
Alfentanil is a potent but short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug, used for anaesthesia in surgery. It is an analogue of fentanyl with around one-fourth to one-tenth the potency, one-third the duration of action, and an onset of action four times faster than that of fentanyl. Alfentanil has a pKa of approximately 6.5, which leads to a very high proportion of the drug being uncharged at physiologic pH, a characteristic responsible for its rapid onset. It is an agonist at mu opioid receptors.

Parafluorofentanyl is an opioid analgesic analogue of fentanyl developed by Janssen Pharmaceuticals in the 1960s.
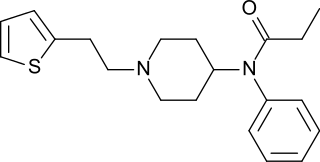
Thiofentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl.

Betahydroxythiofentanyl (β-hydroxythiofentanyl) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl.

3-Methylthiofentanyl is an opioid analgesic and analogue of fentanyl.

α-Methylthiofentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl.

β-Hydroxyfentanyl (Fentanol) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl.

Trefentanil (A-3665) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl and was developed in 1992.

Lofentanil or lofentanyl is one of the most potent opioid analgesics known and is an analogue of fentanyl, which was developed in 1960. It is most similar to the highly potent opioid carfentanil (4-carbomethoxyfentanyl), only slightly more potent. Lofentanil can be described as 3-methylcarfentanil, or 3-methyl-4-carbomethoxyfentanyl. While 3-methylfentanyl is considerably more potent than fentanyl itself, lofentanil is only slightly stronger than carfentanil. This suggests that substitution at both the 3 and 4 positions of the piperidine ring introduces steric hindrance which prevents μ-opioid affinity from increasing much further. As with other 3-substituted fentanyl derivatives such as ohmefentanyl, the stereoisomerism of lofentanil is very important, with some stereoisomers being much more potent than others.
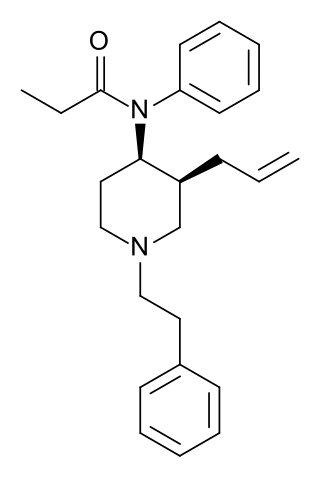
3-Allylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl.
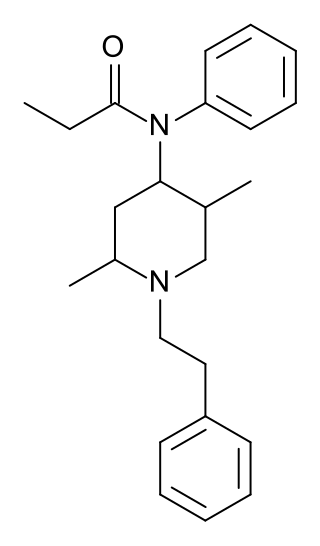
Phenaridine (2,5-dimethylfentanyl) is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl. It was developed in 1972, and is used for surgical anasthesia.

β-Methylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of fentanyl.

Ocfentanil is a potent synthetic opioid structurally related to fentanyl that was developed in the early 1990s as one of a series of potent naloxone-reversible opioids in an attempt to obtain an opioid that had better therapeutic indices in terms of cardiovascular effects and respiratory depression as compared to fentanyl. Ocfentanil was never developed for medical use despite reasonable results in human clinical trials, but subsequently started to be sold as a designer drug starting in around 2013.

4-Phenylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is a derivative of fentanyl. It was developed during the course of research that ultimately resulted in super-potent opioid derivatives such as carfentanil, though it is a substantially less potent analogue. 4-Phenylfentanyl is around eight times the potency of fentanyl in analgesic tests on animals, but more complex 4-heteroaryl derivatives such as substituted thiophenes and thiazoles are more potent still, as they are closer bioisosteres to the 4-carbomethoxy group of carfentanil.

N-Methylnorcarfentanil (R-32395) is an opioid analgesic drug related to the highly potent animal tranquilizer carfentanil, but several thousand times weaker, being only slightly stronger than morphine. It was first synthesised by a team of chemists at Janssen Pharmaceutica led by Paul Janssen, who were investigating the structure-activity relationships of the fentanyl family of drugs. They found that replacing the phenethyl group attached to the piperidine nitrogen of fentanyl with a smaller methyl group, made it so much weaker that it was inactive as an analgesic in animals. However the same change made to the more potent analogue carfentanil retained reasonable opioid receptor activity, reflecting the higher binding affinity produced by the 4-carbomethoxy group.

R-30490 is an opioid analgesic related to the highly potent animal tranquilizer carfentanil, and with only slightly lower potency. It was first synthesised by a team of chemists at Janssen Pharmaceutica led by Paul Janssen, who were investigating the structure-activity relationships of the fentanyl family of drugs. R-30490 was found to be the most selective agonist for the μ-opioid receptor out of all the fentanyl analogues tested, but it has never been introduced for medical use in humans, although the closely related drug sufentanil is widely used for analgesia and anesthesia during major surgery.

3-Methylbutyrfentanyl (3-MBF) is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of butyrfentanyl.

Isobutyrylfentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl and has been sold online as a designer drug. It is believed to be around the same potency as butyrfentanyl but has been less widely distributed on illicit markets, though it was one of the earliest of the "new wave" of fentanyl derivatives to appear, and was reported in Europe for the first time in December 2012.

Thiafentanil is a highly potent opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl, and was invented in 1986. Its analgesic potency is slightly less than that of carfentanil, though with a faster onset of effects, shorter duration of action and a slightly lesser tendency to produce respiratory depression. It is used in veterinary medicine to anesthetise animals such as impala, usually in combination with other anesthetics such as ketamine, xylazine or medetomidine to reduce the prevalence of side effects such as muscle rigidity.

2,2'-Difluorofentanyl is an opioid analgesic that is an analog of fentanyl which has been sold as a designer drug.





















