely a cutaneous soft tissue sarcoma. In many respects, the disease behaves as a benign tumor, but in 2–5% of cases it can metastasize, so it should be considered to have malignant potential. It occurs most often in adults in their thirties; it has been described congenitally, in children, and the elderly. It accounts for approximately 2–6% of soft tissue sarcoma cancers.

A neoplasm is a type of abnormal and excessive growth, called neoplasia, of tissue. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and it persists growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass. When it forms a mass, it may be called a tumor.
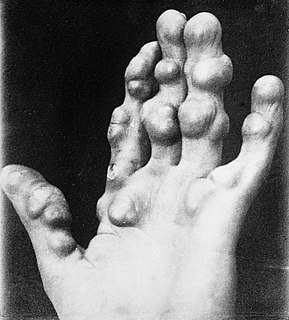
A chondroma is a benign cartilaginous tumor, which is encapsulated with a lobular growing pattern.

A papilloma is a benign epithelial tumor growing exophytically in nipple-like and often finger-like fronds. In this context, papilla refers to the projection created by the tumor, not a tumor on an already existing papilla.
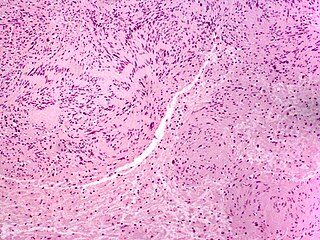
A neuroma is a growth or tumor of nerve tissue. Neuromas tend to be benign ; many nerve tumors, including those that are commonly malignant, are nowadays referred to by other terms.
Adenomyoma is a tumor (-oma) including components derived from glands (adeno-) and muscle (-my-). It is a type of complex and mixed tumor.
A monokine is a type of cytokine produced primarily by monocytes and macrophages.

An adrenocortical adenoma is a benign tumor of the adrenal cortex. It can present with Cushing's syndrome or primary aldosteronism. They may also secrete androgens, causing hyperandrogenism. Also, they are often diagnosed incidentally as incidentalomas.
Embryoma is a mass of rapidly growing cells believed to originate in embryonic (fetal) tissue. Embryonal tumors may be benign or malignant, and include neuroblastomas and Wilms tumors. Also called embryoma. Embryomas have been defined as: "Adult neoplasms expressing one or more embryo-exclusive genes."

Foster Kennedy syndrome is a constellation of findings associated with tumors of the frontal lobe.
A Mixed tumor is a tumor that derives from multiple tissue types.

Medulloepithelioma is a rare, primitive, fast-growing brain tumour thought to stem from cells of the embryonic medullary cavity. Tumours originating in the ciliary body of the eye are referred to as embryonal medulloepitheliomas, or diktyomas.
Emma Louise Call (1847–1937) was an American physician, and one of the first female physicians in the United States. Along with Sigmund Exner, she is one of the namesakes of Call-Exner bodies, a pathognomonic feature of granulosa cell tumors. These tumors are associated with ovarian cancers.
Vulvar tumors are those neoplasms of the vulva. Vulvar and vaginal neoplasms make up a small percentage (3%) of female genital cancers. They can be benign or malignant. Vulvar neoplasms are divided into cystic or solid lesions and other mixed types. Vulvar cancers are those malignant neoplasms that originate from vulvar epithelium, while vulvar sarcomas develop from non-epithelial cells such as bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue. Epithelial and mesenchymal tissue are the origin of vulvar tumors.