Transport in Greece has undergone significant changes in the past two decades, vastly modernizing the country's infrastructure and transportation. Although ferry transport between islands remains the prominent method of transport between the nation's islands, improvements to the road infrastructure, rail, urban transport, and airports have all led to a vast improvement in transportation. These upgrades have played a key role in supporting Greece's economy, which in the past decade has come to rely heavily on the construction industry.
In 1995, the main means of transportation in Moldova were railways and a highway system. The major railway junctions are Chișinău, Bender, Ungheni, Ocnița, Bălți, and Basarabeasca. Primary external rail links connect the republic's network with Odesa on the Black Sea and with the Romanian cities of Iași and Galați; they also lead northward into Ukraine. Highways link Moldova's main cities and provide the chief means of transportation within the country, but roads are in poor repair. The country's major airport is in Chișinău.
Transport in Poland involves air, water, road and rail transportation. The country has a large network of municipal public transport, such as buses, trams and the metro. As a country located at the 'cross-roads' of Europe, Poland is a nation with a large and increasingly modern network of transport infrastructure.

Transport in Slovakia is possible by rail, road, air, or rivers. Slovakia is a developed Central European country with a well-developed rail network (3,662 km) and a highway system (854 km). The main international airport is the M. R. Štefánik Airport in the capital, Bratislava. The most important waterway is the river Danube, which is used by passenger, cargo, and freight ships. The two most important harbours in Slovakia are Komarno harbour and Bratislava harbour.
In railway engineering, "gauge" is the transverse distance between the inner surfaces of the heads of two rails, which for the vast majority of railway lines is the number of rails in place. However, it is sometimes necessary for track to carry railway vehicles with wheels matched to two different gauges. Such track is described as dual gauge – achieved either by addition of a third rail, if it will fit, or by two additional rails. Dual-gauge tracks are more expensive to configure with signals and sidings, and to maintain, than two separate single-gauge tracks. It is therefore usual to build dual-gauge or other multi-gauge tracks only when necessitated by lack of space or when tracks of two different gauges meet in marshalling yards or passenger stations. Dual-gauge tracks are by far the most common configuration, but triple-gauge tracks have been built in some situations.

Rail transport in Australia is a component of the Australian transport system. It is to a large extent state-based, as each state largely has its own operations, with the interstate network being developed ever since Australia's federation in 1901. As of 2022, the Australian rail network consists of a total of 32,929 kilometres (20,461 mi) of track built to three major track gauges: 18,007 kilometres (11,189 mi) of standard gauge, 2,685 kilometres (1,668 mi) of broad gauge, and 11,914 kilometres (7,403 mi) of narrow gauge lines. Additionally, about 1,400 kilometres (870 mi) of 610 mm / 2 ft gauge lines support the sugar-cane industry. 3,488 kilometres (2,167 mi), around 11 per cent of the Australian heavy railways network route-kilometres are electrified.

The Australian state of New South Wales has an extensive network of railways, which were integral to the growth and development of the state. The vast majority of railway lines were government built and operated, but there were also several private railways, some of which operate to this day.

The rail network in Adelaide, South Australia, consists of four lines and 89 stations, totalling 132 km (82 mi). It is operated by Keolis Downer under contract from the Government of South Australia, and is part of the citywide Adelaide Metro public transport system.
Australians generally assumed in the 1850s that railways would be built by the private sector. Private companies built railways in the then colonies of Victoria, opened in 1854, and New South Wales, where the company was taken over by the government before completion in 1855, due to bankruptcy. South Australia's railways were government owned from the beginning, including a horse-drawn line opened in 1854 and a steam-powered line opened in 1856. In Victoria, the private railways were soon found not to be financially viable, and existing rail networks and their expansion were taken over by the colony. Government ownership also enabled railways to be built to promote development, even if not apparently viable in strictly financial terms. The railway systems spread from the colonial capitals, except for a few lines that hauled commodities to a rural port.

The first railway in colonial South Australia was a line from the port of Goolwa on the River Murray to an ocean harbour at Port Elliot, which first operated in December 1853, before its completion in May 1854.

The Australian Rail Track Corporation (ARTC) is an Australian Government-owned statutory corporation.

Transport in Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia, consists of several interlinking modes. Melbourne is a hub for intercity, intracity and regional travel. Road-based transport accounts for most trips across many parts of the city, facilitated by Australia's largest freeway network. Public transport, including the world's largest tram network, trains and buses, also forms a key part of the transport system. Other dominant modes include walking, cycling and commercial-passenger vehicle services such as taxis.
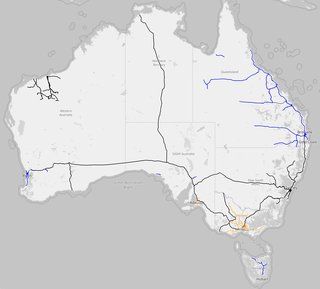
Rail gauges in Australia display significant variations, which has presented an extremely difficult problem for rail transport on the Australian continent since the 19th century. As of 2022, there are 11,914 kilometres (7,403 mi) of narrow-gauge railways, 18,007 kilometres (11,189 mi) of standard gauge railways and 2,685 kilometres (1,668 mi) of broad gauge railways. In the 19th century, each of the colonies of Australia adopted their own gauges.

Transport in Sydney is provided by an extensive network of public transport operating modes including metro, train, bus, ferry and light rail, as well as an expansive network of roadways, cycleways and airports. According to the 2006 census, in terms of travel to work or study Sydney has the highest rate of public transport usage among the Australian capital cities of 26.3% with more than 80% of weekday trips to/from Central Sydney being made by public transport. According to the New South Wales State Plan, the state has Australia's largest public transport system. The public transport network is regulated by Transport for NSW.

The rail network in Queensland, Australia, was the first in the world to adopt 1,067 mm narrow gauge for a main line, and, in 2013, was claimed to the second largest narrow gauge network in the world, consists of:

The earliest trams in Australia operated in the latter decades of the 19th century, hauled by horses or "steam tram motors". At the turn of the 20th century, propulsion almost universally turned to electrification, although cable trams lingered in Melbourne. In cities and towns that had trams, they were a major part of public transport assets.

The rail network of Melbourne, Australia, has a significant number of railway lines and yards serving freight traffic. Rail transport in Victoria is heavily focused on Melbourne, and, as a consequence, much of the state's rail freight passes through the metropolitan network.

The John Holland Group is an infrastructure, building, rail and transport business operating in Australia and New Zealand. Headquartered in Melbourne, it is a subsidiary of China Communications Construction.

Electrification of Australian railways began with the Melbourne and Sydney suburban lines. Melbourne suburban lines were electrified from 1919 using 1,500 V DC. Sydney suburban lines were electrified from 1926 using the same system.
Transport in South Australia is provided by a mix of road, rail, sea and air transport. The capital city of Adelaide is the centre to transport in the state. With its population of 1.4 million people, it has the majority of the state's 1.7 million inhabitants. Adelaide has the state's major airport and sea port.