
A phosphodiesterase inhibitor is a drug that blocks one or more of the five subtypes of the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE), thereby preventing the inactivation of the intracellular second messengers, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) by the respective PDE subtype(s). The ubiquitous presence of this enzyme means that non-specific inhibitors have a wide range of actions, the actions in the heart, and lungs being some of the first to find a therapeutic use.

5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system.
Agmatine, also known as 4-aminobutyl-guanidine, is an aminoguanidine that was discovered in 1910 by Albrecht Kossel. Agmatine is a chemical substance which is naturally created from the amino acid arginine. Agmatine has been shown to exert modulatory action at multiple molecular targets, notably: neurotransmitter systems, ion channels, nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and polyamine metabolism and this provides bases for further research into potential applications.
The galanin receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor, or metabotropic receptor which binds galanin.

The human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M5, encoded by the CHRM5 gene, is a member of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily of integral membrane proteins. It is coupled to Gq protein. Binding of the endogenous ligand acetylcholine to the M5 receptor triggers a number of cellular responses such as adenylate cyclase inhibition, phosphoinositide degradation, and potassium channel modulation. Muscarinic receptors mediate many of the effects of acetylcholine in the central and peripheral nervous system. The clinical implications of this receptor have not been fully explored; however, stimulation of this receptor is known to effectively decrease cyclic AMP levels and downregulate the activity of protein kinase A (PKA).

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 2, is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor that in humans is encoded by the CHRM2 gene. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, also known as cholinergic/acetylcholine receptor M3, or the muscarinic 3, is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor encoded by the human gene CHRM3.

The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4, also known as the cholinergic receptor, muscarinic 4 (CHRM4), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CHRM4 gene.

The adenosine A2B receptor, also known as ADORA2B, is a G-protein coupled adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human adenosine A2b receptor gene which encodes it.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.

Dopamine receptor D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD3 gene.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 (mGluR2) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the GRM2 gene. mGluR2 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that couples with the Gi alpha subunit. The receptor functions as an autoreceptor for glutamate, that upon activation, inhibits the emptying of vesicular contents at the presynaptic terminal of glutamatergic neurons.
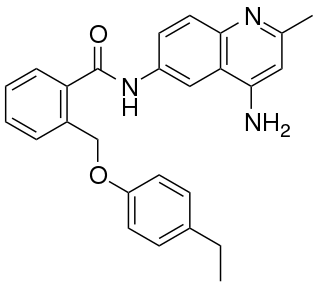
JTC-801 is an opioid analgesic drug used in scientific research.

Xanomeline is a small molecule muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist that was first synthesized in a collaboration between Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk as an investigational therapeutic being studied for the treatment of central nervous system disorders.

Vedaclidine (INN, codenamed LY-297,802, NNC 11-1053) is an experimental analgesic drug which acts as a mixed agonist–antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, being a potent and selective agonist for the M1 and M4 subtypes, yet an antagonist at the M2, M3 and M5 subtypes. It is orally active and an effective analgesic over 3× the potency of morphine, with side effects such as salivation and tremor only occurring at many times the effective analgesic dose. Human trials showed little potential for development of dependence or abuse, and research is continuing into possible clinical application in the treatment of neuropathic pain and cancer pain relief.

CDPPB is a drug used in scientific research which acts as a positive allosteric modulator selective for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. It has antipsychotic effects in animal models, and mGluR5 modulators are under investigation as potential drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia, as well as other applications.

L-741,626 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the dopamine receptor D2. It has good selectivity over the related D3 and D4 subtypes and other receptors. L-741,626 is used for laboratory research into brain function and has proved particularly useful for distinguishing D2 mediated responses from those produced by the closely related D3 subtype, and for studying the roles of these subtypes in the action of cocaine and amphetamines in the brain.
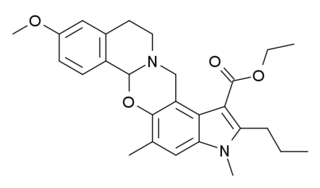
PD-0298029 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4. It was developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, but poor bioavailability and rapid metabolism in animal studies have meant its use is largely limited to in vitro research into the M4 and other muscarinic receptors.
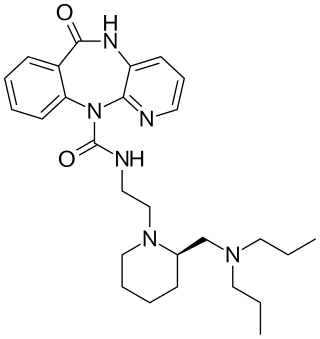
AFDX-384 (BIBN-161) is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, with selectivity for the M2 and M4 subtypes. It is used mainly for mapping the distribution of M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors in the brain, and studying their involvement in the development and treatment of dementia and schizophrenia.


















