In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula CnH2n−2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.
In organometallic chemistry, acetylide refers to chemical compounds with the chemical formulas MC≡CH and MC≡CM, where M is a metal. The term is used loosely and can refer to substituted acetylides having the general structure RC≡CM. Acetylides are reagents in organic synthesis. The calcium acetylide commonly called calcium carbide is a major compound of commerce.
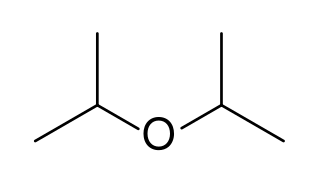
Diisopropyl ether is secondary ether that is used as a solvent. It is a colorless liquid that is slightly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. It is used as an extractant and an oxygenate gasoline additive. It is obtained industrially as a byproduct in the production of isopropanol by hydration of propylene. Diisopropyl ether is sometimes represented by the abbreviation DIPE.

The Knorr pyrrole synthesis is a widely used chemical reaction that synthesizes substituted pyrroles (3). The method involves the reaction of an α-amino-ketone (1) and a compound containing an electron-withdrawing group α to a carbonyl group (2).
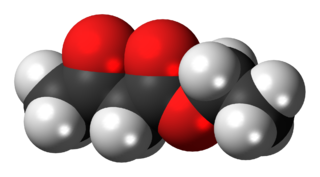
The organic compound ethyl acetoacetate (EAA) is the ethyl ester of acetoacetic acid. It is a colorless liquid. It is widely used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a wide variety of compounds. It is used as a flavoring for food.

tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CLi. As an organolithium compound, it has applications in organic synthesis since it is a strong base, capable of deprotonating many carbon molecules, including benzene. tert-Butyllithium is available commercially as hydrocarbon solutions; it is not usually prepared in the laboratory.

A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.
Chloramines refer to derivatives of ammonia and organic amines wherein one or more N-H bonds have been replaced by N-Cl bonds. Two classes of compounds are considered: inorganic chloramines and organic chloramines.

Organocopper chemistry is the study of the physical properties, reactions, and synthesis of organocopper compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to copper chemical bond. They are reagents in organic chemistry.

sec-Butyllithium is an organometallic compound with the formula CH3CHLiCH2CH3, abbreviated sec-BuLi or s-BuLi. This chiral organolithium reagent is used as a source of sec-butyl carbanion in organic synthesis.
The Glaser coupling is a type of coupling reaction. It is by far the oldest acetylenic coupling and is based on cuprous salts like copper(I) chloride or copper(I) bromide and an additional oxidant like oxygen. The base in its original scope is ammonia. The solvent is water or an alcohol. The reaction was first reported by Carl Andreas Glaser in 1869. He suggested the following process for his way to diphenylbutadiyne:

Catecholborane (abbreviated HBcat) is an organoboron compound that is useful in organic synthesis. This colourless liquid is a derivative of catechol and a borane, having the formula C6H4O2BH.
Organotellurium chemistry describes the synthesis and properties of organotellurium compounds, chemical compounds containing a carbon-tellurium chemical bond. Organotellurium chemistry is a lightly studied area, in part because of it having few applications.

Disiamylborane is an organoborane used in organic synthesis. It is used for hydroboration–oxidation reactions of terminal alkynes, giving aldehydes via anti-Markovnikov hydration followed by tautomerization. Disiamylborane is relatively selective for terminal alkynes and alkenes vs internal alkynes and alkenes. Disiamylborane is prepared by hydroboration of trimethylethylene with diborane. The reaction stops at the secondary borane due to steric hindrance.
In organic chemistry, alkynylation is an addition reaction in which a terminal alkyne is added to a carbonyl group to form an α-alkynyl alcohol.

Vinyllithium is an organolithium compound with the formula LiC2H3. A colorless or white solid, it is encountered mainly as a solution in tetrahydrofuran (THF). It is a reagent in synthesis of organic compounds, especially for vinylations.
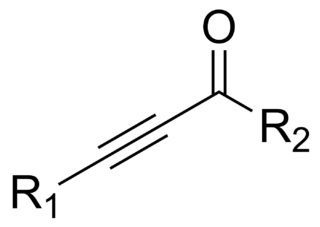
In organic chemistry, an ynone is an organic compound containing a ketone functional group and a C≡C triple bond. Many ynones are α,β-ynones, where the carbonyl and alkyne groups are conjugated. Capillin is a naturally occurring example. Some ynones are not conjugated.

Diethyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2P(O)H. It is a popular reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. Diethyl phosphite is a colorless liquid. The molecule is tetrahedral.
In organometallic chemistry, metal–halogen exchange is a fundamental reaction that converts an organic halide into an organometallic product. The reaction commonly involves the use of electropositive metals and organochlorides, bromides, and iodides. Particularly well-developed is the use of metal–halogen exchange for the preparation of organolithium compounds.