
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride or vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C5H5)2. The molecule is a complex consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound to a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor, that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C5H5)+2. Ferrocene and the ferrocenium cation are sometimes abbreviated as Fc and Fc+ respectively.
Iron(III) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula FeCl3(H2O)x. Also called ferric chloride, these compounds are some of the most important and commonplace compounds of iron. They are available both in anhydrous and in hydrated forms which are both hygroscopic. They feature iron in its +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous derivative is a Lewis acid, while all forms are mild oxidizing agent. It is used as a water cleaner and as an etchant for metals.

Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.

Cobaltocene, known also as bis(cyclopentadienyl)cobalt(II) or even "bis Cp cobalt", is an organocobalt compound with the formula Co(C5H5)2. It is a dark purple solid that sublimes readily slightly above room temperature. Cobaltocene was discovered shortly after ferrocene, the first metallocene. Due to the ease with which it reacts with oxygen, the compound must be handled and stored using air-free techniques.

Vanadium(III) chloride describes the inorganic compound with the formula VCl3 and its hydrates. It forms a purple anhydrous form and a green hexahydrate [VCl2(H2O)4]Cl·2H2O. These hygroscopic salts are common precursors to other vanadium(III) complexes and is used as a mild reducing agent.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene, commonly abbreviated dppf, is an organophosphorus compound commonly used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is related to other bridged diphosphines such as 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe).

Sodium cyclopentadienide is an organosodium compound with the formula C5H5Na. The compound is often abbreviated as NaCp, where Cp− is the cyclopentadienide anion. Sodium cyclopentadienide is a colorless solid, although samples often are pink owing to traces of oxidized impurities.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. While iron adopts oxidation states from Fe(−II) through to Fe(VII), Fe(IV) is the highest established oxidation state for organoiron species. Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.

Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate is an organometallic compound with the formula [Fe(C5H5)2]BF4. This salt is composed of the cation [Fe(C5H5)2]+ and the tetrafluoroborate anion (BF−
4). The related hexafluorophosphate is also a popular reagent with similar properties. The ferrocenium cation is often abbreviated Fc+ or Cp2Fe+. The salt is deep blue in color and paramagnetic. Ferrocenium salts are sometimes used as one-electron oxidizing agents, and the reduced product, ferrocene, is inert and readily separated from ionic products. The ferrocene–ferrocenium couple is often used as a reference in electrochemistry. The standard potential of ferrocene-ferrocenium is dependent on specific electrochemical conditions.
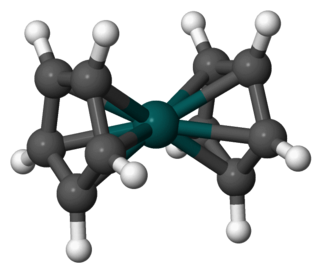
Rhodocene is a chemical compound with the formula [Rh(C5H5)2]. Each molecule contains an atom of rhodium bound between two planar aromatic systems of five carbon atoms known as cyclopentadienyl rings in a sandwich arrangement. It is an organometallic compound as it has (haptic) covalent rhodium–carbon bonds. The [Rh(C5H5)2] radical is found above 150 °C (302 °F) or when trapped by cooling to liquid nitrogen temperatures (−196 °C [−321 °F]). At room temperature, pairs of these radicals join via their cyclopentadienyl rings to form a dimer, a yellow solid.

Decamethylferrocene or bis(pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)iron(II) is a chemical compound with formula Fe(C5(CH3)5)2 or C20H30Fe. It is a sandwich compound, whose molecule has an iron(II) cation Fe2+ attached by coordination bonds between two pentamethylcyclopentadienyl anions (Cp*−, (CH3)5C−5). It can also be viewed as a derivative of ferrocene, with a methyl group replacing each hydrogen atom of its cyclopentadienyl rings. The name and formula are often abbreviated to DmFc, Me10Fc or FeCp*2.

The cyclopropenium ion is the cation with the formula C
3H+
3. It has attracted attention as the smallest example of an aromatic cation. Its salts have been isolated, and many derivatives have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The cation and some simple derivatives have been identified in the atmosphere of the Saturnian moon Titan.
1,1'-Dilithioferrocene is the organoiron compound with the formula Fe(C5H4Li)2. It is exclusively generated and isolated as a solvate, using either ether or tertiary amine ligands bound to the lithium centers. Regardless of the solvate, dilithioferrocene is used commonly to prepare derivatives of ferrocene.

Bis(fulvalene)diiron is the organoiron complex with the formula (C5H4-C5H4)2Fe2. Structurally, the molecule consists of two ferrous centers sandwiched between fulvalene dianions. The compound is an orange solid with lower solubility in benzene than ferrocene. Its structure has been verified by X-ray crystallography. The compound has attracted some interest for its redox properties.

Ferrocenecarboxylic acid is the organoiron compound with the formula (C5H5)Fe(C5H4CO2H). It is the simplest carboxylic acid derivative of ferrocene. It can be prepared in two steps from ferrocene by acylation with a 2-chlorobenzoyl chloride followed by hydrolysis.
1,1'-Diaminoferrocene is the organoiron compound with the formula Fe(C5H4NH2)2. It is the simplest diamine derivative of ferrocene. It is a yellow, air-sensitive solid that is soluble in aqueous acid. The 1,1' part of its name refers to the location of the amine groups on separate rings. Compared to the parent ferrocene, the diamine is about 600 mV more reducing.

1,1'-Ferrocenediisocyanate (1,1'-diisocyanatoferrocene) is the organoiron compound with the formula Fe(C5H4NCO)2. It is the simplest diisocyanate derivative of ferrocene. It can be synthesized by the Curtius rearrangement of the diacyl azide, using several protocols starting from 1,1'-ferrocenedicarboxylic acid. The compound is useful as an intermediate in the synthesis of 1,1'-diaminoferrocene by hydrolysis of the isocyanates. Various poly(siloxane–urethane) crosslinked polymers can be formed by reaction with siloxane-diols. These compounds are of interest as electrochemically active polymers that might have good mechanical properties at low temperature.
A molecular electron-reservoir complex is one of a class of redox-active systems which can store and transfer electrons stoichiometrically or catalytically without decomposition. The concept of electron-reservoir complexes was introduced by the work of French chemist, Didier Astruc. From Astruc's discoveries, a whole family of thermally stable, neutral, 19-electron iron(I) organometallic complexes were isolated and characterized, and found to have applications in redox catalysis and electrocatalysis. The following page is a reflection of the prototypal electron-reservoir complexes discovered by Didier Astruc.















