
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is a type of fossil fuel, formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) and Permian times.

Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United Kingdom and South Africa, a coal mine and its structures are a colliery, a coal mine is called a 'pit', and the above-ground structures are a 'pit head'. In Australia, "colliery" generally refers to an underground coal mine.

Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global oil production is reached, after which production will begin an irreversible decline. It is related to the distinct concept of oil depletion; while global petroleum reserves are finite, the limiting factor is not whether the oil exists but whether it can be extracted economically at a given price. A secular decline in oil extraction could be caused both by depletion of accessible reserves and by reductions in demand that reduce the price relative to the cost of extraction, as might be induced to reduce carbon emissions or from demand destruction triggered by persistently high oil prices.
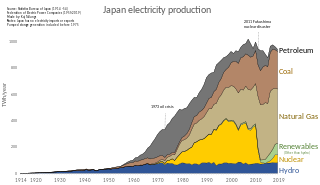
Energy in Japan refers to energy and electricity production, consumption, import and export in Japan. The country's primary energy consumption was 477.6 Mtoe in 2011, a decrease of 5% over the previous year.
The energy policy of India is to increase the locally produced energy in India and reduce energy poverty, with more focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear, solar and wind energy. Net energy import dependency was 40.9% in 2021-22.
World energy resources are the estimated maximum capacity for energy production given all available resources on Earth. They can be divided by type into fossil fuel, nuclear fuel and renewable resources.

The petroleum industry in Russia is one of the largest in the world. Russia has the largest reserves and is the largest exporter of natural gas. It has the second largest coal reserves, the sixth largest oil reserves, and is one of the largest producers of oil. It is the fourth largest energy user.
Peak coal is the peak consumption or production of coal by a human community. The peak of coal's share in the global energy mix was in 2008, when coal accounted for 30% of global energy production. Coal consumption is declining in the United States and Europe, as well as developed economies in Asia. However, consumption is still increasing in countries such as China, Indonesia, India, Russia and Australia, which compensate for the falls in other regions. Global coal consumption reached an all time high in 2022 at 8.3 billion tonnes. Global coal demand is set to remain at record levels in 2023.

China is the world's leader in electricity production from renewable energy sources, with over triple the generation of the second-ranking country, the United States. China's renewable energy sector is growing faster than its fossil fuels and nuclear power capacity, and is expected to contribute 43 per cent of global renewable capacity growth. China's total renewable energy capacity exceeded 1,000 GW in 2021, accounting for 43.5 per cent of the country's total power generation capacity, 10.2 percentage points higher than in 2015. The country aims to have 80 per cent of its total energy mix come from non-fossil fuel sources by 2060, and achieve a combined 1,200 GW of solar and wind capacity by 2030. In 2023, it was reported that China was on track to reach 1,371 gigawatts of wind and solar by 2025, five years ahead of target due to new renewables installations breaking records.
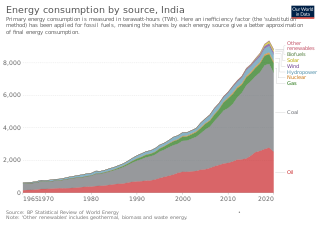
Since 2013, total primary energy consumption in India has been the third highest in the world after China and United States. India is the second-top coal consumer in the year 2017 after China. India ranks third in oil consumption with 22.1 crore tons in 2017 after United States and China. India is net energy importer to meet nearly 47% of its total primary energy in 2019.
Energy in Kazakhstan describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Kazakhstan and the politics of Kazakhstan related to energy.
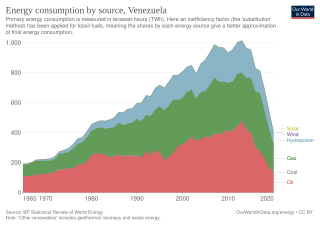
Venezuela was one of the world's largest producers of oil, and the country with the largest proven oil reserves in the world. Venezuela is a member of OPEC.

Energy in Mexico describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Mexico.

China is the largest producer and consumer of coal and the largest user of coal-generated electricity in the world. The share of coal in the Chinese energy mix declined to 55% in 2021 according to the US Energy Information Agency.

South Korea is a major energy importer, importing nearly all of its oil needs and ranking as the second-largest importer of liquefied natural gas in the world. Electricity generation in the country mainly comes from conventional thermal power, which accounts for more than two thirds of production, and from nuclear power.

South Africa produces in excess of 255 million tonnes of coal and consumes almost three-quarters of that domestically. As of 2018, South Africa was the seventh largest producer and consumer of coal in the world. This large industry, means that as of 2015 about 80,000 workers, or .5% of total employment, was from the coal industry, down from a peak in 1981 of 135,000 workers. The coal industry is South Africa's largest contribution to the greenhouse gases that cause climate change.
South Africa has a large energy sector, being the third-largest economy in Africa. The country consumed 227 TWh of electricity in 2018. The vast majority of South Africa's electricity was produced from coal, with the fuel responsible for 88% of production in 2017. South Africa is the 7th largest coal producer in the world. As of July 2018, South Africa had a coal power generation capacity of 39 gigawatts (GW). South Africa is the world's 14th largest emitter of greenhouse gases. South Africa is planning to shift away from coal in the electricity sector and the country produces the most solar and wind energy by terawatt-hours in Africa. The country aims to decommission 34 GW of coal-fired power capacity by 2050. It also aims to build at least 20 GW of renewable power generation capacity by 2030. South Africa aims to generate 77,834 megawatts (MW) of electricity by 2030, with new capacity coming significantly from renewable sources to meet emission reduction targets. Through its goals stated in the Integrated Resource Plan, it announced the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme, which aims to increase renewable power generation through private sector investment.
Energy in the Czech Republic describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in the Czech Republic.












