
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious.

Formaldehyde ( for-MAL-di-hide, fər-) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the formula CH2O and structure H−CHO. The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below). It is stored as aqueous solutions (formalin), which consists mainly of the hydrate CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (R−CHO). It is produced commercially as a precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 2006, the global production rate of formaldehyde was estimated at 12 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Small amounts also occur naturally.

Ethyl carbamate (also called urethane) is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2OC(O)NH2. It is an ester of carbamic acid and a white solid. Despite its name, it is not a component of polyurethanes. Because it is a carcinogen, it is rarely used, but naturally forms in low quantities in many types of fermented foods and drinks.
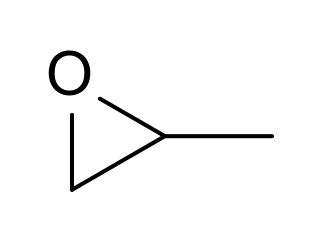
Propylene oxide is an acutely toxic and carcinogenic organic compound with the molecular formula CH3CHCH2O. This colourless volatile liquid with an odour similar to ether, is produced on a large scale industrially. Its major application is its use for the production of polyether polyols for use in making polyurethane plastics. It is a chiral epoxide, although it is commonly used as a racemic mixture.

A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings, and the three-ring compounds anthracene and phenanthrene. PAHs are uncharged, non-polar and planar. Many are colorless. Many of them are found in coal and in oil deposits, and are also produced by the incomplete combustion of organic matter—for example, in engines and incinerators or when biomass burns in forest fires.

Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP or B[a]P) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the result of incomplete combustion of organic matter at temperatures between 300 °C (572 °F) and 600 °C (1,112 °F). The ubiquitous compound can be found in coal tar, tobacco smoke and many foods, especially grilled meats. The substance with the formula C20H12 is one of the benzopyrenes, formed by a benzene ring fused to pyrene. Its diol epoxide metabolites (more commonly known as BPDE) react with and bind to DNA, resulting in mutations and eventually cancer. It is listed as a Group 1 carcinogen by the IARC. In the 18th century a scrotal cancer of chimney sweepers, the chimney sweeps' carcinoma, was already known to be connected to soot.

1,4-Dioxane is a heterocyclic organic compound, classified as an ether. It is a colorless liquid with a faint sweet odor similar to that of diethyl ether. The compound is often called simply dioxane because the other dioxane isomers are rarely encountered.
Substances, mixtures and exposure circumstances in this list have been classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as group 2B: The agent (mixture) is "possibly carcinogenic to humans". The exposure circumstance entails exposures that are possibly carcinogenic to humans. This category is used for agents, mixtures and exposure circumstances for which there is limited evidence of carcinogenicity in humans and less than sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. It may also be used when there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but there is sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. In some instances, an agent, mixture or exposure circumstance for which there is inadequate evidence of carcinogenicity in humans but limited evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals together with supporting evidence from other relevant data may be placed in this group. Further details can be found in the preamble to the IARC Monographs.

Toxaphene was an insecticide used primarily for cotton in the southern United States during the late 1960s and the 1970s. Toxaphene is a mixture of over 670 different chemicals and is produced by reacting chlorine gas with camphene. It can be most commonly found as a yellow to amber waxy solid.

In molecular genetics, a DNA adduct is a segment of DNA bound to a cancer-causing chemical. This process could lead to the development of cancerous cells, or carcinogenesis. DNA adducts in scientific experiments are used as biomarkers of exposure. They are especially useful in quantifying an organism's exposure to a carcinogen. The presence of such an adduct indicates prior exposure to a potential carcinogen, but it does not necessarily indicate the presence of cancer in the subject animal.
Uni-President Enterprises Corporation is an international food conglomerate based in Tainan, Taiwan. It is the largest food production company in Taiwan as well as Asia, and has a significant market share in dairy products, foods and snacks, and beverages. It is also responsible for running Starbucks, 7-Eleven, Mister Donut and Carrefour in Taiwan. In addition, Uni-President has subsidiaries in Mainland China, Vietnam, Thailand and the Philippines.

1,3-Dichloropropene, sold under diverse trade names, is an organochlorine compound. It is colorless liquid with a sweet smell. It dissolves in water and evaporates easily. It is used mainly in farming as a pesticide, specifically as a preplant fumigant and nematicide. It is widely used in the US and other countries, but is banned in 34 countries, including the European Union.

A food contaminant is a harmful chemical or microorganism present in food, which can cause illness to the consumer.

3-MCPD (3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol or 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol) is an organic chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH(OH)CH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid. It is a versatile multifunctional building block. The compound has attracted attention as the most common member of chemical food contaminants known as chloropropanols. It is suspected to be carcinogenic in humans.

1,2,3-Trichloropropane (TCP) is an organic compound with the formula CHCl(CH2Cl)2. It is a colorless liquid that is used as a solvent and in other specialty applications.

Tris(1,3-dichloroisopropyl)phosphate (TDCPP) is a chlorinated organophosphate. Organophosphate chemicals have a wide variety of applications and are used as flame retardants, pesticides, plasticizers, and nerve gases. TDCPP is structurally similar to several other organophosphate flame retardants, such as tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (TCEP) and tris(chloropropyl)phosphate (TCPP). TDCPP and these other chlorinated organophosphate flame retardants are all sometimes referred to as "chlorinated tris".

Lee Kum Kee Company Limited is a Hong Kong-based food company which specializes in manufacturing a wide range of Chinese and Asian sauces. Founded by Lee Kum Sheung in 1888 in Nanshui, Guangdong, Lee Kum Kee produces over 200 Chinese-style sauces, including oyster sauce, soy sauce, hoisin sauce, XO sauce, one-step recipe sauce, chili sauce, cooking ingredients, and dipping sauce. The group also purchased London's landmark Walkie-Talkie skyscraper in July 2017 for £1.3bn, which was a record-breaking transaction for a single building in the UK.

Oyster sauce describes a number of sauces made by cooking oysters. The most common in modern use is a viscous dark brown condiment made from oyster extracts, sugar, salt and water, thickened with corn starch.
Chloropropanols are chlorohydrins related to propanols containing chloride functional group. Eight isomers are possible. Two of these derivatives, 1,3-dichloropropanol (1,3-DCP) and 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol (3-MCPD), are carcinogenic contaminants in processed foods. Several isomers are encountered in industrial chemistry.
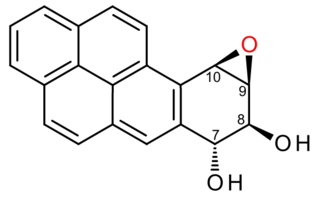
(+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide is an organic compound with molecular formula C20H14O3. It is a metabolite and derivative of benzo[a]pyrene (found in tobacco smoke) as a result of oxidation to include hydroxyl and epoxide functionalities. (+)-Benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-epoxide binds to the N2 atom of a guanine nucleobase in DNA, distorting the double helix structure by intercalation of the pyrene moiety between base pairs through π-stacking. The carcinogenic properties of tobacco smoking are attributed in part to this compound binding and inactivating the tumor suppression ability of certain genes, leading to genetic mutations and potentially to cancer.




















