In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.
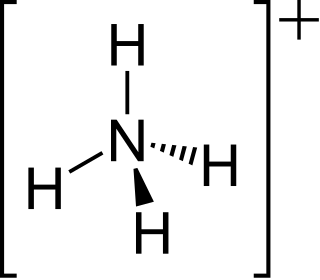
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NH+4 or [NH4]+. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia. Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged (protonated) substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations, where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic or other groups.

Ammonium bicarbonate is an inorganic compound with formula (NH4)HCO3. The compound has many names, reflecting its long history. Chemically speaking, it is the bicarbonate salt of the ammonium ion. It is a colourless solid that degrades readily to carbon dioxide, water and ammonia.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.

Terbium(III,IV) oxide, occasionally called tetraterbium heptaoxide, has the formula Tb4O7, though some texts refer to it as TbO1.75. There is some debate as to whether it is a discrete compound, or simply one phase in an interstitial oxide system. Tb4O7 is one of the main commercial terbium compounds, and the only such product containing at least some Tb(IV) (terbium in the +4 oxidation state), along with the more stable Tb(III). It is produced by heating the metal oxalate, and it is used in the preparation of other terbium compounds. Terbium forms three other major oxides: Tb2O3, TbO2, and Tb6O11.

Silicotungstic acid or tungstosilicic acid is a heteropoly acid with the chemical formula H4[SiW12O40]. It forms hydrates H4[SiW12O40]·nH2O. In freshly prepared samples, n is approximately 29, but after prolonged desiccation, n = 6. It is a white solid although impure samples appear yellow. It is used as a catalyst in the chemical industry.

In chemistry, the heteropolymetalates are a subset of the polyoxometalates, which consist of three or more transition metal oxyanions linked together by shared oxygen atoms to form a closed 3-dimensional molecular framework. In contrast to isopolymetalates, which contain only one kind of metal atom, the heteropolymetalates contain differing main group oxyanions. The metal atoms are usually group 6 or less commonly group 5 transition metals in their highest oxidation states. They are usually colorless to orange, diamagnetic anions. For most heteropolymetalates the W, Mo, or V, is complemented by main group oxyanions phosphate and silicate. Many exceptions to these general statements exist, and the class of compounds includes hundreds of examples.

Phosphotungstic acid (PTA) or tungstophosphoric acid (TPA), is a heteropoly acid with the chemical formula H3PW12O40]. It forms hydrates H3[PW12O40]·nH2O. It is normally isolated as the n = 24 hydrate but can be desiccated to the hexahydrate (n = 6). EPTA is the name of ethanolic phosphotungstic acid, its alcohol solution used in biology. It has the appearance of small, colorless-grayish or slightly yellow-green crystals, with melting point 89 °C (24 H2O hydrate). It is odorless and soluble in water (200 g/100 ml). It is not especially toxic, but is a mild acidic irritant. The compound is known by a variety of names and acronyms (see 'other names' section of infobox).
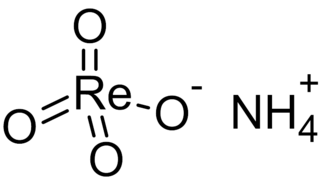
Ammonium perrhenate (APR) is the ammonium salt of perrhenic acid, NH4ReO4. It is the most common form in which rhenium is traded. It is a white salt; soluble in ethanol and water, and mildly soluble in NH4Cl. It was first described soon after the discovery of rhenium.

Ammonium bifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula [NH4][HF2] or [NH4]F·HF. It is produced from ammonia and hydrogen fluoride. This colourless salt is a glass-etchant and an intermediate in a once-contemplated route to hydrofluoric acid.

Lanthanum chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula LaCl3. It is a common salt of lanthanum which is mainly used in research. It is a white solid that is highly soluble in water and alcohols.

Ammonium paratungstate (or APT) is a white crystalline salt with the chemical formula (NH4)10(H2W12O42)·4H2O. It is described as "the most important raw material for all other tungsten products."
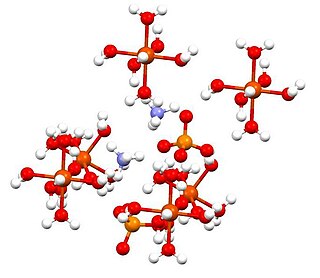
Ammonium iron(II) sulfate, or Mohr's salt, is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2(H2O)6. Containing two different cations, Fe2+ and NH+4, it is classified as a double salt of ferrous sulfate and ammonium sulfate. It is a common laboratory reagent because it is readily crystallized, and crystals resist oxidation by air. Like the other ferrous sulfate salts, ferrous ammonium sulfate dissolves in water to give the aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry. Its mineral form is mohrite.
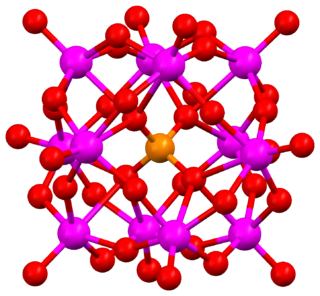
The Keggin structure is the best known structural form for heteropoly acids. It is the structural form of α-Keggin anions, which have a general formula of [XM12O40]n−, where X is the heteroatom, M is the addendum atom, and O represents oxygen. The structure self-assembles in acidic aqueous solution and is a commonly used type of polyoxometalate catalysts.

Phosphomolybdic acid is the heteropolymetalate with the formula H3[Mo12PO40]·12H2O. It is a yellow solid, although even slightly impure samples have a greenish coloration. It is also known as dodeca molybdophosphoric acid or PMA, is a yellow-green chemical compound that is freely soluble in water and polar organic solvents such as ethanol. It is used as a stain in histology and in organic synthesis.

Ammonium iron(III) sulfate, NH4Fe(SO4)2·12 H2O, or NH4[Fe(H2O)6](SO4)2·6 H2O, also known as ferric ammonium sulfate (FAS) or iron alum, is a double salt in the class of alums, which consists of compounds with the general formula AB(SO4)2 · 12 H2O. It has the appearance of weakly violet, octahedrical crystals. There has been some discussion regarding the origin of the crystals' colour, with some ascribing it to impurities in the compound, and others claiming it to be a property of the crystal itself.

Sodium hexachloroplatinate(IV), the sodium salt of chloroplatinic acid, is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2[PtCl6], consisting of the sodium cation and the hexachloroplatinate anion. As explained by Cox and Peters, anhydrous sodium hexachloroplatinate, which is yellow, tends to form the orange hexahydrate upon storage in humid air. The latter can be dehydrated upon heating at 110 °C.
Ammonium orthomolybdate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula (NH4)2MoO4. It is a white solid that is prepared by treating molybdenum trioxide with aqueous ammonia. Upon heating these solutions, ammonia is lost, to give ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O).

Vanadium(II) sulfate describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula VSO4(H2O)x where 0 ≤ x ≤ 7. The hexahydrate is most commonly encountered. It is a violet solid that dissolves in water to give air-sensitive solutions of the aquo complex. The salt is isomorphous with [Mg(H2O)6]SO4. Compared to the V–O bond length of 191 pm in [V(H2O)6]3+, the V–O distance is 212 pm in the [V(H2O)6]SO4. This nearly 10% elongation reflects the effect of the lower charge, hence weakened electrostatic attraction.

Tungsten(II) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula W6Cl12. It is a polymeric cluster compound. The material dissolves in concentrated hydrochloric acid, forming (H3O)2[W6Cl14](H2O)x. Heating this salt gives yellow-brown W6Cl12. The structural chemistry resembles that observed for molybdenum(II) chloride.


![The phosphomolybdate ion, [PMo12O40] . Phosphotungstate-3D-polyhedra.png](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/60/Phosphotungstate-3D-polyhedra.png/150px-Phosphotungstate-3D-polyhedra.png)















