Aromatic compounds or arenes usually refers to organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties:

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.

Phenol is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group bonded to a hydroxy group. Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.

In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. A phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, the phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring.

Peroxidases or peroxide reductases are a large group of enzymes which play a role in various biological processes. They are named after the fact that they commonly break up peroxides.

In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon.

Sphingobium species are different from other sphingomonads in that they are commonly isolated from soil; They can degrade a variety of chemicals in the environment such as aromatic and chloroaromatic compounds, phenols like nonylphenol and pentachlorophenol, herbicides such as (RS)-2-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy) propionic acid and hexachlorocyclohexane, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.

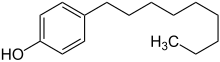
Nonylphenols are a family of closely related organic compounds composed of phenol bearing a 9 carbon-tail. Nonylphenols can come in numerous structures, all of which may be considered alkylphenols. They are used in manufacturing antioxidants, lubricating oil additives, laundry and dish detergents, emulsifiers, and solubilizers. They are used extensively in epoxy formulation in North America but its use has been phased out in Europe. These compounds are also precursors to the commercially important non-ionic surfactants alkylphenol ethoxylates and nonylphenol ethoxylates, which are used in detergents, paints, pesticides, personal care products, and plastics. Nonylphenol has attracted attention due to its prevalence in the environment and its potential role as an endocrine disruptor and xenoestrogen, due to its ability to act with estrogen-like activity. The estrogenicity and biodegradation heavily depends on the branching of the nonyl sidechain. Nonylphenol has been found to act as an agonist of the GPER (GPR30).
In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.
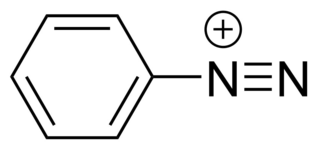
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group [R−N+≡N]X− where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.

The Reimer–Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction used for the ortho-formylation of phenols. with the simplest example being the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde. The reaction was first reported by Karl Reimer and Ferdinand Tiemann.

Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols. An exception is the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom.
The suffix –ol is used in organic chemistry principally to form names of organic compounds containing the hydroxyl (–OH) group, mainly alcohols. The suffix was extracted from the word alcohol.

The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.

In organic chemistry, alkyl nitrites are a group of organic compounds based upon the molecular structure R−O−N=O, where R represents an alkyl group. Formally they are alkyl esters of nitrous acid. They are distinct from nitro compounds.
The molecular formula C15H24O may refer to:

NP-40 is a commercially available detergent with CAS Registry Number 9016-45-9. NP-40 is an ethoxylated nonylphenol for non-ionic surfactants and can act as emulsifier and demulsifier agent.
Nonoxynols also known as nonaethylene glycol or polyethylene glycol nonyl phenyl ether are mixtures of nonionic surfactants used as detergents, emulsifiers, wetting agents or defoaming agents. The most commonly discussed compound nonoxynol-9 is a spermicide, formulated primarily as a component of vaginal foams and creams. Nonoxynol was found to metabolize into free nonylphenol when administered to lab animals. Arkopal-N60, with on average 6 ethylene glycol units is a related used surfactant.

Alkylphenols are a family of organic compounds obtained by the alkylation of phenols. The term is usually reserved for commercially important propylphenol, butylphenol, amylphenol, heptylphenol, octylphenol, nonylphenol, dodecylphenol and related "long chain alkylphenols" (LCAPs). Methylphenols and ethylphenols are also alkylphenols, but they are more commonly referred to by their specific names, cresols and xylenols.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.