
The North Coast railway line (NCL) is a 1,681-kilometre (1,045 mi) 1067 mm gauge railway line in Queensland, Australia. It commences at Roma Street station, Brisbane, and largely parallels the Queensland coast to Cairns in Far North Queensland. The line is electrified between Brisbane and Rockhampton. Along the way, the 1680 km railway passes through the numerous towns and cities of eastern Queensland including Nambour, Bundaberg, Gladstone, Rockhampton, Mackay and Townsville. The line though the centre of Rockhampton runs down the middle of Denison Street.

The Isis Highway is a state highway in southern Queensland, Australia. The highway is relatively short, and runs for 137 kilometres (85 mi) in a north-east / south-west direction between Bundaberg North and the Burnett Highway at Ban Ban Springs. The Isis Highway links the sugar producing Bundaberg and Fraser Coast regions with the cattle farming districts of the North Burnett.
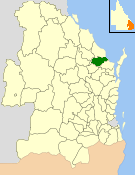
The Shire of Isis was a local government area located in the Wide Bay–Burnett region of Queensland, Australia, to the south of Bundaberg. The Shire, administered from the town of Childers covered an area of 1,702.2 square kilometres (657.2 sq mi), and existed as a local government entity from 1887 until 2008, when it was amalgamated with the City of Bundaberg and the Shires of Burnett and Kolan to form the Bundaberg Region.

Wallaville is a rural town and locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. It is 372 kilometres (231 mi) north of the state capital, Brisbane and 43 kilometres (27 mi) south west of the regional centre of Bundaberg. In the 2021 census, the locality of Wallaville had a population of 363 people.
The Wallaville Branch Railway was a fifty kilometre railway line in Queensland, Australia. It was a branch line from Goondoon railway station southwest to Kalliwa Creek. It was approved in December 1914 to tap the Goodnight Scrub forests and to transport sugar cane to the Wallaville mill established in 1896.

Apple Tree Creek is a rural town and locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. It was formerly known as Bodalla, the Dundaburra people of the Northern Kabi group name from the Gregory River Plum which to first Europeans looked like an apple. Prior to settlement of the Isis District which includes Apple tree Creek, the area was called Buth'arth translating to scrub. The town was renamed as Apple Tree Creek in 1962. In the 2021 census, the locality of Apple Tree Creek had a population of 726 people.

Moreton Central Sugar Mill Cane Tramway is a heritage-listed tramway at Mill Street, Currie Street, and Howard Street, in Nambour, Sunshine Coast Region, Queensland, Australia. It was built c. 1897. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 7 February 2005.

Doolbi is a rural locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Doolbi had a population of 101 people.

Childers Post Office is a heritage-listed former post office at Bruce Highway, Childers, Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Queensland Colonial Architect's Office and built from 1890 to 1910. It is also known as Childers Heritage Shop. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 24 January 2003.

Grand Hotel is a heritage-listed hotel at 106–110 Churchill Street, Childers, Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Anton Hettrich built from 1899 to 1900. It is also known as Childers Hotel. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992.

Queensland National Bank is a heritage-listed former bank building at 50 Churchill Street, Childers, Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Philip Oliver Ellard Hawkes and built in 1919. It is also known as Childers Travel World, Wrench & Cobb, and Ye Olde Boutique. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992.

Childers RSL Club is a heritage-listed former bank and now Returned and Services League of Australia club house at 55 Churchill Street, Childers, Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by James Percy Owen Cowlishaw and built from 1900 to c. 1909. It was formerly a branch of the Commercial Banking Company of Sydney and is also known as the RSSAILA Club or the Isis RSL Club. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992.
Horton is a rural town and locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, the locality of Horton had a population of 205 people.
North Isis is a rural locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, North Isis had a population of 566 people.
Elliott is a rural locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Elliott had a population of 156 people.
Duingal is a locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Duingal had a population of 70 people.

Isis Central is a rural locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Isis Central had a population of 205 people.
Redridge is a locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Redridge had a population of 711 people.
Eureka is a rural locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Eureka had a population of 223 people.

South Isis is a rural locality in the Bundaberg Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, South Isis had a population of 381 people.














