This article needs additional citations for verification .(August 2008) |

Casomorphin is an opioid peptide (protein fragment) derived from the digestion of the milk protein casein. [1]
This article needs additional citations for verification .(August 2008) |

Casomorphin is an opioid peptide (protein fragment) derived from the digestion of the milk protein casein. [1]
Digestive enzymes can break casein down into peptides that have some biological activity in cells and in laboratory animals though conclusive causal effects on humans have not been established. [1]
Although research has shown high rates of use of complementary and alternative therapies for children with autism, including gluten and/or casein exclusion diets, as of 2008 [update] there was a lack of evidence that these diets had any effect. [2]
If opioid peptides breach the intestinal barrier, typically linked to permeability and constrained biosynthesis of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4), they can attach to opioid receptors. Elucidation requires a systemic framework that acknowledges that public-health effects of food-derived opioids are complex with varying genetic susceptibility and confounding factors, together with system-wide interactions and feedbacks. [3]
Also known as morphiceptin
(Note: There is also a form of bovine β-casomorphin 8 that has histidine instead of proline in position 8, depending on whether it is derived from A1 (His) or A2 (Pro) beta-casein.)
Endorphins are peptides produced in the brain that block the perception of pain and increase feelings of wellbeing. They are produced and stored in the pituitary gland of the brain. Endorphins are endogenous painkillers often produced in the brain and adrenal medulla during physical exercise or orgasm and inhibit pain, muscle cramps, and relieve stress.

Casein is a family of related phosphoproteins that are commonly found in mammalian milk, comprising about 80% of the proteins in cow's milk and between 20% and 60% of the proteins in human milk. Sheep and cow milk have a higher casein content than other types of milk with human milk having a particularly low casein content.
A gluten-free casein-free diet, also known as a gluten-free dairy-free diet, is a diet that does not include gluten, and casein. Despite an absence of scientific evidence, there have been advocates for the use of this diet as a treatment for autism and related conditions.

An enkephalin is a pentapeptide involved in regulating nociception in the body. The enkephalins are termed endogenous ligands, as they are internally derived and bind to the body's opioid receptors. Discovered in 1975, two forms of enkephalin have been found, one containing leucine ("leu"), and the other containing methionine ("met"). Both are products of the proenkephalin gene.

β-Endorphin (beta-endorphin) is an endogenous opioid neuropeptide and peptide hormone that is produced in certain neurons within the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. It is one of three endorphins that are produced in humans, the others of which include α-endorphin and γ-endorphin.
Gluten exorphins are a group of opioid peptides formed during the digestion of the gluten protein. These peptides work as external regulators for gastrointestinal movement and hormonal release. The breakdown of gliadin, a polymer of wheat proteins, creates amino acids that stop the gluten epitopes from entering the immune system to activate inflammatory reactions. During this process, gluten does not fully break down, thus increasing the presence of gluten exorphins. Because of this, researchers think this is what might lead to various diseases.

Opioid peptides or opiate peptides are peptides that bind to opioid receptors in the brain; opiates and opioids mimic the effect of these peptides. Such peptides may be produced by the body itself, for example endorphins. The effects of these peptides vary, but they all resemble those of opiates. Brain opioid peptide systems are known to play an important role in motivation, emotion, attachment behaviour, the response to stress and pain, control of food intake, and the rewarding effects of alcohol and nicotine.
The rubiscolins are a group of opioid peptides that are formed during digestion of the ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) protein from spinach leaves. These peptides have much in common with the better-known gluten exorphins.

Endomorphins are considered to be natural opioid neuropeptides central to pain relief. The two known endomorphins, endomorphin-1 and endomorphin-2, are tetrapeptides, consisting of Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe and Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe amino acid sequences respectively. These sequences fold into tertiary structures with high specificity and affinity for the μ-opioid receptor, binding it exclusively and strongly. Bound μ-opioid receptors typically induce inhibitory effects on neuronal activity. Endomorphin-like immunoreactivity exists within the central and peripheral nervous systems, where endomorphin-1 appears to be concentrated in the brain and upper brainstem, and endomorphin-2 in the spinal cord and lower brainstem. Because endomorphins activate the μ-opioid receptor, which is the target receptor of morphine and its derivatives, endomorphins possess significant potential as analgesics with reduced side effects and risk of addiction.
A tetrapeptide is a peptide, classified as an oligopeptide, since it only consists of four amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Many tetrapeptides are pharmacologically active, often showing affinity and specificity for a variety of receptors in protein-protein signaling. Present in nature are both linear and cyclic tetrapeptides (CTPs), the latter of which mimics protein reverse turns which are often present on the surface of proteins and druggable targets. Tetrapeptides may be cyclized by a fourth peptide bond or other covalent bonds.

Dynorphin A is a dynorphin, an endogenous opioid peptide that activates the κ-opioid receptor. Its amino acid sequence is Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys.
Big dynorphin is an endogenous opioid peptide of the dynorphin family that is composed of both dynorphin A and dynorphin B. Big dynorphin has the amino acid sequence: Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Ile-Arg-Pro-Lys-Leu-Lys-Trp-Asp-Asn-Gln-Lys-Arg-Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Arg-Gln-Phe-Lys-Val-Val-Thr. It has nociceptive and anxiolytic-like properties, as well as effects on memory in mice.

β-Neoendorphin is an endogenous opioid peptide with a nonapeptide structure and the amino acid sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Leu-Arg-Lys-Tyr-Pro (YGGFLRKYP).

α-Endorphin (alpha-endorphin) is an endogenous opioid peptide with a length of 16 amino acids, and the amino acid sequence: Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met-Thr-Ser-Glu-Lys-Ser-Gln-Thr-Pro-Leu-Val-Thr. With the use of mass spectrometry, Nicholas Ling was able to determine the primary sequence of a-endorphin.
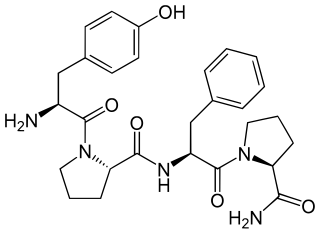
Morphiceptin is a tetrapeptide (Tyr-Pro-Phe-Pro-NH2) that is a selective μ-opioid receptor agonist. It is derived from β-casomorphin and has over 1,000 times selectivity for μ- over δ-opioid receptors. When injected intracerebroventricularly (into the ventricular system of the brain), morphiceptin had an analgesic ED50 of 1.7 nmol per animal. The analgesic effects of morphiceptin were reversed by naloxone, meaning that the analgesic effect is mediated by the μ-opioid receptor.

Hemorphin-4 is an endogenous opioid peptide of the hemorphin family which possesses antinociceptive properties and is derived from the β-chain of hemoglobin in the bloodstream. It is a tetrapeptide with the amino acid sequence Tyr-Pro-Trp-Thr. Hemorphin-4 has affinities for the μ-, δ-, and κ-opioid receptors that are in the same range as the structurally related β-casomorphins, although affinity to the κ-opioid receptor is markedly higher in comparison. It acts as an agonist at these sites. Hemorphin-4 also has inhibitory effects on angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), and as a result, may play a role in the regulation of blood pressure. Notably, inhibition of ACE also reduces enkephalin catabolism.

Casokefamide (INN), also known as β-casomorphin 4027 (β-CM-4027) and [D-Ala2,4,Tyr5]-β-casomorphin-5-amide, is a peripherally-specific, synthetic opioid pentapeptide with the amino acid sequence Tyr-D-Ala-Phe-D-Ala-Tyr-NH2. Derived from the β-casomorphin sequence, it was designed with the intention of improving resistance to digestive enzymes so that it could be used as an antidiarrheal medicine. Unlike other casomorphins, which are generally selective μ-opioid receptor agonists, casokefamide binds to both the μ- and δ-opioid receptors. In a clinical study, casokefamide was found to be effective via the oral route for the treatment of chronic diarrhea, and did not produce any side effects. However, further clinical development was not pursued and it was never marketed.
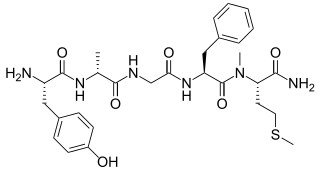
Metkefamide (INN; LY-127,623), or metkephamid acetate (USAN), but most frequently referred to simply as metkephamid, is a synthetic opioid pentapeptide and derivative of [Met]enkephalin with the amino acid sequence Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-Phe-(N-Me)-Met-NH2. It behaves as a potent agonist of the δ- and μ-opioid receptors with roughly equipotent affinity, and also has similarly high affinity as well as subtype-selectivity for the κ3-opioid receptor.
The opioid excess theory is a theory which postulates that autism is the result of a metabolic disorder in which opioid peptides produced through metabolism of gluten and casein pass through an abnormally permeable intestinal membrane and then proceed to exert an effect on neurotransmission through binding with opioid receptors. It is believed by advocates of this hypothesis that autistic children are unusually sensitive to gluten, which results in small bowel inflammation in these children, which in turn allows these opioid peptides to enter the brain.

Endomorphin-1 (EM-1) (amino acid sequence Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2) is an endogenous opioid peptide and one of the two endomorphins. It is a high affinity, highly selective agonist of the μ-opioid receptor, and along with endomorphin-2 (EM-2), has been proposed to be the actual endogenous ligand of the μ-receptor. EM-1 produces analgesia in animals and is equipotent with morphine in this regard. The gene encoding for EM-1 has not yet been identified, and it has been suggested that endomorphins could be synthesized by an enzymatic, non-ribosomal mechanism.