Contents
| 1866 in Brazil |
|---|
| Flag |
 19 stars (1823–70) |
| Timeline of Brazilian history |
| Empire of Brazil |
| Year of Constitution: 1824 |
Events in the year 1866 in Brazil .
| 1866 in Brazil |
|---|
| Flag |
 19 stars (1823–70) |
| Timeline of Brazilian history |
| Empire of Brazil |
| Year of Constitution: 1824 |
Events in the year 1866 in Brazil .

The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadliest and bloodiest inter-state war in Latin American history. Paraguay sustained large casualties, but even the approximate numbers are disputed. Paraguay was forced to cede disputed territory to Argentina and Brazil. The war began in late 1864, as a result of a conflict between Paraguay and Brazil caused by the Uruguayan War. Argentina and Uruguay entered the war against Paraguay in 1865, and it then became known as the "War of the Triple Alliance."

The Battle of Curupayty was a key battle in the Paraguayan War. On the morning on 22 September 1866, the joint force of Brazilian, Argentine, and Uruguayan armies attacked Paraguayan fortified trenches on Curupayty. The Paraguayans were led by general José Eduvigis Díaz. This position was held by 5,000 men and 49 cannons, some of them in hidden places out of the attackers view. The Imperial Brazilian Navy gave support to the 20,000 assailants, but the ships had to keep some distance from the guns at the fortress of Humaitá, which led to the lack of accuracy and impact of the ship's fire. The navy's failure was crucial at the later ground battle result.

The Battle of Tuyutí was a Paraguayan offensive in the Paraguayan War targeting the Triple Alliance encampment of Tuyutí. It is considered to be the bloodiest battle ever in South America. The result of the battle was an Allied victory, which added to the Paraguayan troubles after the loss of its fleet in the Battle of Riachuelo.

Admiral Joaquim Marques Lisboa, Marquis of Tamandaré was a Brazilian admiral of the Imperial Navy of Brazil. He dedicated his life to the Brazilian Navy, including a life-long membership in Brazil's Military and Justice Council, then Supreme Military Court, from its inception until 1891, when the Republican Government granted him leave.

The military history of Brazil comprises centuries of armed actions in the territory encompassing modern Brazil, and the role of the Brazilian Armed Forces in conflicts and peacekeeping worldwide. For several hundreds of years, the area was the site of intertribal wars of indigenous peoples. Beginning in the 16th century, the arrival of Portuguese explorers led to conflicts with the indigenous peoples; a notable example being the revolt of the Tamoio Confederation. Sporadic revolts of African slaves also marked the colonial period, with a notable rebellion led by Zumbi dos Palmares. Conflicts were fought with other European nations as well – two notable examples being the France Antarctique affair, and a conflict with the Netherlands in the early 17th century over control of much of Northeastern Brazil. Although Portugal retained its possessions during conflicts with other nations, it lost control of the colony after the Brazilian war of Independence, which led to the establishment of the Empire of Brazil.

The Battle of Cerro Corá was the last battle of the Paraguayan War, fought on 1 March 1870, in the vicinity of Cerro Corá, 454 kilometres (280 mi) northeast of Paraguay's capital Asunción. It is known for being the battle in which Francisco Solano López, Paraguayan president, was killed at the hands of the Imperial Brazilian Army.

The Armed Forces of the Empire of Brazil were the overall unified military forces of the Empire of Brazil. The Brazilian military was first formed by Emperor Dom Pedro I to defend the new nation against the Portuguese in the Brazilian War of Independence. The Army and Armada were commissioned in 1822 with the objective of defeating and expelling the Portuguese troops from Brazilian soil.

Manuel Marques de Sousa, Count of Porto Alegre, nicknamed "the Gloved Centaur", was an army officer, politician and abolitionist of the Empire of Brazil. Born into a wealthy family of military background, Manuel Marques de Sousa joined the Portuguese Army in Brazil in 1817 when he was little more than a child. His military initiation occurred in the conquest of the Banda Oriental, which was annexed and became the southernmost Brazilian province of Cisplatina in 1821. For most of the 1820s, he was embroiled in the Brazilian effort to keep Cisplatina as part of its territory: first during the struggle for Brazilian independence and then in the Cisplatine War. It would ultimately prove a futile attempt, as Cisplatina successfully separated from Brazil to become the independent nation of Uruguay in 1828.

Manuel Luís Osório, Marquis of Erval was a Brazilian military officer, monarchist and politician. A member of the Imperial Army at the age of fifteen, he climbed all the posts of the military hierarchy of his time thanks to the soldier attributes that consecrated him as "The Legendary". He participated in the main military events of the late nineteenth century in the Río de la Plata region and is considered a hero of the Paraguayan War. He was declared patron of the Cavalry Branch of the Brazilian Army in 1962.

The Brazilian ironclad Tamandaré was an armored gunboat built for the Imperial Brazilian Navy during the Paraguayan War in the mid-1860s. She bombarded the Paraguayan fortifications blocking access up the Paraná and Paraguay Rivers as well as bombarding Paraguayan positions in support of the Imperial Brazilian Army. The ship participated in the Passage of Humaitá in February 1868 and was badly damaged. After Tamandaré was repaired she provided fire support for the army for the rest of the war, aside from bombarding Paraguayan capital of Asunción once. The ship was assigned to the Mato Grosso Flotilla after the war. Tamandaré was decommissioned in 1879 and scrapped afterwards.

The Battle of Curuzú occurred between September 1 and 3, 1866 during the Paraguayan War. After the first Battle of Tuyutí, won by the Allies on 24 May 1866, an Allied council of war decided to use their navy to bombard and capture the Paraguayan battery at Curupayty.

The siege of Uruguaiana was an engagement in the Paraguayan War that began in late August 1865, and ended on 18 September that year when the Paraguayans were forced to surrender due to low food supplies. Paraguayan forces surrendered in spite of President López's order to the Paraguayan commander, Colonel Estigarribia, not to do so. After the allied victory at Uruguaiana, Lopéz withdrew his army from Argentina and Brazil.

José Luís Mena Barreto was an army officer, politician and monarchist of the Empire of Brazil. He came from a wealthy family with a tradition of military service. José Luís entered the army in 1836, during the Ragamuffin War, a secessionist rebellion. The conflict lasted for almost ten years, and he fought in several military engagements at that time.

The Battle of Boquerón was fought on 16 July 1866 and the Battle of Sauce on 18 July 1866, between an allied force of Uruguayans, Brazilians, and Argentines on one side and Paraguay on the other in the Paraguayan War. The Spanish-born Uruguayan officer León de Pallejas (1816–1866) and the Paraguayan officer Elizardo Aquino were killed in the battle.
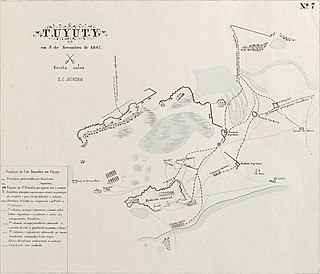
The Second Battle of Tuyutí was fought on 3 November 1867 between the Paraguayan Army and a smaller allied Brazilian-Argentine force. The Paraguayans lost twice as many soldiers as the allies and were defeated.

The Imperial Brazilian Navy was the navy created at the time of the independence of the Empire of Brazil from the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. It existed between 1822 and 1889 during the vacancy of the constitutional monarchy.

The Battle of Paso de Patria was a battle of the Paraguayan War, which took place between April 16 to 23, 1866, on the banks of the Paraná River, in the then fortified position in Paso de Patria, in which the Empire of Brazil emerged victorious. It took place simultaneously with the Battle of Itapirú, during the so-called "crossing of the Paraná River".

José Antônio Correia da Câmara, 2nd Viscount of Pelotas was a Brazilian Marshal, noble, and politician who was notable for his participation in the Battle of Cerro Corá in the Paraguayan War.

The Humaitá campaign or the Cuadrilátero campaign was the third, longest and deadliest campaign of the Paraguayan War. The campaign lasted from 16 April 1866 to 5 August 1868. After the initial Paraguayan success in the Mato Grosso campaign and its failure in the Corrientes campaign, the armed forces of the Triple Alliance, Argentina, the Empire of Brazil and Uruguay, invaded the south of Paraguay. At a very short distance, they found the Paraguayan defensive device made up of four fortifications, the so-called "Cuadrilátero", which obstructed the passage to Asunción both by land and by the Paraguay River. A long series of battles cost huge numbers of casualties on both sides, with operations coming to a complete halt after the allied defeat at the Battle of Curupayty. Casualties on both sides were even higher from disease than from battle due to a cholera epidemic which was added to the appalling food and sanitary conditions.

Vitorino José Carneiro Monteiro, Baron of São Borja (1816-1877) was a Brazilian Lieutenant General of the Paraguayan War. He was one of the primary commanders at the Battle of Tuyutí and had an extensive career during the 19th century.