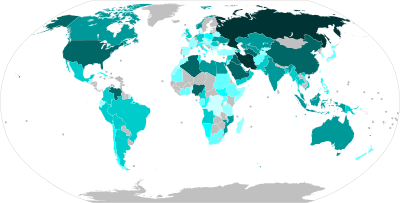
Natural gas is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane (97%) in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and helium are also usually present. Methane is colorless and odorless, and the second largest greenhouse gas contributor to global climate change after carbon dioxide. Because natural gas is odorless, odorizers such as mercaptan are commonly added to it for safety so that leaks can be readily detected.

Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name petroleum covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil and petroleum products that consist of refined crude oil.

Peak oil is the theorized point in time when the maximum rate of global oil production will occur, after which oil production will begin an irreversible decline. The primary concern of peak oil is that global transportation heavily relies upon the use of gasoline and diesel fuel. Switching transportation to electric vehicles, biofuels, or more fuel-efficient forms of travel may help reduce oil demand.

The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating energy information to promote sound policymaking, efficient markets, and public understanding of energy and its interaction with the economy and the environment. EIA programs cover data on coal, petroleum, natural gas, electric, renewable and nuclear energy. EIA is part of the U.S. Department of Energy.

Japan is a major consumer of energy, ranking fifth in the world by primary energy use. Fossil fuels accounted for 88% of Japan's primary energy in 2019. Japan imports most of its energy due to scarce domestic resources. As of 2022, the country imports 97% of its oil and is the larger LNG importer globally.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation, regulation, court decisions, public participation, and other techniques.
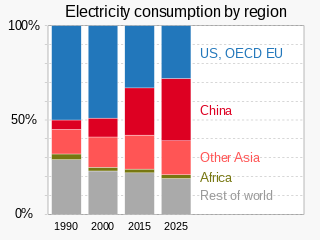
Electric energy consumption is energy consumption in the form of electrical energy. About a fifth of global energy is consumed as electricity: for residential, industrial, commercial, transportation and other purposes. Quickly increasing this share by further electrification is extremely important to limit climate change, because most other energy is consumed by burning fossil fuels thus emitting greenhouse gases which trap heat.

Energy in the United States is obtained from a diverse portfolio of sources, although the majority came from fossil fuels in 2021, as 36% of the nation's energy originated from petroleum, 32% from natural gas, and 11% from coal. Electricity from nuclear power supplied 8% and renewable energy supplied 12%, which includes biomass, wind, hydro, solar and geothermal.

United States energy independence is the concept of eliminating or substantially reducing import of petroleum to satisfy the nation's need for energy. Some proposals for achieving energy independence would permit imports from the neighboring nations of Canada and Mexico, in which case it would be called North American energy independence. Energy independence is espoused by those who want to leave the US unaffected by global energy supply disruptions and would restrict reliance upon politically unstable states for its energy security.

Iran possesses significant energy reserves, holding the position of the world's third-largest in proved oil reserves and the second-largest in natural gas reserves as of 2021. At the conclusion of the same year, Iran's share comprised 24% of the oil reserves in the Middle East and 12% of the worldwide total.

Brazil is the 7th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), the National Council for Energy Policy (CNPE), the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (ANP) and the National Agency of Electricity (ANEEL). State-owned companies Petrobras and Eletrobras are the major players in Brazil's energy sector, as well as Latin America's.
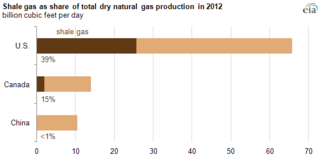
Shale gas is an unconventional natural gas that is found trapped within shale formations. Since the 1990s a combination of horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing has made large volumes of shale gas more economical to produce, and some analysts expect that shale gas will greatly expand worldwide energy supply.

Coal generated about 19.5% of the electricity at utility-scale facilities in the United States in 2022, down from 38.6% in 2014 and 51% in 2001. In 2021, coal supplied 9.5 quadrillion British thermal units (2,800 TWh) of primary energy to electric power plants, which made up 90% of coal's contribution to U.S. energy supply. Utilities buy more than 90% of the coal consumed in the United States. There were over 200 coal powered units across the United States in 2022. Coal plants have been closing since the 2010s due to cheaper and cleaner natural gas and renewables. Due to measures such as scrubbers air pollution from the plants kills far fewer people nowadays, but deaths in 2020 from PM 2.5 have been estimated at 1600. Environmentalists say that political action is needed to close them faster, to also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and better limit climate change.

Petroleum has been a major industry in the United States since the 1859 Pennsylvania oil rush around Titusville, Pennsylvania. Commonly characterized as "Big Oil", the industry includes exploration, production, refining, transportation, and marketing of oil and natural gas products. The leading crude oil-producing areas in the United States in 2023 were Texas, followed by the offshore federal zone of the Gulf of Mexico, North Dakota and New Mexico.
The National Energy Modeling System (NEMS) is an economic and energy model of United States energy markets created at the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). NEMS projects the production, consumption, conversion, import, export, and pricing of energy. The model relies on assumptions for economic variables, including world energy market interactions, resource availability, technological choice and characteristics, and demographics.

Between 2009 and 2014, gas consumption, production, and imports in China have grown dramatically, with two-digit growth. According to CNPC, the installed capacity of gas-fired power plants in the country is expected to reach around 138 million-154 million kilowatts in 2025, and further grow to 261 million-308 million kilowatts by 2030.

Natural gas was the United States' largest source of energy production in 2016, representing 33 percent of all energy produced in the country. Natural gas has been the largest source of electrical generation in the United States since July 2015.