In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.
Articles related to anatomy include:

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The greater occipital nerve is a nerve of the head. It is a spinal nerve, specifically the medial branch of the dorsal primary ramus of cervical spinal nerve 2. It arises from between the first and second cervical vertebrae, ascends, and then passes through the semispinalis muscle. It ascends further to supply the skin along the posterior part of the scalp to the vertex. It supplies sensation to the scalp at the top of the head, over the ear and over the parotid glands.

The obliquus capitis inferior muscle is a muscle in the upper back of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the spinous process of the axis; its superior attachment is at the transverse process of the atlas. It is innervated by the suboccipital nerve. The muscle rotates the head to its side.

The obliquus capitis superior muscle is a small muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. It attaches inferiorly at the transverse process of the atlas ; it attaches superiorly at the external surface of the occipital bone. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve.

The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system, the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of brain.

The rectus capitis posterior major is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the spinous process of the axis ; its superior attachment is onto the outer surface of the occipital bone on and around the side part of the inferior nuchal line. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve. The muscle acts to extend the head and rotate the head to its side.
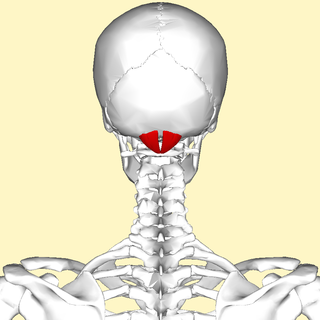
The rectus capitis posterior minor is a muscle in the upper back part of the neck. It is one of the suboccipital muscles. Its inferior attachment is at the posterior arch of atlas; its superior attachment is onto the occipital bone at and below the inferior nuchal line. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve. The muscle acts as a weak extensor of the head.

The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.

The deep cervical vein is the vena comitans of the deep cervical artery. The vein is formed in the suboccipital region by the convergence of communicating branches of the occipital vein, veins draining the suboccipital muscles, and veins from the venous plexuses that surround cervical nerves. The vein and corresponding artery then pass in between the semispinalis capitis muscle and the semispinalis colli muscle. The vein passes anterior-ward in between the transverse process of the 7th cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib to terminate in the vertebral vein.
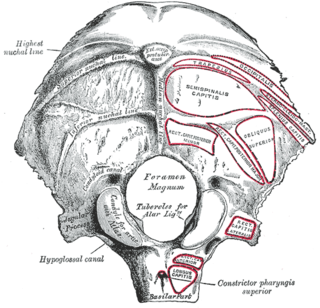
The condylar canal is a canal in the condyloid fossa of the lateral parts of occipital bone behind the occipital condyle. Resection of the rectus capitis posterior major and minor muscles reveals the bony recess leading to the condylar canal, which is situated posterior and lateral to the occipital condyle. It is immediately superior to the extradural vertebral artery, which makes a loop above the posterior C1 ring to enter the foramen magnum. The anteriomedial wall of the condylar canal thickens to join the foramen magnum rim and connect to the occipital condyle.
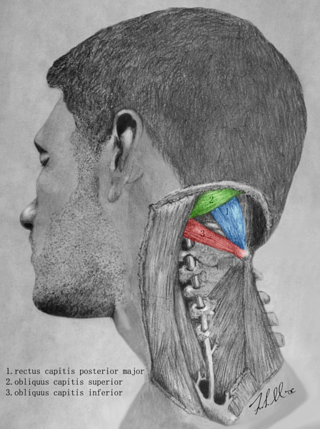
The suboccipital triangle is a region of the neck bounded by the following three muscles of the suboccipital group of muscles:

The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve, posterior ramus of spinal nerve, or posterior primary division is the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The dorsal rami provide motor innervation to the deep muscles of the back, and sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior portion of the head, neck and back.
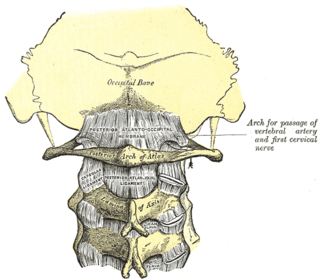
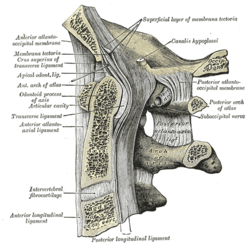
The posterior atlantooccipital membrane is a broad but thin membrane extending between the posterior margin of the foramen magnum above, and posterior arch of atlas below. It forms the floor of the suboccipital triangle.

The posterior branches of cervical nerves branch from the dorsal rami of the cervical nerves.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The cervical spinal nerve 1 (C1) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. C1 carries predominantly motor fibres, but also a small meningeal branch that supplies sensation to parts of the dura around the foramen magnum.
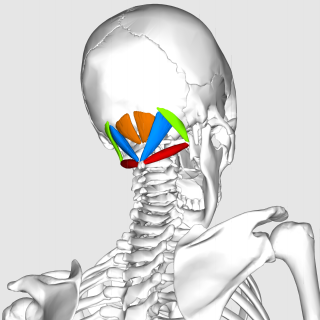
The suboccipital muscles are a group of muscles defined by their location to the occiput. Suboccipital muscles are located below the occipital bone. These are four paired muscles on the underside of the occipital bone; the two straight muscles (rectus) and the two oblique muscles (obliquus).
The myodural bridge or miodural ligament is a bridge of connective tissue that extends between the suboccipital muscles and the cervical spinal dura mater, the outer membrane that envelops the spinal cord. It provides a physical connection between the musculoskeletal and nervous systems, and the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Its importance has been highlighted by various authors.