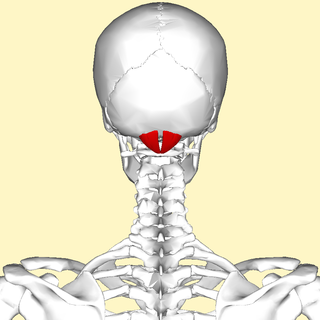
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.
Articles related to anatomy include:

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

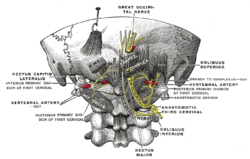
The lesser occipital nerve is a cutaneous spinal nerve of the cervical plexus. It arises from second cervical (spinal) nerve (C2). It innervates the skin of the back of the upper neck and of the scalp posterior to the ear.

The great auricular nerve is a cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It originates from the second and third cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3) of the cervical plexus. It provides sensory innervation to the skin over the parotid gland and the mastoid process, parts of the outer ear, and to the parotid gland and its fascia.

The scalp is the area of the head where head hair grows. It is made up of skin, layers of connective and fibrous tissues, and the membrane of the skull. Anatomically, the scalp is part of the epicranium, a collection of structures covering the cranium. The scalp is bordered by the face at the front, and by the neck at the sides and back. The scientific study of hair and scalp is called trichology.

In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The other two meningeal layers are the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. It envelops the arachnoid mater, which is responsible for keeping in the cerebrospinal fluid. It is derived primarily from the neural crest cell population, with postnatal contributions of the paraxial mesoderm.

The obliquus capitis inferior muscle is a muscle in the upper back of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the spinous process of the axis; its superior attachment is at the transverse process of the atlas. It is innervated by the suboccipital nerve. The muscle rotates the head to its side.

The obliquus capitis superior muscle is a small muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. It attaches inferiorly at the transverse process of the atlas ; it attaches superiorly at the external surface of the occipital bone. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve.

The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system, the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of brain.

The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve also conveys post-ganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the otic ganglion to the parotid gland.

The rectus capitis posterior major is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the spinous process of the axis ; its superior attachment is onto the outer surface of the occipital bone on and around the side part of the inferior nuchal line. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve. The muscle acts to extend the head and rorate the head to its side.
The rectus capitis posterior minor is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the posterior arch of atlas; its superior attachment is onto the occipital bone at and below the inferior nuchal line. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve. The muscle acts as a weak extensor of the head.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and also behind the sympathetic trunk, the middle cervical ganglion resting upon the vessel.
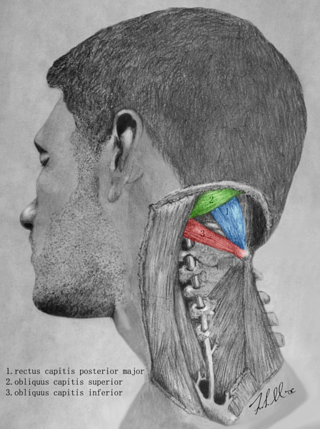
The suboccipital triangle is a region of the neck bounded by the following three muscles of the suboccipital group of muscles:

The posterior branches of cervical nerves branch from the dorsal rami of the cervical nerves.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The cervical spinal nerve 2 (C2) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. It is a part of the ansa cervicalis along with the C1 and C3 nerves sometimes forming part of superior root of the ansa cervicalis. it also connects into the inferior root of the ansa cervicalis with the C3.

The parapharyngeal space, is a potential space in the head and the neck. It has clinical importance in otolaryngology due to parapharyngeal space tumours and parapharyngeal abscess developing in this area. It is also a key anatomic landmark for localizing disease processes in the surrounding spaces of the neck; the direction of its displacement indirectly reflects the site of origin for masses or infection in adjacent areas, and consequently their appropriate differential diagnosis.