Peroxidases or peroxide reductases (EC number 1.11.1.x) are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides.

Peroxidases or peroxide reductases (EC number 1.11.1.x) are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides.
Peroxidases typically catalyze a reaction of the form:
For many of these enzymes the optimal substrate is hydrogen peroxide, but others are more active with organic hydroperoxides such as lipid peroxides. Peroxidases can contain a heme cofactor in their active sites, or alternately redox-active cysteine or selenocysteine residues.
The nature of the electron donor is very dependent on the structure of the enzyme.
Protein families that serve as peroxidases include: [1]
The glutathione peroxidase family consists of 8 known human isoforms. Glutathione peroxidases use glutathione as an electron donor and are active with both hydrogen peroxide and organic hydroperoxide substrates. Gpx1, Gpx2, Gpx3, and Gpx4 have been shown to be selenium-containing enzymes, whereas Gpx6 is a selenoprotein in humans with cysteine-containing homologues in rodents.
Amyloid beta, when bound to heme, has been shown to have peroxidase activity. [2]
A typical group of peroxidases are the haloperoxidases. This group is able to form reactive halogen species and, as a result, natural organohalogen substances.
A majority of peroxidase protein sequences can be found in the PeroxiBase database.
While the exact mechanisms have yet to be determined, peroxidases are known to play a part in increasing a plant's defenses against pathogens. [3] Many members of the Solanaceae, notably Solanum melongena (eggplant/aubergine) and Capsicum chinense (the habanero/Scotch bonnet varieties of chili peppers) use Guaiacol and the enzyme guaiacol peroxidase as a defense against bacterial parasites such as Ralstonia solanacearum : the gene expression for this enzyme commences within minutes of bacterial attack. [4]
Peroxidase can be used for treatment of industrial waste waters. For example, phenols, which are important pollutants, can be removed by enzyme-catalyzed polymerization using horseradish peroxidase. Thus phenols are oxidized to phenoxy radicals, which participate in reactions where polymers and oligomers are produced that are less toxic than phenols. It also can be used to convert toxic materials into less harmful substances.
There are many investigations about the use of peroxidase in many manufacturing processes like adhesives, computer chips, car parts, and linings of drums and cans. Other studies have shown that peroxidases may be used successfully to polymerize anilines and phenols in organic solvent matrices. [5]
Peroxidases are sometimes used as histological markers. Cytochrome c peroxidase is used as a soluble, easily purified model for cytochrome c oxidase.
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants are frequently added to industrial products, such as polymers, fuels, and lubricants, to extend their usable lifetimes. Foods are also treated with antioxidants to forestall spoilage, in particular the rancidification of oils and fats. In cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, can prevent damage from oxidative stress.
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane.

The cytochrome complex, or cyt c, is a small hemeprotein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where it plays a critical role in cellular respiration. It transfers electrons between Complexes III and IV. Cytochrome c is highly water-soluble, unlike other cytochromes. It is capable of undergoing oxidation and reduction as its iron atom converts between the ferrous and ferric forms, but does not bind oxygen. It also plays a major role in cell apoptosis. In humans, cytochrome c is encoded by the CYCS gene.

A hemeprotein, or heme protein, is a protein that contains a heme prosthetic group. They are a very large class of metalloproteins. The heme group confers functionality, which can include oxygen carrying, oxygen reduction, electron transfer, and other processes. Heme is bound to the protein either covalently or noncovalently or both.

Heme, or haem, is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecular component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.

Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage. The biochemical function of glutathione peroxidase is to reduce lipid hydroperoxides to their corresponding alcohols and to reduce free hydrogen peroxide to water.

Cytochrome c peroxidase, or CCP, is a water-soluble heme-containing enzyme of the peroxidase family that takes reducing equivalents from cytochrome c and reduces hydrogen peroxide to water:

In biochemistry, ABTS is a chemical compound used to observe the reaction kinetics of specific enzymes. A common use for it is in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect the binding of molecules to each other.

The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.
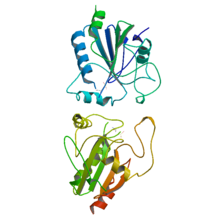
Ascorbate peroxidase (or L-ascorbate peroxidase, APX or APEX) (EC 1.11.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme horseradish peroxidase (HRP), found in the roots of horseradish, is used extensively in biochemistry applications. It is a metalloenzyme with many isoforms, of which the most studied type is C. It catalyzes the oxidation of various organic substrates by hydrogen peroxide.
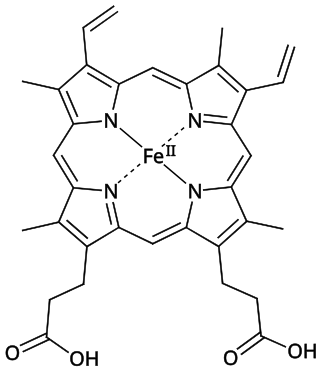
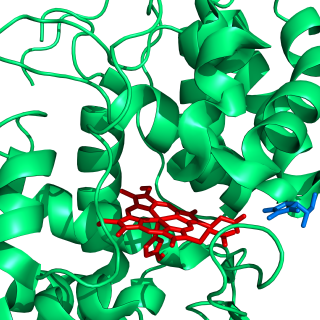
Heme B or haem B is the most abundant heme. Hemoglobin and myoglobin are examples of oxygen transport proteins that contain heme B. The peroxidase family of enzymes also contain heme B. The COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes (cyclooxygenase) of recent fame, also contain heme B at one of two active sites.

Nitric oxide dioxygenase (EC 1.14.12.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of nitric oxide (NO) to nitrate (NO−
3) . The net reaction for the reaction catalyzed by nitric oxide dioxygenase is shown below:
Chloride peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.10) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the chlorination of organic compounds. This enzyme combines the inorganic substrates chloride and hydrogen peroxide to produce the equivalent of Cl+, which replaces a proton in hydrocarbon substrate:
In enzymology, a manganese peroxidase (EC 1.11.1.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Haloperoxidases are peroxidases that are able to mediate the oxidation of halides by hydrogen peroxide. Both halides and hydrogen peroxide are widely available in the environment.
Haem peroxidases (or heme peroxidases) are haem-containing enzymes that use hydrogen peroxide as the electron acceptor to catalyse a number of oxidative reactions. Most haem peroxidases follow the reaction scheme:
Oxidation response is stimulated by a disturbance in the balance between the production of reactive oxygen species and antioxidant responses, known as oxidative stress. Active species of oxygen naturally occur in aerobic cells and have both intracellular and extracellular sources. These species, if not controlled, damage all components of the cell, including proteins, lipids and DNA. Hence cells need to maintain a strong defense against the damage. The following table gives an idea of the antioxidant defense system in bacterial system.

Eosinophil peroxidase is an enzyme found within the eosinophil granulocytes, innate immune cells of humans and mammals. This oxidoreductase protein is encoded by the gene EPX, expressed within these myeloid cells. EPO shares many similarities with its orthologous peroxidases, myeloperoxidase (MPO), lactoperoxidase (LPO), and thyroid peroxidase (TPO). The protein is concentrated in secretory granules within eosinophils. Eosinophil peroxidase is a heme peroxidase, its activities including the oxidation of halide ions to bacteriocidal reactive oxygen species, the cationic disruption of bacterial cell walls, and the post-translational modification of protein amino acid residues.

Bis(trifluoromethyl)peroxide (BTP) is a fluorocarbon derivative first produced by Frédéric Swarts. It has some utility as a radical initiator for polymerisation reactions. BTP is unusual in the fact that, unlike many peroxides, it is a gas, is non-explosive, and has good thermal stability.