
Herman Boerhaave was a Dutch botanist, chemist, Christian humanist, and physician of European fame. He is regarded as the founder of clinical teaching and of the modern academic hospital and is sometimes referred to as "the father of physiology," along with Venetian physician Santorio Santorio (1561–1636). Boerhaave introduced the quantitative approach into medicine, along with his pupil Albrecht von Haller (1708–1777) and is best known for demonstrating the relation of symptoms to lesions. He was the first to isolate the chemical urea from urine. He was the first physician to put thermometer measurements to clinical practice. His motto was Simplex sigillum veri: 'Simplicity is the sign of the truth'. He is often hailed as the "Dutch Hippocrates".

John Ray FRS was a Christian English naturalist widely regarded as one of the earliest of the English parson-naturalists. Until 1670, he wrote his name as John Wray. From then on, he used 'Ray', after "having ascertained that such had been the practice of his family before him". He published important works on botany, zoology, and natural theology. His classification of plants in his Historia Plantarum, was an important step towards modern taxonomy. Ray rejected the system of dichotomous division by which species were classified by repeated sub-division into groups according to a pre-conceived series of characteristics they have or have not, and instead classified plants according to similarities and differences that emerged from observation. He was among the first to attempt a biological definition for the concept of species, as "a group of morphologically similar organisms arising from a common ancestor". Another significant contribution to taxonomy was his division of plants into those with two seedling leaves (dicotyledons) or only one (monocotyledons), a division used in taxonomy today.

Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble carbonate rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by features like poljes above and drainage systems with sinkholes and caves underground. More weathering-resistant rocks, such as quartzite, can also occur, given the right conditions.

1665 (MDCLXV) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 1665th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 665th year of the 2nd millennium, the 65th year of the 17th century, and the 6th year of the 1660s decade. As of the start of 1665, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

Magnolia is a large genus of about 210 to 340 flowering plant species in the subfamily Magnolioideae of the family Magnoliaceae. The natural range of Magnolia species is disjunct, with a main center in east and southeast Asia and a secondary center in eastern North America, Central America, the West Indies, and some species in South America.

Family is one of the nine major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family".

Sir Hans Sloane, 1st Baronet, was an Anglo-Irish physician, naturalist, and collector, with a collection of 71,000 items which he bequeathed to the British nation, thus providing the foundation of the British Museum, the British Library, and the Natural History Museum, London. He was elected to the Royal Society at the age of 24. Sloane travelled to the Caribbean in 1687 and documented his travels and findings with extensive publications years later. Sloane was a renowned medical doctor among the aristocracy, and was elected to the Royal College of Physicians at age 27. Though he is credited with the invention of chocolate milk, it is more likely that he learned the practice of adding milk to drinking chocolate while living and working in Jamaica. Streets and places were later named after him, including Hans Place, Hans Crescent, and Sloane Square in and around Chelsea, London – the area of his final residence – and also Sir Hans Sloane Square in Killyleagh, his birthplace in Ulster.

Johann Weikhard Freiherr von Valvasor or Johann Weichard Freiherr von Valvasor or simply Valvasor was a natural historian and polymath from Carniola, present-day Slovenia, and a fellow of the Royal Society in London.
The year 1738 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1729 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1715 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1703 in science and technology involved some significant events.

The year 1672 in science and technology involved some significant events.

Giovanni Antonio Scopoli was an Italian physician and naturalist. His biographer Otto Guglia named him the "first anational European" and the "Linnaeus of the Austrian Empire".

Pierre Magnol was a French botanist. He was born in the city of Montpellier, where he lived and worked for most of his life. He became Professor of Botany and Director of the Royal Botanic Garden of Montpellier and held a seat in the Académie Royale des Sciences de Paris for a short while. He was one of the innovators who devised the botanical scheme of classification. He was the first to publish the concept of plant families as they are understood today, a natural classification of groups of plants that have features in common.

Lake Cerknica is an intermittent lake in the southern part of the Cerknica Polje, a karst polje in Inner Carniola, a region in southwestern Slovenia. The lake, oriented in the Dinaric direction from northwest to southeast, is present for the most part of the year. When full, it is the largest lake in the country. The plain is surrounded by the Javornik Hills to the south and Slivnica to the north, both belonging to Dinaric Alps. The area of the lake mainly reaches 28 square kilometres (11 sq mi), but can reach up to 38 km2 (15 sq mi) and the surface level varies from 546 m (1,791 ft) to 551 m (1,808 ft) above sea level. The lake is an important wildlife resort, especially as a nesting place for many bird species. Botanically, it is distinguished by amphibious plants. It is therefore a part of two Natura 2000 areas of protection and the focus of the Inner Carniola Regional Park, which covers additional Natura 2000 areas in the broader region. The climate in the area is continental, with a mean temperature of 9.2 °C (48.6 °F) and the annual precipitation about 1,700 millimetres (67 in). The largest settlement at the border of the lake is Cerknica, located north of the lake. Various watersports, including rowing, are popular on the lake.
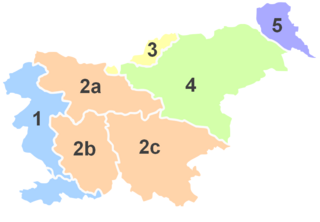
Inner Carniola is a traditional region of Slovenia, the southwestern part of the larger Carniola region. It comprises the Hrušica karst plateau up to Postojna Gate, bordering the Slovenian Littoral in the west. Its administrative and economic center of the region is Postojna, and other minor centers include Vrhnika, Logatec, Cerknica, Pivka, and Ilirska Bistrica.
James Jurin FRS FRCP was an English scientist and physician, particularly remembered for his early work in capillary action and in the epidemiology of smallpox vaccination. He was a staunch proponent of the work of Sir Isaac Newton and often used his gift for satire in Newton's defence.
Antoine Magnol was a French physician and botanist born in Montpellier. He was the son of the notable botanist Pierre Magnol (1638–1715).
Sir Tancred Robinson was an English physician, known also as a naturalist.













