Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor to ice as the water vapor reaches the freezing point. In temperate climates, it most commonly appears on surfaces near the ground as fragile white crystals; in cold climates, it occurs in a greater variety of forms. The propagation of crystal formation occurs by the process of nucleation.

Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 32 °F, 0 °C, or 273.15 K. Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color.

Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions. In turn, fog affects many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare.

Altostratus is a middle-altitude cloud genus made up of water droplets, ice crystals, or a mixture of the two. Altostratus clouds are formed when large masses of warm, moist air rise, causing water vapor to condense. Altostratus clouds are usually gray or blueish featureless sheets, although some variants have wavy or banded bases. The sun can be seen through thinner altostratus clouds, but thicker layers can be quite opaque.

Mist is a phenomenon caused by small droplets of water suspended in the cold air, usually by condensation. Physically, it is an example of a dispersion. It is most commonly seen where water vapor in warm, moist air meets sudden cooling, such as in exhaled air in the winter, or when throwing water onto the hot stove of a sauna. It can be created artificially with aerosol canisters if the humidity and temperature conditions are right. It can also occur as part of natural weather, when humid air cools rapidly, notably when the air comes into contact with surfaces that are much cooler than the air.

Ice crystals are solid ice in symmetrical shapes including hexagonal columns, hexagonal plates, and dendritic crystals. Ice crystals are responsible for various atmospheric optic displays and cloud formations.

In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor, so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation but colloids, because the water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate. Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called showers.
In physics and chemistry, flash freezing is the process whereby objects are frozen in just a few hours by subjecting them to cryogenic temperatures, or through direct contact with liquid nitrogen at −196 °C (−320.8 °F). It is commonly used in the food industry.

Cloud physics is the study of the physical processes that lead to the formation, growth and precipitation of atmospheric clouds. These aerosols are found in the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere, which collectively make up the greatest part of the homosphere. Clouds consist of microscopic droplets of liquid water, tiny crystals of ice, or both, along with microscopic particles of dust, smoke, or other matter, known as condensation nuclei. Cloud droplets initially form by the condensation of water vapor onto condensation nuclei when the supersaturation of air exceeds a critical value according to Köhler theory. Cloud condensation nuclei are necessary for cloud droplets formation because of the Kelvin effect, which describes the change in saturation vapor pressure due to a curved surface. At small radii, the amount of supersaturation needed for condensation to occur is so large, that it does not happen naturally. Raoult's law describes how the vapor pressure is dependent on the amount of solute in a solution. At high concentrations, when the cloud droplets are small, the supersaturation required is smaller than without the presence of a nucleus.

Rime ice forms when supercooled water droplets freeze onto surfaces. In the atmosphere, there are three basic types of rime ice:

In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears. For example, if a volume of water is cooled below 0 °C, it will tend to freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0 °C often stay completely free of ice for long periods (supercooling). At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures nucleation is fast, and ice crystals appear after little or no delay.
The Wegener–Bergeron–Findeisen process, is a process of ice crystal growth that occurs in mixed phase clouds in regions where the ambient vapor pressure falls between the saturation vapor pressure over water and the lower saturation vapor pressure over ice. This is a subsaturated environment for liquid water but a supersaturated environment for ice resulting in rapid evaporation of liquid water and rapid ice crystal growth through vapor deposition. If the number density of ice is small compared to liquid water, the ice crystals can grow large enough to fall out of the cloud, melting into rain drops if lower level temperatures are warm enough.

Freezing drizzle is drizzle that freezes on contact with the ground or an object at or near the surface. Its METAR code is FZDZ.

Graupel, also called soft hail, hominy snow, or snow pellets, is precipitation that forms when supercooled water droplets in air are collected and freeze on falling snowflakes, forming 2–5 mm (0.08–0.20 in) balls of crisp, opaque rime.

Ice fog is a type of fog consisting of fine ice crystals suspended in the air. It occurs only in cold areas of the world, as water droplets suspended in the air can remain liquid down to −40 °C (−40 °F). It should be distinguished from diamond dust, a precipitation of sparse ice crystals falling from a clear sky.
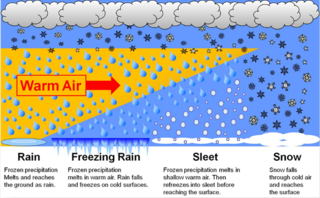
In meteorology, the different types of precipitation often include the character, formation, or phase of the precipitation which is falling to ground level. There are three distinct ways that precipitation can occur. Convective precipitation is generally more intense, and of shorter duration, than stratiform precipitation. Orographic precipitation occurs when moist air is forced upwards over rising terrain and condenses on the slope, such as a mountain.

Airport weather stations are automated sensor suites which are designed to serve aviation and meteorological operations, weather forecasting and climatology. Automated airport weather stations have become part of the backbone of weather observing in the United States and Canada and are becoming increasingly more prevalent worldwide due to their efficiency and cost-savings.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the field of Meteorology.

A snowflake is a single ice crystal that has achieved a sufficient size, and may have amalgamated with others, which falls through the Earth's atmosphere as snow. Each flake nucleates around a tiny particle in supersaturated air masses by attracting supercooled cloud water droplets, which freeze and accrete in crystal form. Complex shapes emerge as the flake moves through differing temperature and humidity zones in the atmosphere, such that individual snowflakes differ in detail from one another, but may be categorized in eight broad classifications and at least 80 individual variants. The main constituent shapes for ice crystals, from which combinations may occur, are needle, column, plate, and rime. Snow appears white in color despite being made of clear ice. This is due to diffuse reflection of the whole spectrum of light by the small crystal facets of the snowflakes.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.