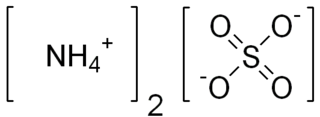Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3. A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45 percent of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. It is estimated that around 40% of the nitrogen in human beings originally comes from industrial ammonia production. As such, its importance can hardly be overstated.
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.

Perchloric acid is a mineral acid with the formula HClO4. Usually found as an aqueous solution, this colorless compound is a stronger acid than sulfuric acid, nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxidizer when hot, but aqueous solutions up to approximately 70% by weight at room temperature are generally safe, only showing strong acid features and no oxidizing properties. Perchloric acid is useful for preparing perchlorate salts, especially ammonium perchlorate, an important rocket fuel component. Perchloric acid is dangerously corrosive and readily forms potentially explosive mixtures.
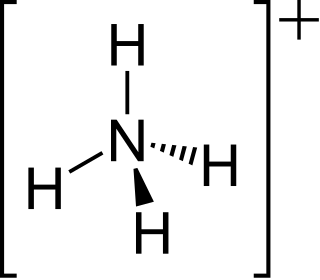
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula [NH4]+. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia. Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations, where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups.

Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula NH4NO3. It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is predominantly used in agriculture as a high-nitrogen fertilizer. Global production was estimated at 21.6 million tonnes in 2017.
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although the name ammonium hydroxide suggests an alkali with composition [NH+
4][OH−
], it is actually impossible to isolate samples of NH4OH. The ions NH+
4 and OH− do not account for a significant fraction of the total amount of ammonia except in extremely dilute solutions.
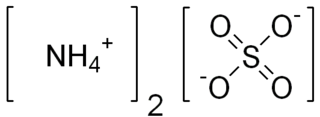
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen and 24% sulfur.
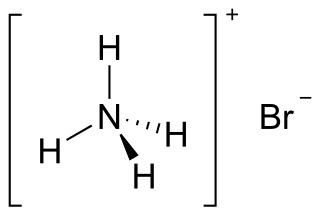
Ammonium bromide, NH4Br, is the ammonium salt of hydrobromic acid. The chemical crystallizes in colorless prisms, possessing a saline taste; it sublimes on heating and is easily soluble in water. On exposure to air it gradually assumes a yellow color because of the oxidation of traces of bromide (Br−) to bromine (Br2).

Ammonium chlorate is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4ClO3.

Ammonium nitrite, [NH4]NO2, is the ammonium salt of nitrous acid. It is not used in pure isolated form since it is highly unstable and decomposes into water and nitrogen, even at room temperature.

Ammonium thioglycolate, also known as perm salt, is the salt of thioglycolic acid and ammonia. It has the formula HSCH2CO2NH4 and has use in perming hair.

Ammonium acetate, also known as spirit of Mindererus in aqueous solution, is a chemical compound with the formula NH4CH3CO2. It is a white, hygroscopic solid and can be derived from the reaction of ammonia and acetic acid. It is available commercially.
Pelargonic acid, also called nonanoic acid, is an organic compound with structural formula CH3(CH2)7CO2H. It is a nine-carbon fatty acid. Nonanoic acid is a colorless oily liquid with an unpleasant, rancid odor. It is nearly insoluble in water, but very soluble in organic solvents. The esters and salts of pelargonic acid are called pelargonates or nonanoates.
The Kjeldahl method or Kjeldahl digestion (Danish pronunciation: [ˈkʰelˌtɛˀl]) in analytical chemistry is a method for the quantitative determination of nitrogen contained in organic substances plus the nitrogen contained in the inorganic compounds ammonia and ammonium (NH3/NH4+). Without modification, other forms of inorganic nitrogen, for instance nitrate, are not included in this measurement. Using an empirical relation between Kjeldahl nitrogen content and protein content it is an important method for analyzing proteins. This method was developed by Johan Kjeldahl in 1883.
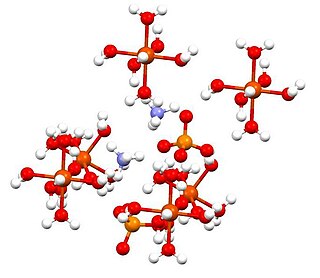
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate, or Mohr's salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2(H2O)6. Containing two different cations, Fe2+ and NH4+, it is classified as a double salt of ferrous sulfate and ammonium sulfate. It is a common laboratory reagent because it is readily crystallized, and crystals resist oxidation by air. Like the other ferrous sulfate salts, ferrous ammonium sulfate dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. Its mineral form is mohrite.

Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, bad smells, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing offensive odor, and avoiding the spread of dirt and contaminants to oneself and others. Some cleaning agents can kill bacteria and clean at the same time. Others, called degreasers, contain organic solvents to help dissolve oils and fats.

Ammonium polyphosphate is an inorganic salt of polyphosphoric acid and ammonia containing both chains and possibly branching. Its chemical formula is [NH4 PO3]n(OH)2 showing that each monomer consists of an orthophosphate radical of a phosphorus atom with three oxygens and one negative charge neutralized by an ammonium cation leaving two bonds free to polymerize. In the branched cases some monomers are missing the ammonium anion and instead link to three other monomers.
The deliming operation in leather processing is a drum/paddle or pit based operation where two main objectives are met:

Ammonium iron(III) sulfate, NH4Fe(SO4)2·12 H2O, or NH4[Fe(H2O)6](SO4)2·6 H2O, also known as ferric ammonium sulfate (FAS) or iron alum, is a double salt in the class of alums, which consists of compounds with the general formula AB(SO4)2 · 12 H2O. It has the appearance of weakly violet, octahedrical crystals. There has been some discussion regarding the origin of the crystals' colour, with some ascribing it to impurities in the compound, and others claiming it to be a property of the crystal itself.

Ammonium arsenate is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)3AsO4. It is prepared by treating a concentrated solution of arsenic acid with ammonia, resulting in precipitation of colorless crystals of the trihydrate. Upon heating, it releases ammonia.