| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1368 History of France • Timeline • Years | ||||
This article lists events related to France in the year 1368.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1368 History of France • Timeline • Years | ||||
This article lists events related to France in the year 1368.


Charles IV, also known as Charles of Luxembourg, born Wenceslaus, was the first King of Bohemia to become Holy Roman Emperor. He was a member of the House of Luxembourg from his father's side and the Bohemian House of Přemyslid from his mother's side; he emphasized the latter due to his lifelong affinity for the Bohemian side of his inheritance, and also because his direct ancestors in the Přemyslid line included two saints.
Year 1368 (MCCCLXVIII) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar.

Joan of Navarre, also known as Joanna was Duchess of Brittany by marriage to Duke John IV and later Queen of England as the second wife of King Henry IV. She served as regent of Brittany from 1399 until 1403 during the minority of her son. She also served as regent of England during the absence of her stepson Henry V in 1415. Four years later he imprisoned her and confiscated her money and land. Joan was released in 1422, shortly before Henry V's death.

Charles VI, nicknamed the Beloved and later the Mad, was King of France from 1380 until his death in 1422. He is known for his mental illness and psychotic episodes that plagued him throughout his life.

Charles V, called the Wise, was King of France from 1364 to his death in 1380. His reign marked an early high point for France during the Hundred Years' War, with his armies recovering much of the territory held by the English, and successfully reversed the military losses of his predecessors.

Lionel of Antwerp, Duke of Clarence, was the third son, but the second son to survive infancy, of the English king Edward III and Philippa of Hainault. He was named after his birthplace, at Antwerp in the Duchy of Brabant. Lionel was a grandson of William I, Count of Hainaut. He grew to be nearly seven feet (210 cm) in height and had an athletic build.

Philip III was Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonged. During his reign, the Burgundian State reached the apex of its prosperity and prestige, and became a leading centre of the arts.

Charles of Blois-Châtillon, nicknamed "the Saint", was the legalist Duke of Brittany from 1341 until his death, via his marriage to Joan, Duchess of Brittany and Countess of Penthièvre, holding the title against the claims of John of Montfort. The cause of his possible canonization was the subject of a good deal of political maneuvering on the part of his cousin, Charles V of France, who endorsed it, and his rival, Montfort, who opposed it. The cause fell dormant after Pope Gregory XI left Avignon in 1376, but was revived in 1894. Charles of Blois was beatified in 1904.

The Count of Valentinois was originally the official in charge of the region (county) around Valence. It evolved in a hereditary title of nobility, still indicating control of the Valentinois and often of the Diois. The title later became the Duke of Valentinois.
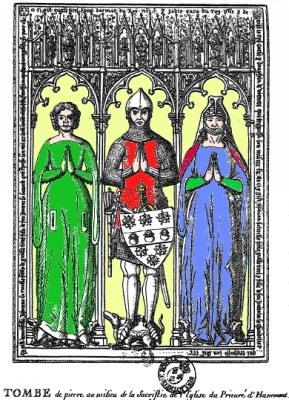
Guillaume Tirel, known as Taillevent, was an important figure in the early history of French cuisine. He was cook to the Court of France at the time of the first Valois kings and the Hundred Years' War. His first position was enfant de cuisine to Queen Jeanne d'Évreux. From 1326 he was queux, head chef, to Philip VI. In 1347, he became squire to the Dauphin de Viennois and his queux in 1349. In 1355 he became squire to the Duke of Normandy, in 1359 his queux and in 1361 his serjeant-at-arms. The Duke of Normandy became Charles V in 1368 and Tirel continued in his service. From 1381 he was in service to Charles VI. Guillaume Tirel is generally considered one of the first truly "professional" master chefs. He died in 1395 at around 80 years of age.

Charles I d'Albret was the Lord of Albret and the Constable of France from 1402 until 1411, and again from 1413 until 1415. He was also the co-commander of the French army at the Battle of Agincourt where he was killed by the English forces led by King Henry V.
The former French diocese of Thérouanne controlled a large part of the left bank of the river Scheldt during the Middle Ages. Territorially it was part of the county of Artois which belonged to the county of Flanders.
Events from the 1420s in England.

Catherine of France was a princess of France as the daughter of Charles V, King of France, and became the Countess of Montpensier as the wife of John of Berry, Count of Montpensier.

Robert of Geneva was elected to the papacy as Clement VII by the cardinals who opposed Pope Urban VI and was the first antipope residing in Avignon, France. His election led to the Western Schism.
Events from the year 1422 in France

Count of Diois is a title of nobility, originally in French peerage. It was created in 1350 inside Dauphine of Viennois Patrimony by Philip VI of France when Humbert II of Viennois sold his lands and titles to King Philip VI of France. All patrimony of Dauphine consisted in: Count of Albon, Grésivaudan, Briançonnais, Grenoble, Oisans, Briançon, Embrun and Gaph, Baron de La Tour du Pin, Dauphin of Viennois, count of Valentinois, and given to Cesar Borgia join to Duke of Valentinois by Louis XII of France.
Events from the year 1415 in France.
The Duchy of Pomerania-Neustettin, also known as the Duchy of Neustettin, and the Duchy of Szczecinek, was a feudal duchy of the Holy Roman Empire located in Middle Pomerania. It existed between 1372 and 1478. Its capital was Szczecinek. It was formed from the part of the territories Pomerania-Wolgast on 8 June 1368 and existed until 1390 when it was incorporated back into Pomerania-Wolgast. Its only ruler was Duke Wartislaw V of the House of Griffins.