Related Research Articles

The Battle of Mactan was fought on a beach in Mactan Island between Spanish forces led by the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan along with local allies, and Lapulapu, the chieftain of the island, on the early morning hours of April 27, 1521. Magellan, a Portuguese-born commander serving the Spanish Empire who led an expedition that ultimately circumnavigated the world for the first time, commanded a small Spanish contingent in an effort to subdue Mactan led by Lapulapu under the Spanish crown. The sheer number of Lapulapu's forces, compounded with issues on the location and armor, ultimately resulted in a disastrous defeat to the Europeans and the death of Magellan. Surviving members of Magellan's crew continued the expedition under the command of Juan Sebastian de Elcano, who completed the journey in September 1522.

Lapulapu or Lapu-Lapu, whose name was first recorded as Çilapulapu, was a datu (chief) of Mactan, an island now part of the Philippines. Lapulapu is known for the 1521 Battle of Mactan, where he and his men defeated Spanish forces led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan and his native allies Rajah Humabon and Datu Zula. Magellan's death in battle ended his voyage of circumnavigation and delayed the Spanish occupation of the islands by over forty years until the expedition of Miguel López de Legazpi in 1564.

Conquistadors or conquistadores was a term used to refer to Spanish and Portuguese colonialists of the early modern period. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond the Iberian Peninsula to the Americas, Oceania, Africa and Asia, establishing new colonies and trade routes. They brought much of the "New World" under the dominion of Spain and Portugal.
Ruy López de Villalobos was a Spanish explorer who led a failed attempt to colonize the Philippines in 1544, attempting to assert Spanish control there under the terms of the treaties of Tordesillas and Zaragoza. Unable to feed his men through barter, raiding, or farming and unable to request resupply from Mexico due to poor knowledge of the Pacific's winds and currents, Villalobos abandoned his mission and fled to the Portuguese-held Moluccas, where he died in prison. He is chiefly remembered for some sources crediting him with naming Leyte the "Philippine Island" in honor of the Spanish crown prince Philip. The name was later extended across the entire Philippine Archipelago and its nation.

Samar is the third-largest and seventh-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total population of 1,909,537 as of the 2020 census. It is located in the eastern Visayas, which are in the central Philippines. The island is divided into three provinces: Samar, Northern Samar, and Eastern Samar. These three provinces, along with the provinces on the nearby islands of Leyte and Biliran, are part of the Eastern Visayas region.

Duarte Barbosa was a Portuguese writer and officer from Portuguese India. He was a scrivener in a feitoria in Kochi, and an interpreter of the local language, Malayalam. Barbosa wrote the Book of Duarte Barbosa c. 1516, making it one of the earliest examples of Portuguese travel literature.

Magellan's Cross Pavilion is a stone kiosk in Cebu City, Philippines. The structure is situated on Plaza Sugbo beside the Basilica del Santo Niño It houses a Christian cross that was planted by explorers of the Spanish expedition of the first circumnavigation of the world, led by Ferdinand Magellan, upon arriving in Cebu in the Philippines on April 21, 1521.

João Rodrigues Serrão, also known as Juan Rodríguez Serrano, was a Portuguese and Spanish pilot and explorer. He served in the Portuguese India Armadas that secured control of the Indian Ocean and the Strait of Malacca for the Portuguese but is most well known for his participation in Ferdinand Magellan's 1519–1521 expedition to the Spice Islands for Charles I of Spain, which discovered a path around South America to the Pacific and initiated Spanish involvement in the Philippines. Serrão and Duarte Barbosa became leaders of the expedition after Magellan's death at the Battle of Mactan but did not live to complete the circumnavigation with Elcano. They were both killed shortly thereafter during a massacre of the Spanish by their supposed convert and ally Humabon, raja of Cebu.

Francisco Serrão was a Portuguese explorer and a possible cousin of Ferdinand Magellan. His 1512 voyage was the first known European sailing east past Malacca through modern Indonesia and the East Indies. He became a confidant of Sultan Bayan Sirrullah, the ruler of Ternate, becoming his personal advisor. He remained in Ternate where he died around the same time Magellan died.

The Legazpi-Sikatuna Blood Compact or Sandugo was a blood compact, performed in the island of Bohol in the Philippines, between the Spanish explorer Miguel López de Legazpi and Datu Sikatuna, chieftain of Bohol, on March 16, 1565, to seal their friendship following tribal tradition. This is considered the first treaty of friendship between the Spaniards and Filipinos. "Sandugo" is a Visayan word which means "one blood".

The Magellan expedition, sometimes termed the Magellan–Elcano expedition, was a 16th-century Spanish expedition planned and led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan. One of the most important voyages in the Age of Discovery—and in the history of exploration—its purpose was to cross the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans to open a trade route with the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, in present-day Indonesia. The expedition departed Spain in 1519 and returned there in 1522 led by Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, who crossed the Indian Ocean after Magellan's death in the Philippines. Totaling 60,440 km, or 37,560 mi, the nearly three-year voyage achieved the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. It also revealed the vast scale of the Pacific Ocean and proved that ships could sail around the world on a western sea route.

Ferdinand Magellan was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies, which achieved the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. During the expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fleet to pass from the Atlantic into the Pacific Ocean and perform the first European navigation to Asia via the Pacific. Magellan died in the Philippines during his voyage, and his crew completed the return trip to Spain in 1522.

The Treaty of Zaragoza or Saragossa, also called the Capitulation of Zaragoza or Saragossa, was a peace treaty between Castile and Portugal, signed on 22 April 1529 by King John III of Portugal and the Habsburg emperor Charles V in the Aragonese city of Zaragoza. The treaty defined the areas of Castilian and Portuguese influence in Asia in order to resolve the "Moluccas issue", which had arisen because both kingdoms claimed the lucrative Spice Islands for themselves, asserting that they were within their area of influence as specified in 1494 by the Treaty of Tordesillas. The conflict began in 1520, when expeditions from both kingdoms reached the Pacific Ocean, because no agreed meridian of longitude had been established in the far east.
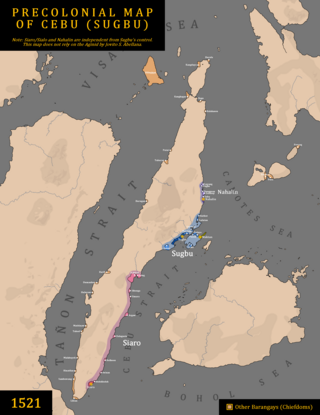
The Rajahnate of Cebu or Cebu also called as Sugbu, was an Indianized Raja monarchy Mandala (Polity) on the island of Cebu in the Philippines prior to the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors. It is known in ancient Chinese records as the nation of Sokbu (束務). According to Visayan oral legend, it was founded by Sri Lumay or Rajamuda Lumaya, a minor prince of the Tamil Chola dynasty. He was sent by the Chola emperor from southern India to establish a base for expeditionary forces, but he rebelled and established his own independent polity. The capital of the nation was Singhapala (சிங்கப்பூர்) which is Tamil-Sanskrit for "Lion City", the same rootwords with the modern city-state of Singapore.
Early Polynesian explorers reached nearly all Pacific islands by 1200 CE, followed by Asian navigation in Southeast Asia and the West Pacific. During the Middle Ages, Muslim traders linked the Middle East and East Africa to the Asian Pacific coasts, reaching southern China and much of the Malay Archipelago. Direct European contact with the Pacific began in 1512, with the Portuguese encountering its western edges, soon followed by the Spanish arriving from the American coast.

The Magellan expedition was the first voyage around the world in human history. It was a Spanish expedition that sailed from Seville in 1519 under the initial command of Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese sailor, and completed in 1522 by Spanish Basque navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano.

The first documented Catholic Mass in the Philippines was held on March 31, 1521, Easter Sunday. It was conducted by Father Pedro de Valderrama of Ferdinand Magellan's expedition along the shores of what was referred to in the journals of Antonio Pigafetta as "Mazaua".
Transpacific crossings are voyages of passengers and cargo across the Pacific Ocean between Asia, Oceania, and the Americas. Transpacific voyages frequently cross the International Date Line. The first recorded crossing of the Pacific was a Spanish expedition led by the Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan of 1521. Commercial transpacific flights have been available since 1935.

Elcano & Magellan: The First Voyage Around the World is a 2019 Spanish animated adventure film directed by Ángel Alonso and written by José Antonio Vitoria and Garbiñe Losana. The film retells the story of 1519 circumnavigation led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan and Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano.

The Blockade of Cebu was a failed Portuguese naval action against the Spanish colony in the present-day city of Cebu, Philippines in 1568. The Portuguese fleet under captain-general Gonzalo Pereira blockaded Cebu in an effort to starve and expel the Spanish. However, the Spanish colony proved to be resistant to the blockade and the Portuguese fleet eventually suffered from typhoid fever. Pereira then decided to lift the blockade and sail the fleet to the Maluku Islands.
References
- ↑ Grun, Bernard (1991). The Timetables of History (3rd ed.). New York: Simon & Schuster. p. 233. ISBN 0-671-74919-6.