Related Research Articles

Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.

Pimecrolimus is an immunomodulating agent of the calcineurin inhibitor class used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema). It is available as a topical cream, once marketed by Novartis under the trade name Elidel.
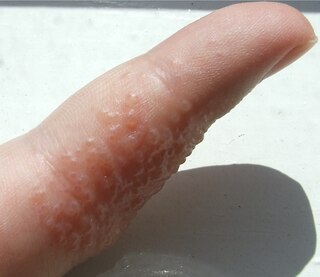
Dyshidrosis is a type of dermatitis that is characterized by itchy blisters on the palms of the hands and bottoms of the feet. Blisters are generally one to two millimeters in size and heal over three weeks. However, they often recur. Redness is not usually present. Repeated attacks may result in fissures and skin thickening.

Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare, inflammatory skin disease where painful pustules or nodules become ulcers that progressively grow. Pyoderma gangrenosum is not infectious.

Geographic tongue, also known by several other terms, is a condition of the mucous membrane of the tongue, usually on the dorsal surface. It is a common condition, affecting approximately 2–3% of the general population. It is characterized by areas of smooth, red depapillation which migrate over time. The name comes from the map-like appearance of the tongue, with the patches resembling the islands of an archipelago. The cause is unknown, but the condition is entirely benign, and there is no curative treatment. Uncommonly, geographic tongue may cause a burning sensation on the tongue, for which various treatments have been described with little formal evidence of efficacy.
Bromoderma is a skin condition characterized by an eruption of papules and pustules on the skin. It is caused by hypersensitivity to bromides, such as those found in certain drugs. There is at least one reported case of bromoderma caused by excessive consumption of a soft drink containing brominated vegetable oil.
A TNF inhibitor is a pharmaceutical drug that suppresses the physiologic response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF), which is part of the inflammatory response. TNF is involved in autoimmune and immune-mediated disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma, so TNF inhibitors may be used in their treatment. The important side effects of TNF inhibitors include lymphomas, infections, congestive heart failure, demyelinating disease, a lupus-like syndrome, induction of auto-antibodies, injection site reactions, and systemic side effects.

The term pustular psoriasis is used for a heterogeneous group of diseases that share pustular skin characteristics.

Neonatal acne, also known as acne neonatorum, is an acneiform eruption that occurs in newborns or infants within the first 4-6 weeks of life, and presents with open and closed comedones on the cheeks, chin and forehead.

Psoriatic onychodystrophy or psoriatic nails is a nail disease. It is common in those with psoriasis, with reported incidences varying from 10% to 78%. Elderly patients and those with psoriatic arthritis are more likely to have psoriatic nails.
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is an extremely rare type of psoriasis that can present in a variety of forms. Unlike the most general and common forms of psoriasis, GPP usually covers the entire body and with pus-filled blisters rather than plaques. GPP can present at any age, but is rarer in young children. It can appear with or without previous psoriasis conditions or history, and can reoccur in periodic episodes.

Pustulosis palmaris et plantaris is a chronic recurrent pustular dermatosis localized on the palms and soles only, characterized histologically by intraepidermal pustules filled with neutrophils. It can occur as part of the SAPHO syndrome.

Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare skin reaction that in 90% of cases is related to medication.
Adult-onset immunodeficiency syndrome is a type of immunodeficiency. It is linked to vulnerability to disseminated infections brought on by opportunistic pathogens. People with this condition have increased levels of anti-interferon-gamma autoantibodies. These particular immune system proteins mistakenly target an individual's own tissues. It is most commonly reported among previously healthy Southeast Asians. The average age of onset is between 30 and 50 years. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria, non-typhoidal salmonella, cytomegalovirus, Penicillium marneffei, and varicella zoster virus are some of the pathogens that can cause infections in patients with this illness. Symptoms vary depending on the infection(s) present in each individual.
Stasis papillomatosis is a disease characterized by chronic congestion of the extremities, with blood circulation interrupted in a specific area of the body. A consequence of this congestion and inflammation is long-term lymphatic obstruction. It is also typically characterized by the appearance of numerous papules. Injuries can range from small to large plates composed of brown or pink, smooth or hyperkeratotic papules. The most typical areas where injuries occur are the back of the feet, the toes, the legs, and the area around a venous ulcer formed in the extremities, although the latter is the rarest of all. These injuries include pachydermia, lymphedema, lymphomastic verrucosis and elephantosis verrucosa. The disease can be either localized or generalized; the localized form makes up 78% of cases. Treatment includes surgical and pharmaceutical intervention; indications for partial removal include advanced fibrotic lymphedema and elephantiasis. Despite the existence of these treatments, chronic venous edema, which is a derivation of stasis papillomatosis, is only partially reversible. The skin is also affected and its partial removal may mean that the skin and the subcutaneous tissue are excised. A side effect of the procedure is the destruction of existing cutaneous lymphatic vessels. It also risks papillomatosis, skin necrosis and edema exacerbation.
Interleukin 36, or IL-36, is a group of cytokines in the IL-1 family with pro-inflammatory effects. The role of IL-36 in inflammatory diseases is under investigation.
Risankizumab, sold under the brand name Skyrizi, is a humanized monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It is designed to target interleukin 23A (IL-23A). It is given by subcutaneous injection.
Spesolimab, sold under the brand name Spevigo, is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). It is an interleukin-36 receptor (IL-36R) antagonist. It is given via injection into a vein.
Joel M. Gelfand is an American dermatologist and epidemiologist at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He currently serves as the James J. Leyden Professor in Clinical Investigation, the Vice Chair of Clinical Research, the director of the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center, and the medical director of the Clinical Studies Unit in the Department of Dermatology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. He studies systemic comorbidities of psoriasis and much of his research has centered on the connection between cardiovascular disease and psoriasis.
References
- ↑ Varman, Katherine M.; Namias, Nicholas; Schulman, Carl I.; Pizano, Louis R. (2014-06-01). "Acute generalized pustular psoriasis, von Zumbusch type, treated in the burn unit. A review of clinical features and new therapeutics". Burns. 40 (4): e35–e39. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2014.01.003. ISSN 0305-4179. PMID 24491419.
- 1 2 3 4 Griffiths, C; Barker, Jonathan; Bleiker, Tanya; Chalmers, Robert; Creamer, Daniel (2016). Rook's textbook of dermatology. John Wiley & Sons Inc. ISBN 9781118441190. OCLC 949329582.
- ↑ Varman, Katherine M.; Namias, Nicholas; Schulman, Carl I.; Pizano, Louis R. (2014-06-01). "Acute generalized pustular psoriasis, von Zumbusch type, treated in the burn unit. A review of clinical features and new therapeutics". Burns: Journal of the International Society for Burn Injuries. 40 (4): e35–39. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2014.01.003. ISSN 1879-1409. PMID 24491419.
- ↑ Choon, Siew Eng; Lai, Nai Ming; Mohammad, Norshaleyna A.; Nanu, Nalini M.; Tey, Kwee Eng; Chew, Shang Fern (2014-06-01). "Clinical profile, morbidity, and outcome of adult-onset generalized pustular psoriasis: analysis of 102 cases seen in a tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia". International Journal of Dermatology. 53 (6): 676–684. doi:10.1111/ijd.12070. ISSN 1365-4632. PMID 23967807. S2CID 44470715.
- ↑ Robinson, Amanda; Van Voorhees, Abby S.; Hsu, Sylvia; Korman, Neil J.; Lebwohl, Mark G.; Bebo, Bruce F.; Kalb, Robert E. (2012-08-01). "Treatment of pustular psoriasis: from the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 67 (2): 279–288. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011.01.032. ISSN 1097-6787. PMID 22609220.
- ↑ Viguier, Manuelle; Aubin, François; Delaporte, Emmanuel; Pagès, Cécile; Paul, Carle; Beylot-Barry, Marie; Goujon, Catherine; Rybojad, Michel; Bachelez, Hervé (2012-12-01). "Efficacy and safety of tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in acute generalized pustular psoriasis". Archives of Dermatology. 148 (12): 1423–1425. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamadermatol.80 . ISSN 1538-3652. PMID 23247492.
- ↑ Zumbusch, Leo Ritter von (1909-02-01). "Psoriasis und pustulöses Exanthem". Archiv für Dermatologie und Syphilis (in German). 99 (1–2): 335–346. doi:10.1007/BF01910970. ISSN 0365-6020. S2CID 11086906.