
Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized from cholesterol and secreted mainly from the gonads, though they can also be formed from adrenal androgens in adipose tissue. Relative to estradiol, both estrone and estriol have far weaker activity as estrogens. Estrone can be converted into estradiol, and serves mainly as a precursor or metabolic intermediate of estradiol. It is both a precursor and metabolite of estradiol.

Estrone sulfate, also known as E1S, E1SO4 and estrone 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester and conjugate.

Estriol succinate, sold under the brand name Synapause among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection.
An estrogen ester is an ester of an estrogen, most typically of estradiol but also of other estrogens such as estrone, estriol, and even nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Esterification renders estradiol into a prodrug of estradiol with increased resistance to first-pass metabolism, slightly improving its oral bioavailability. In addition, estrogen esters have increased lipophilicity, which results in a longer duration when given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection due to the formation of a long-lasting local depot in muscle and fat. Conversely, this is not the case with intravenous injection or oral administration. Estrogen esters are rapidly hydrolyzed into their parent estrogen by esterases once they have been released from the depot. Because estradiol esters are prodrugs of estradiol, they are considered to be natural and bioidentical forms of estrogen.
Estradiol stearate (E2-17-St), also known as estradiol octadecanoate and sold under the brand name Depofollan, is a naturally occurring estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the C17β stearate ester of estradiol. It occurs in the body as a very long-lasting metabolite and prohormone of estradiol. The compound is one of the components that collectively constitute lipoidal estradiol, another of which is estradiol palmitate. It is extremely lipophilic and hydrophobic. Estradiol stearate has no affinity for the estrogen receptor, requiring transformation into estradiol via esterases for its estrogenic activity. The compound does not bind to sex hormone-binding globulin or α-fetoprotein, instead being transported by lipoproteins such as high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein.

Ethinylestradiol sulfonate (EES), sold under the brand names Deposiston and Turisteron among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in birth control pills for women and in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It has also been investigated in the treatment of breast cancer in women. The medication was combined with norethisterone acetate in birth control pills. EES is taken by mouth once per week.

A steroid ester is an ester of a steroid. They include androgen esters, estrogen esters, progestogen esters, and corticosteroid esters. Steroid esters may be naturally occurring/endogenous like DHEA sulfate or synthetic like estradiol valerate. Esterification is useful because it is often able to render the parent steroid into a prodrug of itself with altered chemical properties such as improved metabolic stability, water solubility, and/or lipophilicity. This, in turn, can enhance pharmacokinetics, for instance by improving the steroid's bioavailability and/or conferring depot activity and hence an extended duration with intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.

8,9-Dehydroestrone, or Δ8-estrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10),8-tetraen-3-ol-17-one, is a naturally occurring estrogen found in horses which is closely related to equilin, equilenin, and estrone, and, as the 3-sulfate ester sodium salt, is a minor constituent (3.5%) of conjugated estrogens (Premarin). It produces 8,9-dehydro-17β-estradiol as an important active metabolite, analogously to conversion of estrone or estrone sulfate into estradiol. The compound was first described in 1997. In addition to 8,9-dehydroestrone and 8,9-dehydro-17β-estradiol, 8,9-dehydro-17α-estradiol is likely also to be present in conjugated estrogens, but has not been identified at this time.

16α-Hydroxyestrone (16α-OH-E1), or hydroxyestrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α-diol-17-one, is an endogenous steroidal estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone, as well as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of estriol. It is a potent estrogen similarly to estrone, and it has been suggested that the ratio of 16α-hydroxyestrone to 2-hydroxyestrone, the latter being much less estrogenic in comparison and even antiestrogenic in the presence of more potent estrogens like estradiol, may be involved in the pathophysiology of breast cancer. Conversely, 16α-hydroxyestrone may help to protect against osteoporosis.

Estradiol glucuronide, or estradiol 17β-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estradiol. It is formed from estradiol in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estradiol. Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates.

Estradiol sulfamate, or estradiol-3-O-sulfamate, is a steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitor which is under development for the treatment of endometriosis. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of estradiol, and was originally thought to be a prodrug of estradiol. The drug was first synthesized as an STS inhibitor along with its oxidized version estrone 3-O-sulfamate (EMATE) in the group of Professor Barry V L Potter at the University of Bath, UK, working together with Professor Michael J Reed at Imperial College, London and was found to be highly estrogenic in rodents. Such aryl sulfamate esters were shown to be "first-in-class" highly potent active site-directed irreversible STS inhibitors. Compounds of this class are thought to irreversibly modify the active site formylglycine residue of STS. The drug shows profoundly reduced susceptibility to first-pass metabolism relative to estradiol, and was believed to be the first "potent" estradiol prodrug to be discovered. It was clinically investigated for possible use as an estrogen for indications like hormonal contraception and menopausal hormone therapy. However, it showed no estrogenic effects in women. The potent non-estrogenic clinical STS inhibitor Irosustat (STX64/667-Coumate) was used to explore the possibility that STS might be responsible for the hydrolysis of estrogen sulphamates. Results demonstrated convincingly that STS is the enzyme responsible for the removal of the sulfamoyl group from estrogen sulfamates and has a crucial role in regulating the estrogenicity associated with this class of drug. Thus, STS inhibition blocks the conversion of E2MATE into estradiol and thereby abolishes its estrogenicity in humans. Irosustat has completed a number of clinical trials in oncology as an STS inhibitor currently up to Phase II.

Estrone sulfamate, or estrone-3-O-sulfamate, is a steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitor which has not yet been marketed. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of the estrogen estrone. Unlike other estrogen esters however, EMATE is not an effective prodrug of estrogens. A closely related compound is estradiol sulfamate (E2MATE), which is extensively metabolized into EMATE and has similar properties to it.

Estriol (E3), sold under the brand name Ovestin among others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which is used in menopausal hormone therapy. It is also used in veterinary medicine as Incurin to treat urinary incontinence due to estrogen deficiency in dogs. The medication is taken by mouth in the form of tablets, as a cream that is applied to the skin, as a cream or pessary that is applied in the vagina, and by injection into muscle.

Estrone (E1), sold under the brand names Estragyn, Kestrin, and Theelin among many others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy and for other indications. It has been provided as an aqueous suspension or oil solution given by injection into muscle and as a vaginal cream applied inside of the vagina. It can also be taken by mouth as estradiol/estrone/estriol and in the form of prodrugs like estropipate and conjugated estrogens.

EC508, also known as estradiol 17β-(1- -L-proline), is an estrogen which is under development by Evestra for use in menopausal hormone therapy and as a hormonal contraceptive for the prevention of pregnancy in women. It is an orally active estrogen ester – specifically, a C17β sulfonamide–proline ester of the natural and bioidentical estrogen estradiol – and acts as a prodrug of estradiol in the body. However, unlike oral estradiol and conventional oral estradiol esters such as estradiol valerate, EC508 undergoes little or no first-pass metabolism, has high oral bioavailability, and does not have disproportionate estrogenic effects in the liver. As such, it has a variety of desirable advantages over oral estradiol, similarly to parenteral estradiol, but with the convenience of oral administration. EC508 is a candidate with the potential to replace not only oral estradiol in clinical practice, but also ethinylestradiol in oral contraceptives. Evestra intends to seek Investigational New Drug status for EC508 in the second quarter of 2018.
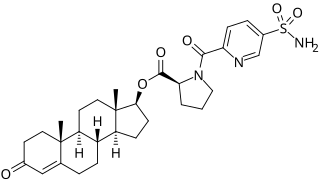
EC586, also known as testosterone 17β-(1- -L-proline), is an androgen and anabolic steroid which is under development by Evestra for use in androgen replacement therapy in men. It is an orally active androgen ester – specifically, a C17β sulfonamide–proline ester of the natural and bioidentical androgen testosterone – and acts as a prodrug of testosterone in the body. However, unlike oral testosterone and conventional oral testosterone esters such as testosterone undecanoate, EC586 has high oral potency, may undergo little or no first-pass metabolism, and may not have disproportionate androgenic effects in the liver. As such, it may have a variety of desirable advantages over oral testosterone, similarly to parenteral testosterone, but with the convenience of oral administration. Evestra intends to seek Investigational New Drug status for EC586 in the fourth quarter of 2018.

Ethinylestradiol sulfamate, or 17α-ethynylestradiol 3-O-sulfamate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester which was never marketed. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of ethinylestradiol. The drug shows considerably improved oral estrogenic potency (uterotrophic) relative to ethinylestradiol in rats but without an increase in hepatic estrogenic potency. Related compounds like ethinylestradiol N,N-diethylsulfamate (J271) and ethinylestradiol pyrrolidinosulfonate (J272) have also been developed, and have similar properties in animals. However, the closely related compound estradiol sulfamate (E2MATE) failed to show estrogenic activity in humans, which is due to the fact that it is additionally a highly potent inhibitor of steroid sulfatase and prevents its own bioactivation into estradiol.

Polyestriol phosphate, sold under the brand names Gynäsan, Klimadurin, and Triodurin, is an estrogen medication which was previously used in menopausal hormone therapy and is no longer available.

Estriol phosphate (E3P), or estriol 17β-phosphate, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α,17β-triol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate), is an estrogen which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester, specifically an ester of estriol with phosphoric acid, and acts as a prodrug of estriol by cleavage via phosphatase enzymes in the body. Estriol phosphate is contained within the chemical structure of polyestriol phosphate, and this medication has been marketed for medical use.
















