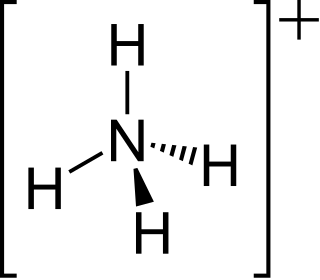
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NH+4 or [NH4]+. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia. Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged (protonated) substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations, where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic or other groups.

Bisulfide is an inorganic anion with the chemical formula HS−. It contributes no color to bisulfide salts, and its salts may have a distinctive putrid smell. It is a strong base. Bisulfide solutions are corrosive and attack the skin.
Classical qualitative inorganic analysis is a method of analytical chemistry which seeks to find the elemental composition of inorganic compounds. It is mainly focused on detecting ions in an aqueous solution, therefore materials in other forms may need to be brought to this state before using standard methods. The solution is then treated with various reagents to test for reactions characteristic of certain ions, which may cause color change, precipitation and other visible changes.

Ammonium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula [NH4]SH.

Sodium thioantimoniate or sodium tetrathioantimonate(V) is an inorganic compound with the formula Na3SbS4. The nonahydrate of this chemical, Na3SbS4·9H2O, is known as Schlippe's salt, named after Johann Karl Friedrich von Schlippe (1799–1867). These compounds are examples of sulfosalts. They were once of interest as species generated in qualitative inorganic analysis.

Ammonium bifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula [NH4][HF2] or [NH4]F·HF. It is produced from ammonia and hydrogen fluoride. This colourless salt is a glass-etchant and an intermediate in a once-contemplated route to hydrofluoric acid.

Vanadium(III) fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula VF3. This yellow-green, refractory solid is obtained in a two-step procedure from V2O3. Similar to other transition-metal fluorides (such as MnF2), it exhibits magnetic ordering at low temperatures (e.g. V2F6.4H2O orders below 12 K).
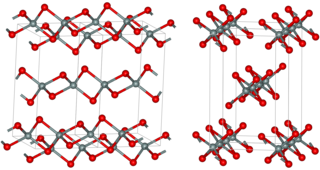
Silicon disulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula SiS2. Like silicon dioxide, this material is polymeric, but it adopts a 1-dimensional structure quite different from the usual forms of SiO2.

Ammonium dichromate is an inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Cr2O7. In this compound, as in all chromates and dichromates, chromium is in a +6 oxidation state, commonly known as hexavalent chromium. It is a salt consisting of ammonium ions and dichromate ions.

Hexafluorophosphate is an anion with chemical formula of [PF6]−. It is an octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. [PF6]− is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, [SiF6]2−, and hexafluoroantimonate [SbF6]−. In this anion, phosphorus has a valence of 5. Being poorly nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion.
Molybdenum dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula MoO2. It is a violet-colored solid and is a metallic conductor. The mineralogical form of this compound is called tugarinovite, and is only very rarely found.

Molybdenum blue is a term applied to:

Ammonium thiocyanate is an inorganic compound with the formula [NH4]+[SCN]−. It is an ammonium salt of thiocyanic acid. It consists of ammonium cations [NH4]+ and thiocyanate anions [SCN]−.

In chemistry, a molybdate is a compound containing an oxyanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6: O−−Mo(=O)2−O−. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxyanions, which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxyanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxyanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.

The S3 molecule, known as trisulfur, sulfur trimer, thiozone, or triatomic sulfur, is a cherry-red allotrope of sulfur. It comprises about 10% of vaporised sulfur at 713 K and 1,333 Pa. It has been observed at cryogenic temperatures as a solid. Under ordinary conditions it converts to cyclooctasulfur.
Ammonium orthomolybdate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2MoO4. It is a white solid that is prepared by treating molybdenum trioxide with aqueous ammonia. Upon heating these solutions, ammonia is lost, to give ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O).
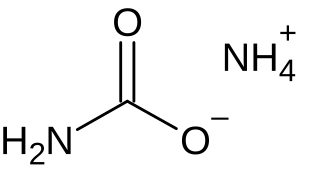
Ammonium carbamate is a chemical compound with the formula [NH4][H2NCO2] consisting of ammonium cation NH+4 and carbamate anion NH2COO−. It is a white solid that is extremely soluble in water, less so in alcohol. Ammonium carbamate can be formed by the reaction of ammonia NH3 with carbon dioxide CO2, and will slowly decompose to those gases at ordinary temperatures and pressures. It is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of urea (NH2)2CO, an important fertilizer.
Ammonium dimolybdate (ADM) is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Mo2O7. It is a white, water-soluble solid. ADM is an intermediate in the production of molybdenum compounds from its ores. Roasting typical ore produces crude molybdenum(VI) oxides, which can be extracted into aqueous ammonia, affording ammonium molybdate. Heating solutions of ammonium molybdate gives ADM. Upon heating, solid ammonium dimolybdate decomposes to molybdenum trioxide:
Lanthanide trichlorides are a family of inorganic compound with the formula LnCl3, where Ln stands for a lanthanide metal. The trichlorides are standard reagents in applied and academic chemistry of the lanthanides. They exist as anhydrous solids and as hydrates.
Rhenium compounds are compounds formed by the transition metal rhenium (Re). Rhenium can form in many oxidation states, and compounds are known for every oxidation state from -3 to +7 except -2, although the oxidation states +7, +4, and +3 are the most common. Rhenium is most available commercially as salts of perrhenate, including sodium and ammonium perrhenates. These are white, water-soluble compounds. The tetrathioperrhenate anion [ReS4]− is possible.


![The [MoS4] anion. MoS4.png](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/a/a1/MoS4.png/100px-MoS4.png)













