
Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.

16α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone is an endogenous metabolite of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). Both 16α-OH-DHEA and its 3β-sulfate ester, 16α-OH-DHEA-S, are intermediates in the biosynthesis of estriol from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). 16α-OH-DHEA has estrogenic activity.

Estriol succinate, sold under the brand name Synapause among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection.
An estrogen ester is an ester of an estrogen, most typically of estradiol but also of other estrogens such as estrone, estriol, and even nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Esterification renders estradiol into a prodrug of estradiol with increased resistance to first-pass metabolism, slightly improving its oral bioavailability. In addition, estrogen esters have increased lipophilicity, which results in a longer duration when given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection due to the formation of a long-lasting local depot in muscle and fat. Conversely, this is not the case with intravenous injection or oral administration. Estrogen esters are rapidly hydrolyzed into their parent estrogen by esterases once they have been released from the depot. Because estradiol esters are prodrugs of estradiol, they are considered to be natural and bioidentical forms of estrogen.

Quinestradol, also known as quinestradiol or quinestriol, as well as estriol 3-cyclopentyl ether (E3CPE), is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ether which is no longer marketed. It is the 3-cyclopentyl ether of estriol. The medication has been studied in the treatment of stress incontinence in elderly women, with effectiveness observed.
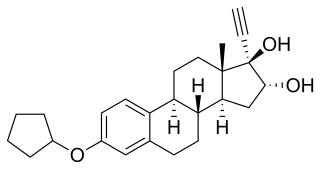
Nilestriol (INN), also known as nylestriol, is a synthetic estrogen which was patented in 1971 and is marketed in China. It is the 3-cyclopentyl ether of ethinylestriol, and is also known as ethinylestriol cyclopentyl ether (EE3CPE). Nilestriol is a prodrug of ethinylestriol, and is a more potent estrogen in comparison. It is described as a slowly-metabolized, long-acting estrogen and derivative of estriol. Nilestriol was assessed in combination with levonorgestrel for the potential treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis, but this formulation ultimately was not marketed.

Estradiol hemisuccinate, or simply estradiol succinate, also known as estradiol 17β-hemisuccinate, is an estrogen medication and an estrogen ester – specifically, the hemisuccinate ester of estradiol. It is used as a component of hormone replacement therapy for menopause. Like other estrogens, estradiol hemisuccinate has been found to have beneficial effects on the skin, with improvement of skin thickness observed.

Estriol acetate benzoate (JAN), or oestriol diacetate benzoate (BAN), is an estrogen medication. It is an estrogen ester, specifically, an ester of estriol.

Estrone acetate is a semisynthetic, steroidal estrogen. It is an estrogen ester, specifically, an ester of estrone.
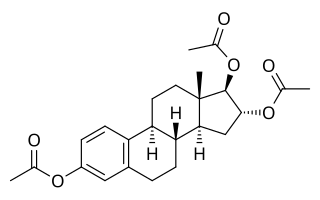
Estriol triacetate is an estrogen medication and an estrogen ester – specifically, the triacetate ester of estriol – which was never marketed. It has been said to be 10 times as physiologically active as estriol.

Estramustine is an estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 normustine ester of estradiol – and acts in part as a prodrug of estradiol in the body. Estramustine phosphate, the C17β phosphate ester of estramustine and a prodrug of estramustine, estromustine, estradiol, and estrone, is marketed and used in the treatment of prostate cancer.

Estriol (E3), sold under the brand name Ovestin among others, is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone which is used in menopausal hormone therapy. It is also used in veterinary medicine as Incurin to treat urinary incontinence due to estrogen deficiency in dogs. The medication is taken by mouth in the form of tablets, as a cream that is applied to the skin, as a cream or pessary that is applied in the vagina, and by injection into muscle.
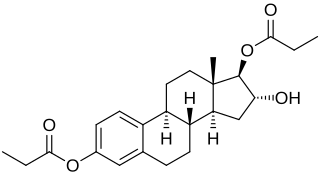
Estriol dipropionate, or estriol 3,17β-dipropionate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 and C17β dipropionate ester of estriol – which was first described in 1963 and was never marketed. Following a single intramuscular injection of 6.94 mg estriol dipropionate in an oil solution, peak levels of estriol occurred after 0.83 days, an elimination half-life of 12.7 hours was observed, and estriol levels remained elevated for up to 4 days. For comparison, the duration of estriol was much shorter, while that of estriol dihexanoate was much longer.
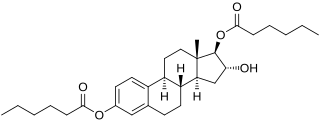
Estriol dihexanoate, or estriol 3,17β-dihexanoate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 and C17β dihexanoate ester of estriol – which was first described in 1963 and was never marketed. Following a single intramuscular injection of 8.90 mg estriol dihexanoate in an oil solution, peak levels of estriol occurred after 2.1 to 3.4 days, an elimination half-life of 187 to 221 hours was observed, and estriol levels remained elevated for up to 20 to 50 days. For comparison, the durations of estriol and estriol dipropionate were far shorter.

Ethinylestradiol benzoate, or 17α-ethynylestradiol 3-benzoate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 benzoate ester of ethinylestradiol – which was first described in the late 1930s and was never marketed.

Estriol sulfamate, or estriol 3-O-sulfamate, is a synthetic estrogen and estrogen ester which was never marketed. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of estriol. The drug shows substantially improved oral estrogenic potency relative to estriol in rats but without an increase in hepatic estrogenic potency. However, the closely related compound estradiol sulfamate (E2MATE) failed to show estrogenic activity in humans, which is due to the fact that it is additionally a highly potent inhibitor of steroid sulfatase which regulates the estrogenicity of such compounds and thus it prevents its own bioactivation into estradiol.

Polyestriol phosphate, sold under the brand names Gynäsan, Klimadurin, and Triodurin, is an estrogen medication which was previously used in menopausal hormone therapy and is no longer available.

Estriol phosphate (E3P), or estriol 17β-phosphate, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α,17β-triol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate), is an estrogen which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester, specifically an ester of estriol with phosphoric acid, and acts as a prodrug of estriol by cleavage via phosphatase enzymes in the body. Estriol phosphate is contained within the chemical structure of polyestriol phosphate, and this medication has been marketed for medical use.
















